What Is White Box Testing?: Examples, Types, And Techniques
- Learning Hub
- What Is White Box Testing?: Examples, Types, And Techniques
OVERVIEW
White box testing is a software testing method in which the internal structure and implementation of the software being tested are known and used as the basis for designing the test cases. It involves testing the software at the code level and requires a deep understanding of the code and the design of the software. It is also known as glass box, transparent box, clear box, or structural testing.
Most testers have already had some experience with this box-testing at some point in their careers. Techniques like this are battling for existence in a world that is becoming increasingly agile-driven. Adopting agile approaches does not include putting off any tasks to meet the project effectively.
Testing is one of the main areas, especially in white-box, where we see projects in the most impacted areas and teams cut corners for agility. In this tutorial, we will covers what whitebox testing is, why do we use it, advantages & disadvantages, types, and different techniques to perform, and various scope.
What is White box testing?
White box testing evaluates a software application's code and internal structure. It ensures that internal operations are carried out according to the specifications when you know an application's internal structure. Additionally, each interior component must follow a proper framework.
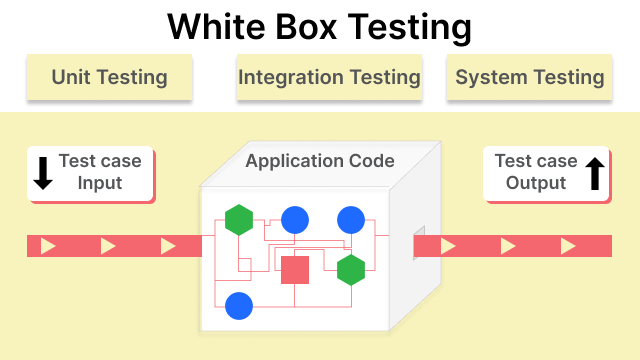
A tester who understands the test codes is able to see the internal workings of the software and has access to the source code, so they can design test cases that thoroughly, test the different code paths and ensure that the software is working correctly. As a result, the tester must always possess knowledge of or access to the system's source code, typically provided in specification papers.
Let's say that a software application consists of three components. Before integration testing is performed, each component is tested independently by the tester as part of the development cycle. In the early stages of the development cycle, bugs can be found very early, saving time.
A tester will then be able to construct and carry out test cases that cover all conceivable situations and circumstances that the system component is supposed to handle after they have access to the amount of technical information that is often only exposed to a developer.
Why should you perform white box testing?
A white box test is often described in terms of Static Application Security Testing (SAST), which checks source code or binaries and provides feedback about bugs. This process examines a code's inner workings and provides inputs.
Before performing whitebox testing, there are some entry and exit requirements that needs to checked which are mentioned below:
- Intra-company security gaps.
- Paths in the coding processes that are broken or poorly organized.
- The particular inputs sent through the code.
- Expected results.
- Conditional loops' capabilities.
- Independent testing of each statement, object, and function.
When implementing white-box testing approach to test software applications, testers can consider the following two approaches:
- Be aware of the source code: A tester will frequently study and comprehend the application's source code as their initial step. The tester must have an extensive understanding of the programming languages used in the apps since it entails testing an application's internal workings.
The tester must also be well knowledgeable about secure coding techniques. Often, one of the main goals of software testing is security. The tester should be able to identify security flaws and thwart assaults from hackers and gullible users who could willfully or accidentally introduce harmful code into the application.
- Build and use test cases: This box-testing's second fundamental stage entails examining the application's source code to ensure correct flow. Writing extra code to test the application's source code is one approach. For each procedure in the application—or set of processes—the tester will create a simple test. This approach, which the developer frequently carries out, necessitates the tester's thorough understanding of the code.
Let's discuss the pointers that describe why should you perform white-box testing:
- Whitebox testing is frequently reserved for mission-critical systems and components because they require the focus on detail that this technique can deliver.
- Any system that offers a business, organization, or government such essential functionality must be bug-free. Such systems cannot tolerate faults or downtime since they provide imperative duties for all parties involved. Therefore, such systems must function as intended.
- Customers who find themselves in potentially life-altering circumstances, such as paying for a loved one's emergency medical care, may be unable to access their money. And a broken IT system might jeopardize the entire system’s security.
Therefore, ensuring that crucial systems and components are bug-free is essential. And thorough testing is necessary to ensure that a mission-critical system is bug-free. Ensure the high-quality performance of your systems through testing. Nevertheless, it is an integral and essential approach.
Phases of White box testing
In this section of the white-box testing tutorial, let's look at the phases of the whitebox testing process.
- Identify the program, feature, or component that requires testing: The smaller your target system component is, the better it is for whitebox testing. Individually testing each feature allows you to concentrate on a small portion of the code given what we're attempting to do: test all potential scenarios and use cases for a specific feature.
You should focus initially on the smallest logical module or component of the system under test and then jump to the next one.
- Draw all potential routes in a flowchart: This stage is the bulk of your test planning and execution of the White box strategy. Understanding scope is essential for any endeavor, whether development or testing. Furthermore, path coverage offers a complete answer to test coverage.
Here you're attempting to understand each testable path for a specific feature, component, or module. Writing test cases to cover each of the various pathways is aided by identifying them. You can create a flow diagram to highlight the desired pathways.
- Create test cases that address each step in the flowchart: After you've shown all the alternative pathways on the flowgraph, you can write test cases to examine each. The test execution phase can begin whenever you have many test cases that you are confident will cover every possible path.
- Implementations of components: Testers will use the developed projects and perform standard producer tests by mixing and integrating various third-party innovations, making it possible for end-users to communicate with one another.
- Implement, then repeat: After identifying the system, component, or module, you can implement the whitebox testing. Additionally, you have the flowchart and test cases required to finish the testing. That is how you can organize and carry out whitebox testing.
Types of white box testing
Let's now have a look at different types of testing modules that are included under the domain of whitebox testing.
- Unit testing: It is typically used as the first technique of software application testing. The developer performs unit testing. As a software developer, you write a few lines of code, a function, or an object, test it to ensure that it works, and then move on. Unit testing helps in the early detection of the majority of defects in software development. Bugs discovered at this stage are less costly and easier to fix.
- Testing for memory leaks: Applications that run slowly often have memory leaks. If you have a software application that runs slowly, you need a highly-skilled software tester to find memory leaks.
- White box penetration testing: In this testing, the developer or tester has complete access to the software's codebase and comprehensive network, IP, and server data. The objective is to attack the code in various ways to reveal security risks.
- White box mutation testing: It involves frequently finding the best coding practices to apply while growing a software solution.
- Basis path testing: In this method, the number of independent pathways in a control flow graph, or its cyclomatic complexity, is determined. Using the cyclomatic complexity, you can find the minimum number of test cases we can generate for each independent path in the flow graph.
- Loop testing: One of the most often used programming tools is the loop. It only makes it logical to have a testing method based on loops because they are the fundamental building blocks of so many algorithms. There are three kinds of loops: concatenated, nested, and straightforward.
Upsides & Downsides of White box testing
Traditionally, there has been a distinct division between developers and quality assurance testers in the software development process. To ensure that the functionality they have built satisfies the requirements, developers install it and conduct QA tests.
White-box testing is carried out by someone well-versed in the application's internal structure. Following are some of the advantages of whitebox testing.
- It provides simple principles that allow testers to determine when testing is complete.
- A developer has to hire fewer testers and incurs fewer costs because the procedures are simple to automate.
- It highlights bottlenecks so that programmers can easily optimize the application.
- The testing team can begin working without waiting for the development team to finish building the user interface.
- Code-based testing is more comprehensive since it covers all code routes.
- It aids in the removal of code sections that are unnecessary for the application's operation.
Following are some of the disadvantages of whitebox testing:
- Testing only the available code could leave out certain functionalities.
- The tedious process discourages many developers.
- Redesigning the codes and rewriting test cases is time-consuming as they must be rewritten.
- In contrast to black-box testing, whitebox requires resources and professional skills. A white-box tester should understand the mechanisms of the application's codebase and have strong programming language skills.
One of the primary aims of white-box test is to cover as much source code as possible. Code coverage is a metric that shows how much of an application's code contains unit tests that validate its functioning.
Using techniques such as statement coverage, branch coverage, and path coverage, it is possible to check how much of an application's logic is executed and verified by the unit test suite under code coverage. These techniques are discussed further below:
- Statement coverage: A statement in a programming language is just a piece of code or instruction that the machine is supposed to comprehend and follow. When a report is compiled, turned to object code, and executes the specified action while the program is executing, that statement is said to be an executable statement. Therefore, statement coverage ensures that every line of code gets run at least once.
- Branch coverage: In a programming language, "branch" is equivalent to "IF statements." True and False are the two branches of an IF statement. Therefore, in branch coverage, we verify if each branch is executed at least once. Branch coverage is also known as decision coverage.
There are two test criteria for an "IF statement":
- To authenticate the actual branch.
- To authenticate the false branch.
- Path coverage: Path coverage analyzes all of the program's pathways. This robust strategy ensures that all program routes are traversed at least once. Its coverage is more effective than branch coverage. This method is handy for testing sophisticated applications.
White box Testing Vs. Black box Testing
Let's look at the differences between these two box-testing methods:
| White-box testing | Black-box testing |
|---|---|
| It is usually done by developers. | It is usually done by testers. |
| The tester is familiar with the software's internal structure and code. | During this type of software testing, the program or code's internal structure or code is hidden. |
| It requires code implementation. | It does not require code implementation. |
| It is the structural testing of an application. | It is the functional testing of an application. |
| Software testing begins after the detailed design document is completed. | This testing can start with the required specifications documentation. |
| It is a time-consuming process. | It is the least time-consuming method. |
| It is ideal for algorithm testing. | It is not ideal for algorithm testing. |
| It is mainly applicable to lower levels of software testing. | It applies primarily to higher levels of software testing. |
White box testing tools
A tester can try every possible combination and permutation the program may produce by testing at the source code level. You can compile and fix any potential evolving flaws once testing completes satisfactorily.
- JSUnit.net: It is an open-source JavaScript testing tool. JSUnit is a JUnit component and can be used for whitebox testing. Because JSUnit is entirely open-source and released under the GNU Public License 2.0, developers are not required to pay a license fee for any use, including profit.
- CppUnit: CppUnit is a component of JUnit in the same way that JSUnit is. Depending on the tester's needs, the tool can output in plain text or XML format and construct unit tests using its classes. The LGPL is the license for the CppUnit.
- Veracode: Veracode includes several robust tools using test.NET, C++, Java, and other languages. However, it is not available for free. You can implement it in desktop, online, and mobile applications.
- NUnit: The framework created in C# offers data-driven testing for Net languages. Functionality-wise, it can support concurrent and parallel execution and provide test-runner programs in addition to a class framework. The NUnit's usability is one of its standout qualities.
- CSUnit: CSUnit facilitates unit testing in the .Net framework, just as NUnit. It supports languages like VB.Net and C#. Factoring procedures and other sorts of practices utilized in the agile development strategy of the SDLC are supported by CSUnit natively.
Scope of white box testing
Writing test cases that provide comprehensive coverage of the application logic is necessary. You must have a solid understanding of the application, the testing requirements, and the source code. Also, familiarity with logic and computer languages is necessary.
However, testing every conceivable outcome of the application's loops is not feasible. It implies that testing in depth is not viable for complex systems. Nevertheless, white-box is still effective as it is realistically practicable and valuable to test by choosing significant logical routes and data structures.
White-box testing ensures a module has run through each of its separate pathways at least once. Below are the scope of whitebox testing:
- Identify the software application’s issues.
- Logical errors frequently appearing can be fixed after the development and implementation of controls, conditions, or functions that do not include in the software application.
- One can tackle the design flaws resulting from a mismatch between the application's logical flow and implementation, syntax checking, and typographical correction.
How does it fits with other QA methods?
Testing is required at the system, integration, and unit levels of software development. Verifying an application's operational flow is one of the fundamental aims of whitebox testing. It compares a sequence of specified inputs to desired or expected outputs to identify bugs when detailed information does not provide the desired outcome.
- A statistic known as code coverage reflects how extensively you analyze the system's code base.
- Segment coverage is the second phase, in which you should ensure wherein each coding instruction executes only once.
- Coverage testing ensures a feasible code branch, often known as node testing or branch coverage.
- Basis path testing verifies each line of code.
- Data flow testing (DFT) defines the collection of intermediate pathways via the code by following the specified variables through each potential computation. Dependencies often reflect DFT but primarily by sequences of data manipulation. By monitoring each data variable, the application confirmation takes place. This method frequently reveals issues such as variables that are declared but never used or that are utilized but never initialized.
- Path testing involves defining and covering all potential routes via the code. It necessitates oodles of time.
- The loop testing method supports single, concatenated, and nested loops. This algorithm checks individual and completely reliant code loops and values.
Wrapping up!
Developing white-box software testing, it is a valuable method for carrying it out. Even while this testing strategy can be costly and time-consuming, it is still the only method to ensure that you test all aspects of the code. The evaluated application has a significant impact on the complexity involved.
While more extensive programming programs take days, weeks, or even longer to thoroughly test, a small application that executes a single straightforward function may be white box tested in minutes. A software application should undergo whitebox tests throughout development, after writing, and once again following each revision.
So, get familiar with the code and implement white-box testing in full swing!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are three main white-box testing techniques?
There are several techniques that can be used in white-box testing to validate the internal structure and implementation of a software application. Here are three main whitebox testing techniques: Statement Coverage, Branch Coverage. and Path Coverage.
What is black box testing vs. white box testing?
Black-box testing focuses on the functionality of a software application and does not require knowledge of the internal structure or implementation of the code. On the other hand, White-box testing involves testing the internal structure and implementation of the code.
Why white-box testing is called white?
The term 'white' comes from the metaphor of a white-box, which is transparent and allows the user to see inside. That’s why white-box testing is also known as transparent box testing, clear box testing, glass box testing, or structural testing.
Who performs whitebox testing?
Developers are responsible for implementing a code, and have a deep understanding. As a result, they are well-suited to perform whitebox testing, as they can use their knowledge of the code to design test cases that exercise all the different code paths and identify issues such as logic errors, code defects, and security vulnerabilities.
What is white-box testing in software testing?
White-box testing is a method of testing in which the internal structure of the software being tested is known to the tester and is used to design the test cases. It is used to test the internal structure and logic of a program, and it is typically done by developers as part of the testing process.
What is a white box testing?
White-box testing is a software testing technique where internal code structure is examined to assess functionality, logic, and coverage. It involves scrutinizing the code directly, allowing testers to identify and rectify errors. This approach ensures comprehensive test coverage and enhances software quality and reliability.
What is white box penetration testing?
White box penetration testing is a comprehensive security assessment where the tester has full knowledge of the internal workings and structure of the target system. It involves analyzing the source code, architecture, and design, allowing for a thorough evaluation of vulnerabilities and potential exploitation.
What are the advantages of performing static white box testing?
Performing static white box testing offers several advantages. It enables early detection of coding errors, helps uncover security vulnerabilities, enhances code maintainability, and facilitates code review. Moreover, it aids in optimizing software performance and promotes adherence to coding standards. Ultimately, it contributes to the development of robust and reliable software systems.
What is static white box testing?
Static white box testing is a software testing technique that examines the internal structure and code of a program without executing it. It aims to identify potential defects, vulnerabilities, and code quality issues. Through careful analysis, developers and testers can ensure the reliability and efficiency of the software.
Reviewer's Profile

Shahzeb Hoda
Shahzeb currently holds the position of Senior Product Marketing Manager at LambdaTest and brings a wealth of experience spanning over a decade in Quality Engineering, Security, and E-Learning domains. Over the course of his 3-year tenure at LambdaTest, he actively contributes to the review process of blogs, learning hubs, and product updates. With a Master's degree (M.Tech) in Computer Science and a seasoned expert in the technology domain, he possesses extensive knowledge spanning diverse areas of web development and software testing, including automation testing, DevOps, continuous testing, and beyond.
Try LambdaTest Now !!
Get 100 minutes of automation test minutes FREE!!
 Christmas Deal is on: Save 25% off on select annual plans for 1st year.
Christmas Deal is on: Save 25% off on select annual plans for 1st year.