- Testing Basics
- Home
- /
- Learning Hub
- /
- Test Scripts Tutorial
- -
- September 18 2023
Test Scenario: Detailed Guide With Templates And Samples.
Elevate software quality with effective test scripts. Learn their significance and creation for successful testing in this comprehensive guide.
OVERVIEW
Test scripts are a set of instructions or procedures written in a scripting language that are used to execute a series of test cases on a software application or system. In other words, test scripts are line-by-line descriptions that include related information and must be performed to validate the application under test. It lists the steps that need to be taken to meet the expected results.
In the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC), testing is the phase that ensures the fixation of any bug or error. However, software applications have diverse components and functionalities that must be tested. It is essential to include all such aspects in software testing to ensure the quality of the software applications. A well-written test script allows the QA team to test each software application component on various environments.
This comprehensive guide aims to provide a detailed understanding of testing scripts, their significance, and how to create effective test scripts for successful testing.
What are Test Scripts?
Testing scripts are detailed, step-by-step instructions used to test a test case, encompassing individual steps to check and verify each functionality. These scripts are programs that execute tests on software products or applications. Testers must write and run these scripts to confirm if the application meets the business requirements.
We all know that test cases are the foundation for creating test scripts. There can be multiple scripts and different testing environments in a single test case. While most scripts are associated with automation testing, they can also be part of manual testing. However, testers write automated scripts to generate data for testing various functionalities.
Typically, these scripts run automatically, checking each test case with different input data. Python, Ruby, Perl, Java, VB Script, etc., are some scripting languages used for writing test scripts. Once written, a test script can execute multiple test instances to assess a single application function. Due to their detailed and extensive nature, writing scripts in a reusable format is an excellent practice that simplifies the tester's work.
Why Use Test Script?
Using test scripts in the software testing process offers several advantages, which is why they are commonly employed in testing activities. They contain information regarding the function of the software applications, which needs to be performed to validate and verify the working of the software application. Here are some of the key reasons why to use test scripts.
- Comprehensive Testing: Provides a dependable means of ensuring that no steps are overlooked during testing, leading to accurate and desired testing outcomes.
- Specific User Requirements: Scripts are particularly valuable when user requirements are clear, helping to meet precise criteria.
- Controlled User Performance: It allows for controlled and structured user interactions, ensuring consistent and reliable testing.
- Unambiguous Execution: When testers navigate software freely and assume expected outcomes, test scripts prevent ambiguities and provide clear directions for each test scenario.
- Reduced Errors: A well-prepared test script minimizes the likelihood of errors during the testing process, enhancing overall testing efficiency and effectiveness.
Type of Test Scripts
Typically, scripts are divided into two types aligned with manual and automated testing approaches. Here are some of those:
Manual Test Scripts
Manual test scripts are mainly written and executed by human testers without assistance from automation tools. They only adhere to a predetermined set of steps and instructions to manually assess the software applications. This approach proves valuable for exploratory testing, usability testing, ad-hoc testing, and scenarios that evade automation. Despite its resource-intensive nature, manual testing offers a unique advantage in detecting specific issues that may bypass the automated testing approach.
Automated Test Scripts
On the other hand, automated scripts are particularly written in a programming language and run with the help of automation testing tools. These scripts use automation testing frameworks to mimic user interactions, interact with the application, and automatically verify expected outcomes. Within the category of automated scripts, there are further subtypes contingent on the level of testing and the extent of automation.
- Unit Testing Scripts: These concentrate on assessing individual units or components of the software applications, typically composed by developers during the development phase.
- Integration Testing Scripts: These ascertain the seamless interaction between multiple components, ensuring maintained operations.
- Functional Testing Scripts: These validate that the software application functions impeccably per the specified requirements.
- Regression Testing Scripts: These affirm that existing functionalities remain unaffected following new changes or updates done in the software applications.
- Performance Testing Scripts: These help the application performance under diverse load conditions.
- End-to-End (E2E) Testing Scripts These simulate real-world scenarios to comprehensively evaluate the entire application flow from inception to completion.
- Smoke Testing Scripts: These are swift assessments aimed at verifying the basic functionality of the software application after significant updates.
- Security Testing Scripts: These assess the software application's resilience against security threats.
The choice between manual and automated testing depends on the specific software project requirements, complexity, and the available resources. Manual and automation testing is often deployed to ensure exhaustive test coverage and detect any vulnerabilities or discrepancies within the application.
Revamp testing and ensure software quality with LambdaTest. Try it now and experience a new level of testing excellence! Try LambdaTest Now!
Test Script vs. Test Case
Here are the key differences between the test script and the test case.
| Test Case | Test Script |
| Step-by-step procedure for testing an application. | A set of instructions to automatically test an application. |
| Used in a manual testing environment. | Utilized in an automation testing environment. |
| Performed manually by testers. | Executed based on a scripting format. |
| It includes test id, test data, test procedure, actual and expected results, etc. | Comprises different commands to develop a script. |
Understanding Test Script Template
Writing test scripts involves a template, which eases this process in software testing. It is a standardized document with pre-selected and essential information for creating good-quality scripts. Such documents can be reused whenever there is a need to develop scripts for any test. These scripts serve as testers' guidelines, ensuring consistency and uniformity in structure and content.
The test script template outlines the required format and specifies what information should be incorporated into each test case. Generally, a test script template has sections on the test case name, test objective, test environment, expected result, and others. Its detailed information is as follows.
- The test case name: It is a unique identifier or name of the test cases to differentiate it from others.
- Test objective: It highlights the objective of the test cases.
- Test steps: It gives detailed steps to run during the test.
- Expected result: It includes information on the specific outcomes expected when test steps are run accurately.
- Test data: It has specific data or inputs needed for test cases. It includes values, parameters, or variables that the test case needs to process during its execution.
- Test environment: It has information on hardware, software, operation systems, and configurations.
- Test preconditions: These are the starting points or prerequisites necessary for the test to be valid and accurate.
- Test execution steps: It has the instruction to run a test case with particular information on setup and configuration.
- Actual result: The real outcomes observed when the test is executed.
- Pass and fail criteria: These criteria show test cases that have passed or failed based on expected and actual results.
- Notes and comments: Any additional notes, comments, or observations related to the test case or its execution.
Utilizing a standardized template within the team helps save time and reduce errors in software testing. It also promotes consistent script creation and fosters effective communication among team members.
Information in Test Script
What makes test scripts beneficial? A well-written test script always includes valuable information. This information serves the purpose or aim of the script, outlining the actions to be performed during software testing.
The key components of potential information are as follows.
- Inputs and Expected Results: The test script contains the raw content, including inputs and sometimes the expected results.
- User Information: This section outlines the user-related details, such as the data to be provided to the script, the required software state during script execution, and the software's condition after the test.
- Usage Information: Testers may include additional useful information, such as explanations of specific usage scenarios or references to related tests that might require modifications.
- Annotation: Comments embedded within the script explain the logical steps and actions performed with the software being tested.
Including this essential information ensures the test script is clear, comprehensive, and effective in validating the software's functionality.
Approaches for Writing a Test Script
To write a test script, different approaches are utilized by the software tester depending on the complexity of the software application. Here are some standard procedures that are used to write a test script.
- Record/Playback: The tester records the user's actions without writing any code in this method. The recorded actions serve as the test script, and the tester may need to add code to address any issues or customize automation behavior. This method is simpler than starting from scratch since the complete code is readily available. It is commonly employed in simplified programming languages like VBScript.
- Keyword/Data-Driven Scripting: A clear separation exists between testers and developers. Testers define tests using keywords without knowledge of the underlying code. The developers are responsible for implementing the test script code for the defined keywords and updating it as necessary. Testers need not concern themselves with the software application's intricacies but heavily rely on development resources for automating new functionalities.
- Writing Code Using the Programming Language: Testers can still record or playback to generate a basic script if they choose this method. However, testers must go beyond record/playback to utilize this approach effectively and learn how to code simple scripts. It is essential to understand that testers can choose a programming language, even if the application is written in Java. They can opt for a more manageable language like JavaScript or Ruby to write scripts rather than struggle with Java's complexity.
When to Use the Test Script Approach?
There are various scenarios where the test script approach is employed. While the approaches mentioned earlier are prevalent in software testing, there are instances in the testing process where they are essential.
- Testing scripts come in handy for automating repetitive or manual tests, saving time and effort.
- In regression testing, they enable the execution of multiple test cases to check for changes in new code.
- For large and complex software applications, scripts simplify the management of numerous test cases.
- In data-driven testing, they execute multiple test data sets efficiently.
- They are also valuable in load and performance testing, simulating multiple users, and test scenarios.
Hence, using the test script approach in these scenarios enhances the testing process's efficiency, accuracy, and reliability, leading to better software quality.
Now, let us understand in detail test scripts with examples in the next section.
Test Scripting Tools
The software applications, which possess user-friendly interfaces, are designed to facilitate the seamless creation, editing, and execution of scripts. These tools empower testers and developers alike to write scripts without requiring extensive programming knowledge. Some test scripting tools include the following:
- Selenium: It is one of the most used automation testing tools, which is open source. A fantastic feature of Selenium is that it supports multiple programming languages like Java, Python, and C#. It helps testers to interact with web elements that mimic user actions and verify the expected outcome.
- Appium: Appium is an open-source testing tool compatible with iOS and Android platforms, enabling testers to create scripts for native, hybrid, and mobile web applications.
- Cypress: Cypress is a modern JavaScript-based test automation tool focusing on front-end testing. Cypress offers a developer-friendly environment replete with real-time reloading and advanced debugging capabilities.
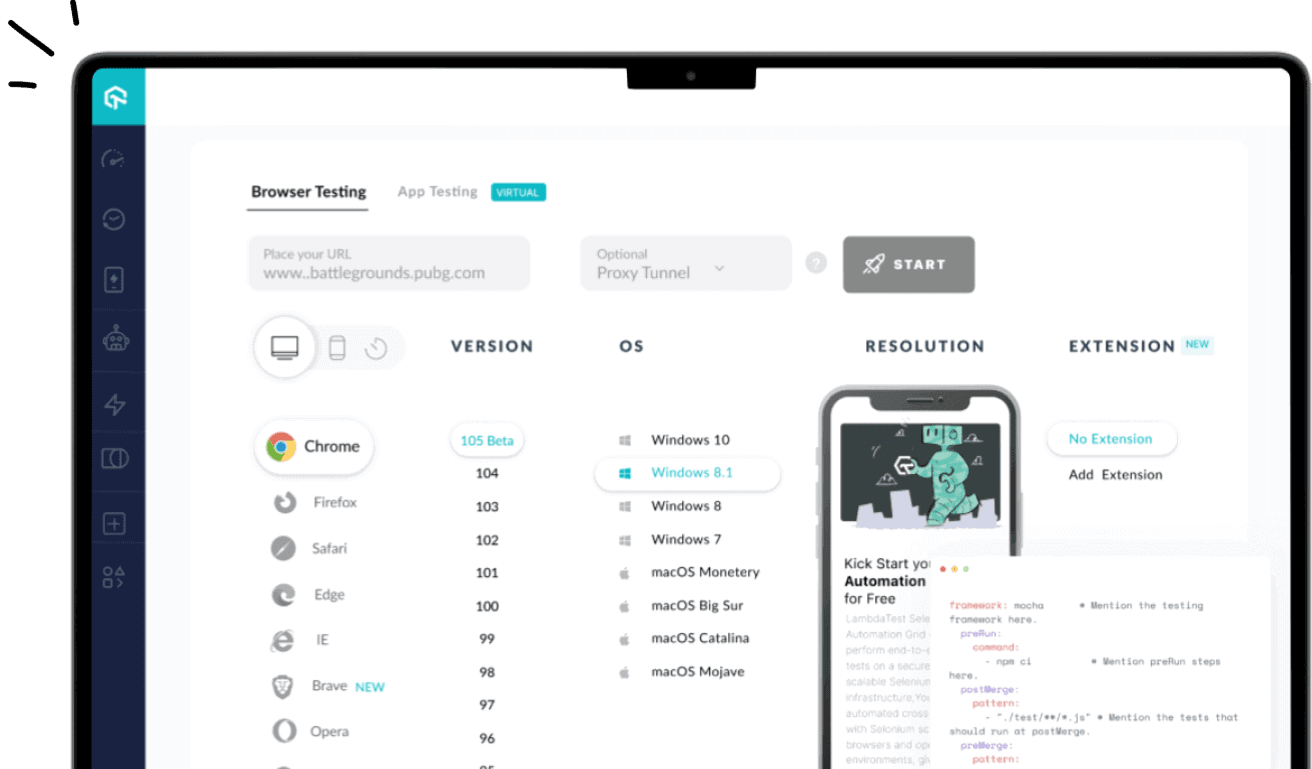
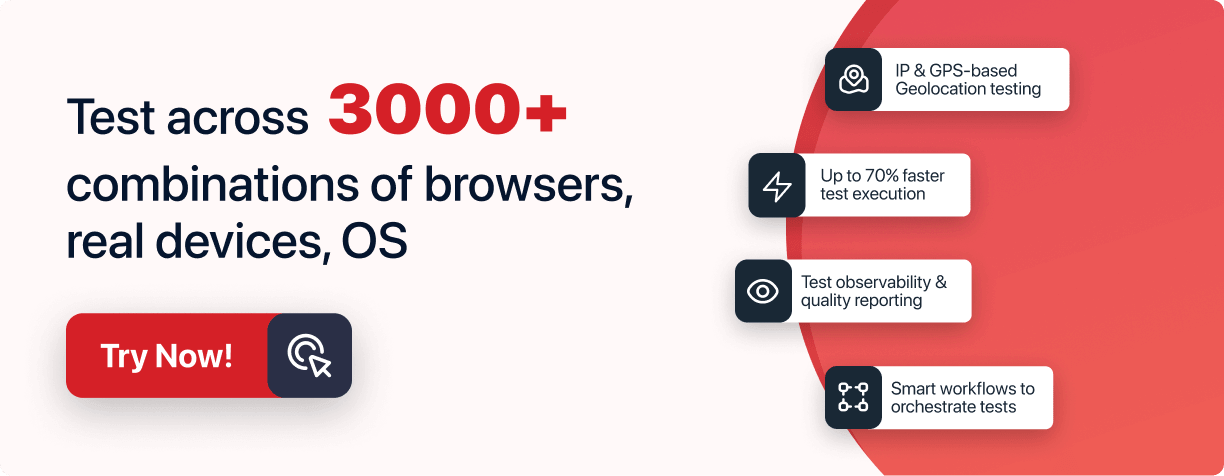
You can leverage the above automation testing tools for writing scripts using a cloud-based platform like LambdaTest. LambdaTest is an AI-powered test orchestration and execution platform based on its cloud infrastructure for manual and automation testing. You can test your website or web application across 3000+ real devices and OS combinations on the scalable and robust cloud. Here are some critical offerings of LambdaTest.
- Users can perform real-time testing on various devices, including smartphones and tablets, running operating systems like Android and iOS.
- It supports automation testing frameworks like Selenium, Cypress, Playwright, Appium, etc. This, in turn, allows you to write automated scripts based on different programming languages.
- It gives API documentation and sample code examples for various programming languages. It helps developers to integrate their scripts with the platform.
- Users can upload their existing scripts and execute them on the LambdaTest platform, allowing them to leverage their test codebase.
Subscribe to our LambdaTest YouTube Channel for the latest updates on tutorials around Selenium testing, Playwright testing, and more.
Test Scripting Frameworks
Test automation frameworks provide a structured approach to effectively organize and manage test automation scripts, ensuring their reusability and scalability and simplifying the long-term maintenance of test automation projects. Various test automation scripting frameworks encompass these aspects. Mentioned below are some of the major categorizations of the frameworks.
Data-driven Framework: This framework divides test data from test scripts and helps the software testers set up and execute the tests with diverse datasets. It will, in turn, enrich test coverage and mitigate redundancy.
Keyword-driven Framework: It is the framework where the test cases adopt a tabular format, and the inclusion of keywords represents various test actions. With the help of the framework, testers can quickly write scripts without going deep into programming and using predefined keywords.
Behavior-driven Development (BDDFramework: BDD frameworks, like the Cucumber framework, develop collaboration between technical and non-technical team members. These scripts are written in a human-readable format using the Gherkin language. It eventually leads to creating better communication and understanding.
Hybrid Framework: Hybrid frameworks combine the strengths of multiple frameworks used to write scripts. It gives the testers the flexibility to leverage the advantages of each approach. It provides adaptability to meet diverse testing needs.
Page Object Model (POM): POM, a design pattern, creates a logical representation of web pages, effectively separating page elements from test logic, thus enhancing test script maintainability and reusability.
Selecting the appropriate test scripting tools and frameworks mainly depends on various factors, including requirement analysis, application type, team expertise, and the scalability of the automation effort. The rightly chosen tools and frameworks streamline the automation process, expand test coverage, and ultimately contribute to the overall success of software testing endeavors.
Simplify test automation with LambdaTest! Elevate your projects effortlessly. Try LambdaTest Now!
Now, let us understand how to write a test script.
Test Script Development Process
Writing test scripts follow a set of processes to address all the required testing needs. Some primary phases of test script development allow for writing quality scripts.
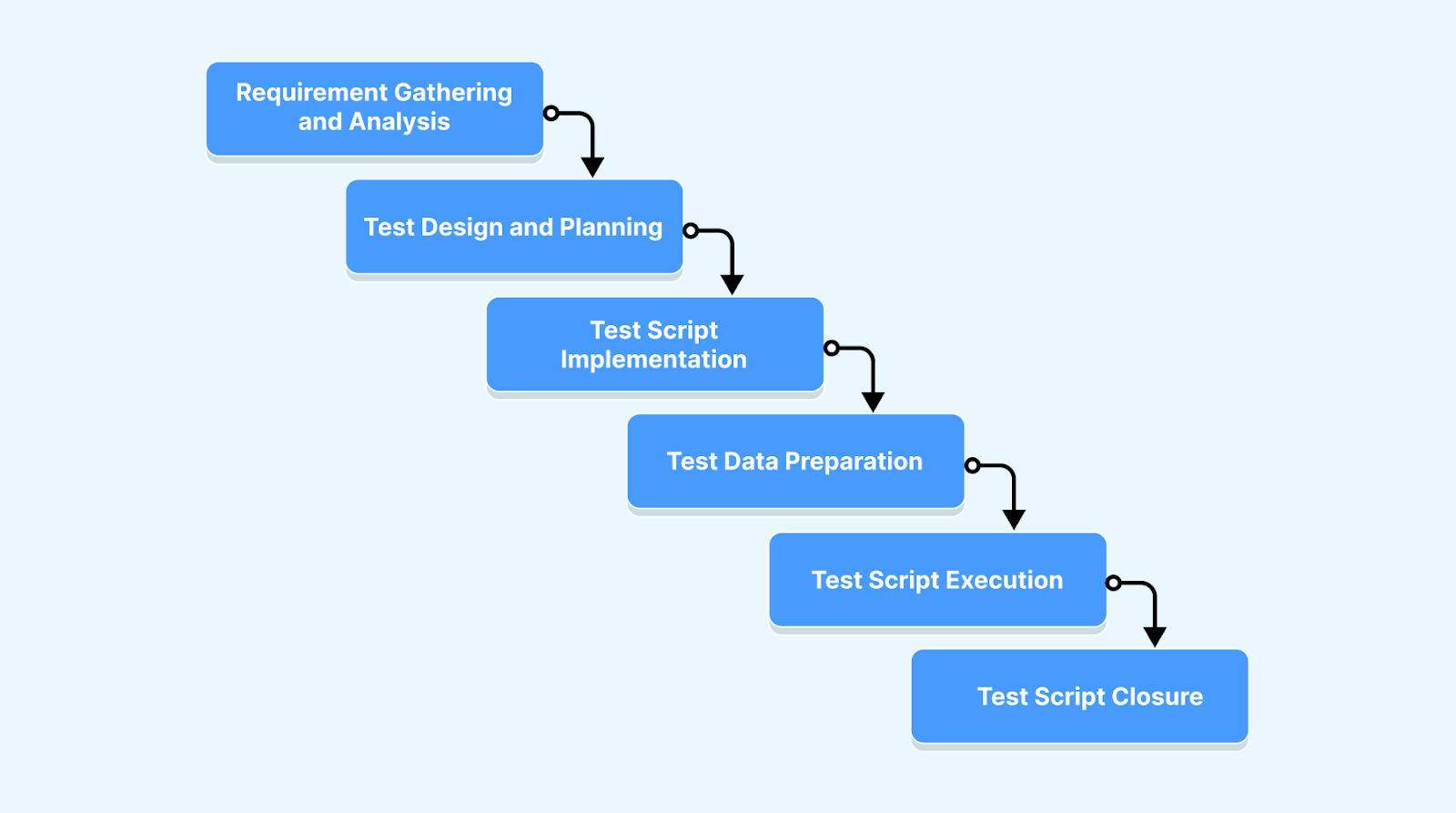
- Requirement Gathering and Analysis
- Test Design and Planning
- Test Script Implementation
- Test Data Preparation
- Test Script Execution
- Test Script Closure
Before indulging in writing testing scripts, the testing team collaborates with stakeholders like product owners, developers, and business analysts to have information on the software requirements for the tested application. The main aim of this phase is to understand the function, performance, and behavior of the software applications so that the script includes all the related test cases that require testing.
Here, the software testers carefully evaluate the requirement so that they can identify the testable scenarios, any underlying risks, or specific conditions that need to be covered by the test scripts.
In this phase, the software testers develop a comprehensive testing strategy based on the requirements and evaluation performed in the first phase. Here, they outline the test objective, testing scope, different testing approaches, and related factors. Based on this, the test case includes diverse types of functionality, edge cases, and test scenarios.
When software testers develop test cases, they proceed with the implementation phase, which includes composing scripts using scripting languages and software testing tools. These scripts contain various commands that simulate interactions with the software application, such as clicking buttons, inputting data, and validating test outcomes.
There is a requirement to have essential data that includes various test scenarios and conditions like boundary values, valid and invalid inputs, and diverse user roles to execute the test scripts. These are important for the successful execution of tests.
In the test script execution phase, the scripts are run against the software application being tested. On the different test environments and configurations, the scripts are executed so that it is easy to assess the behavior and functionality of the software application. Here, the application's responses and checks are carefully made for discrepancies between expected and actual outcomes.
A test closure report is a summary paper describing all the tests done while making software. It includes what tests were finished, the results, and a chart showing which tests are complete.
Throughout the Test Script Development Process, documentation is crucial to maintain traceability, track progress, and facilitate collaboration among team members.
Test Script Example
Below is an example of a test script that will help you understand its key concepts.
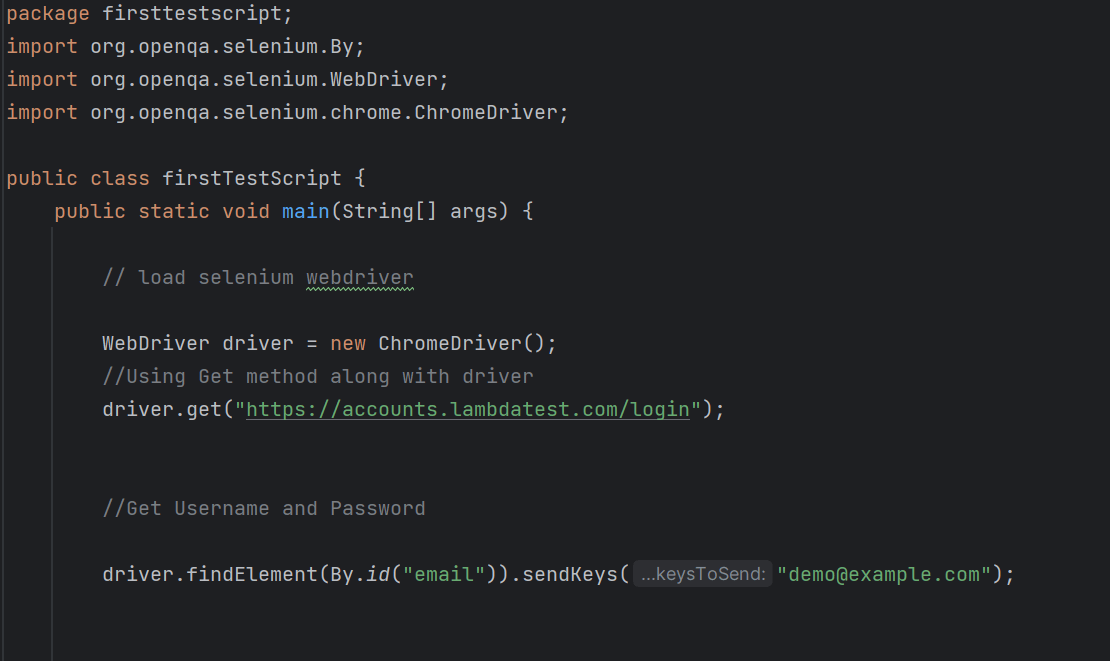
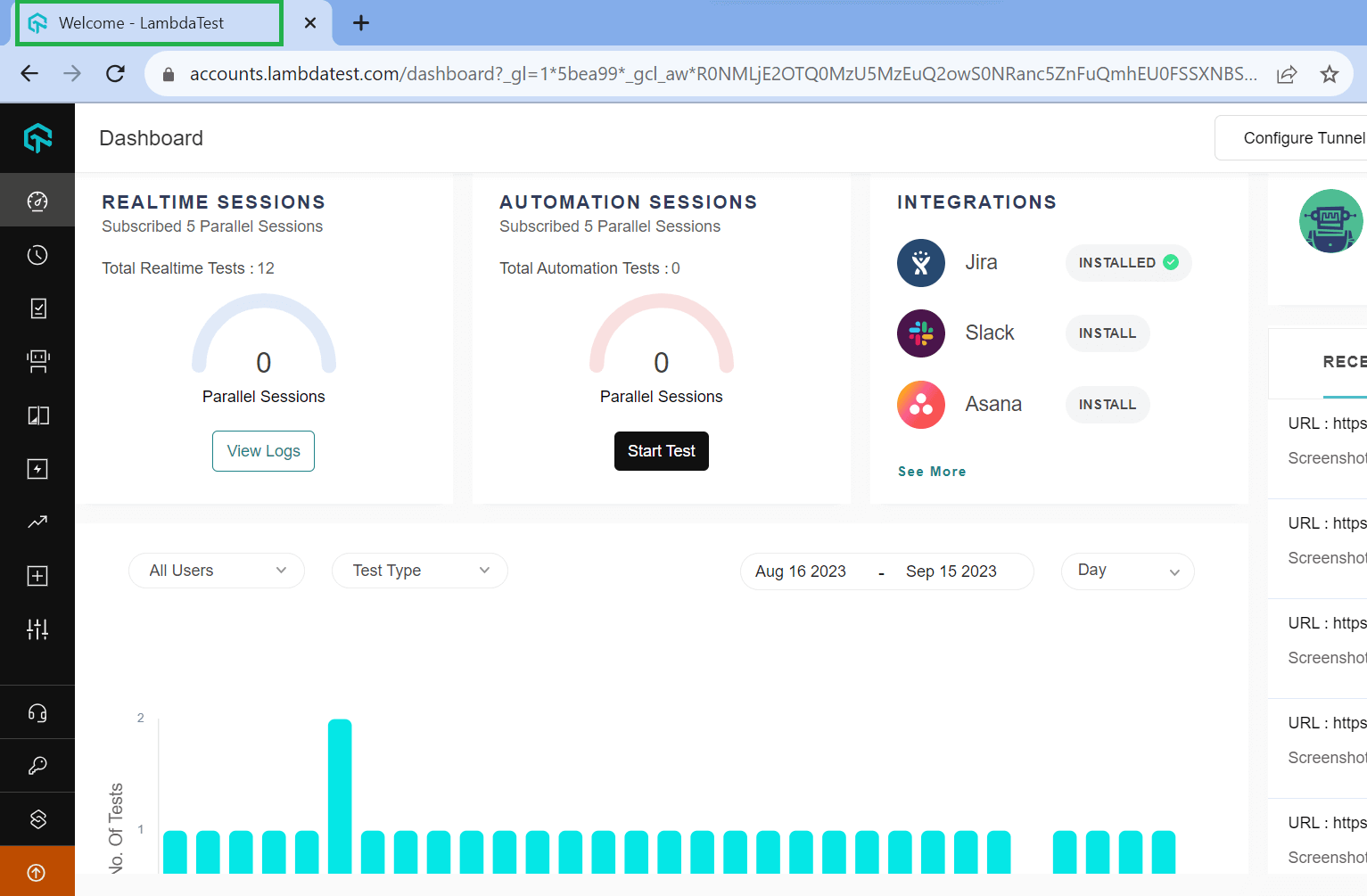
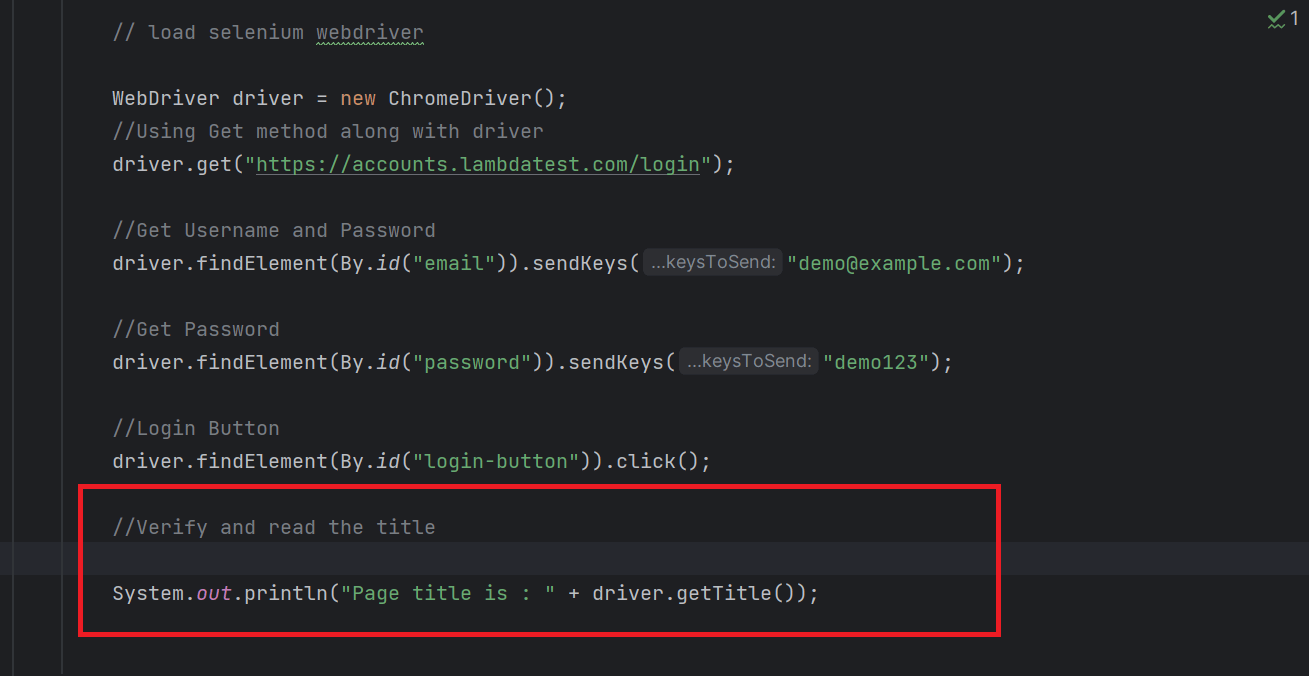
While testing login functionality on the LambdaTest website, the test script will perform the following steps.
- Visit the LambdaTest Login Page.
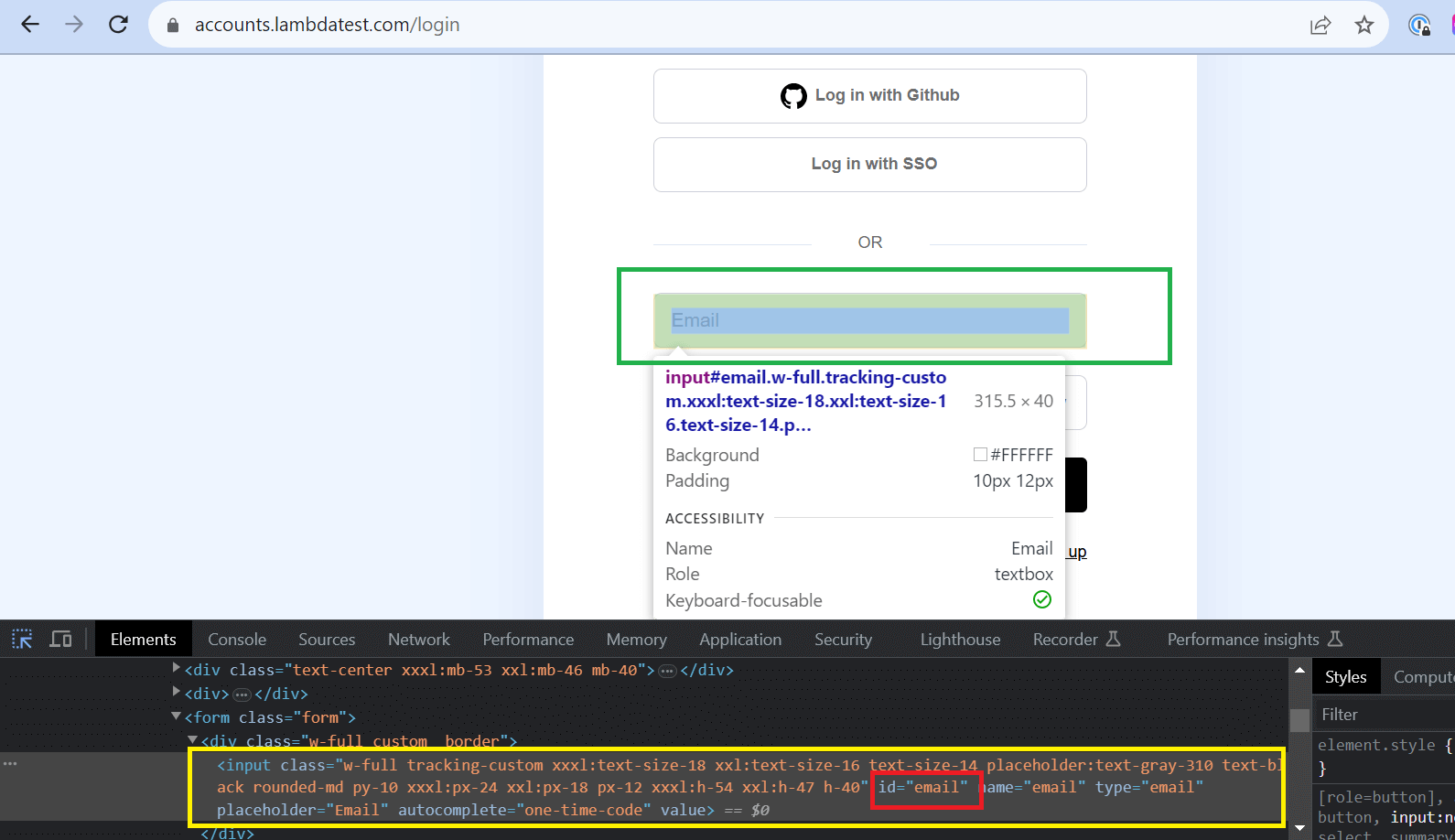
- Define the method or locator strategy to locate the "Email" and "Password" fields on the login screen using their element IDs.
- Locating Username/Email: Get the unique value of that particular Email field.
- Locating Password: Get the unique value of that particular Password field.
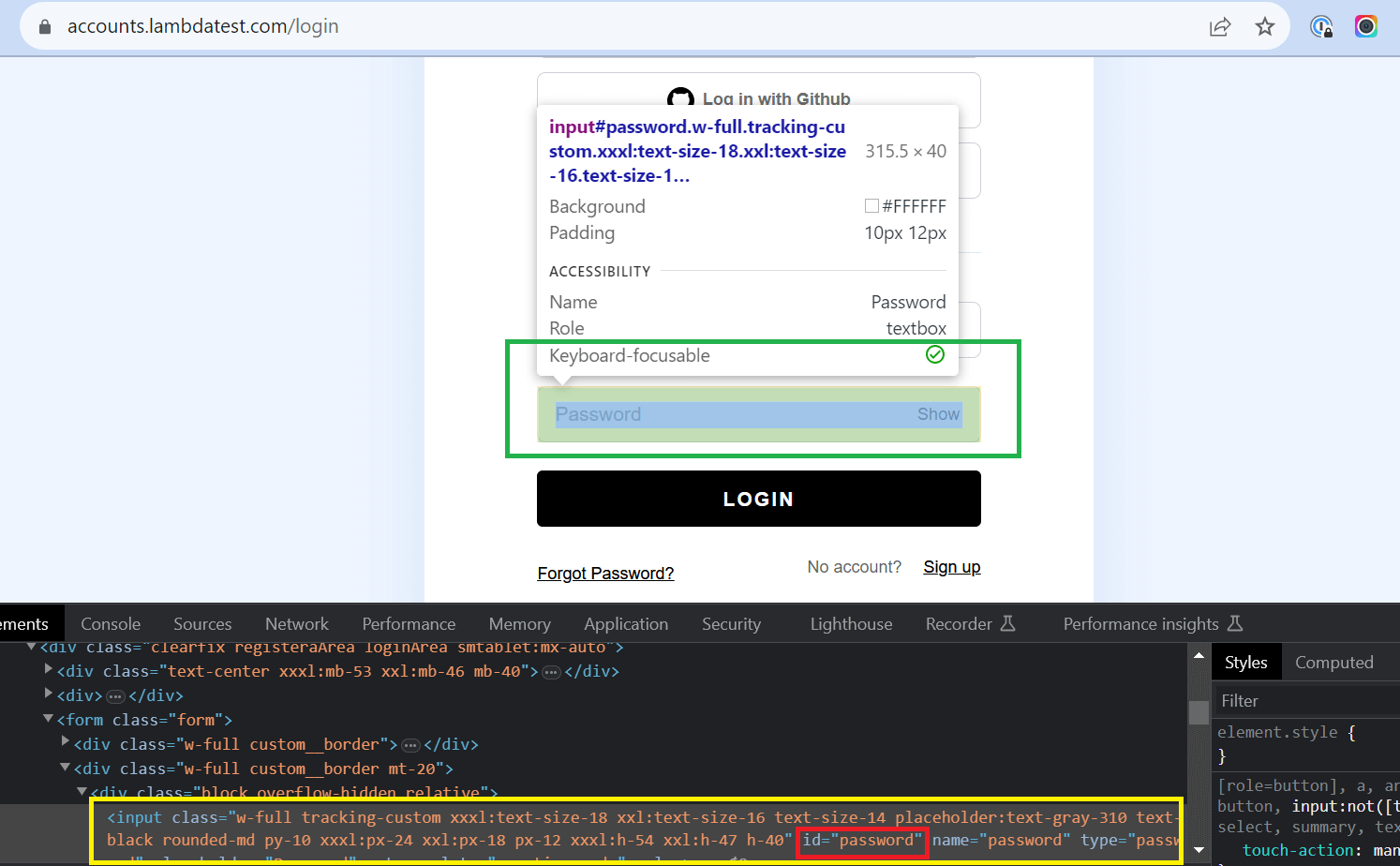
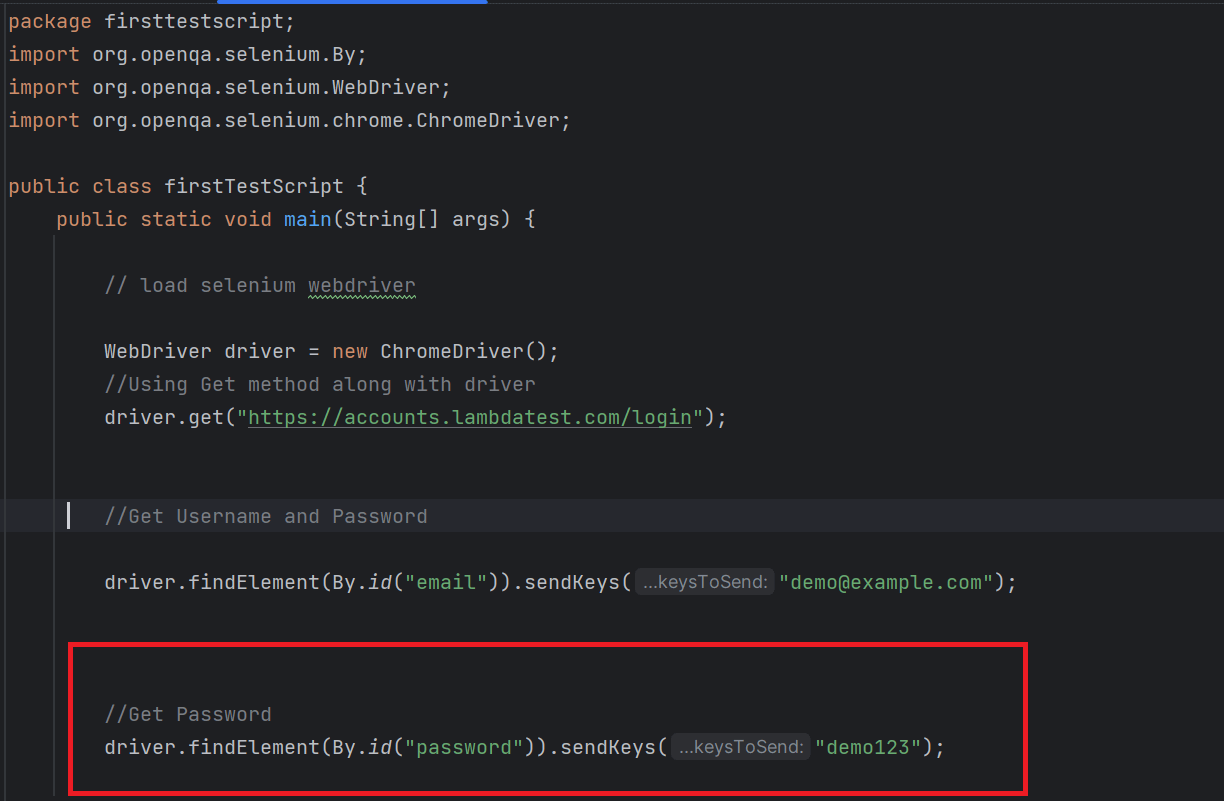
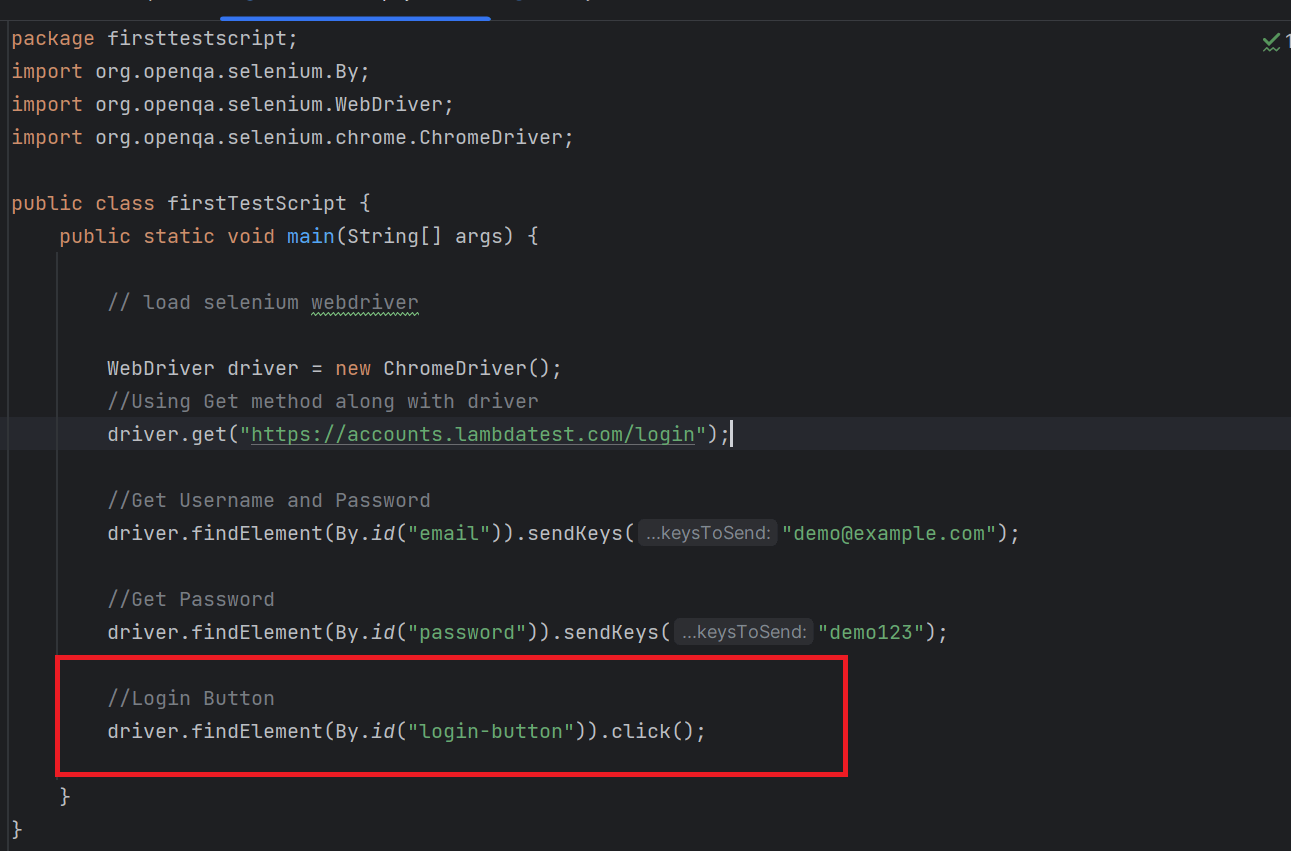
- Load the website's homepage and click the "LOGIN" link. Ensure the Login screen appears and the "Username" and "Password" fields are visible.
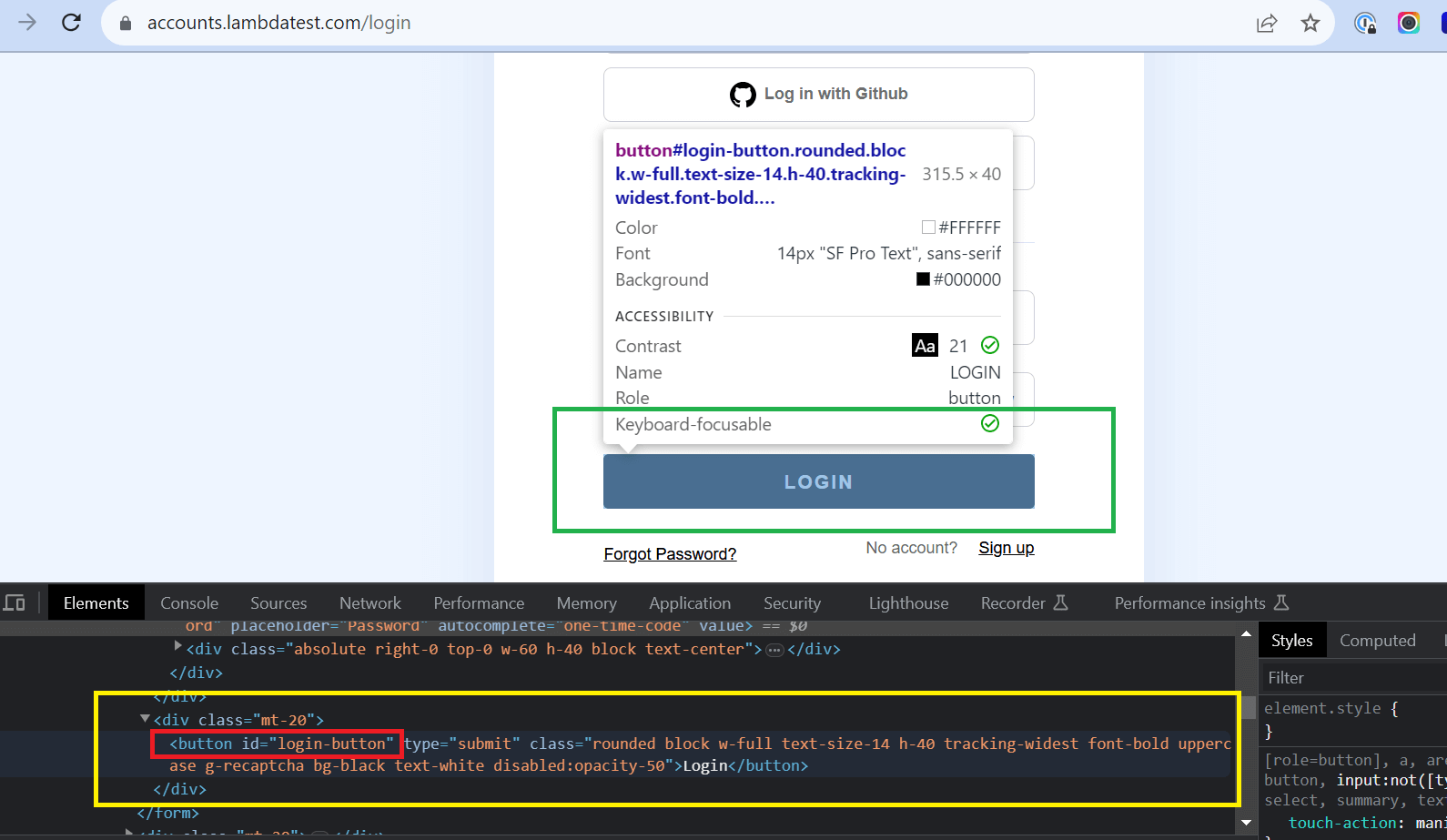
- Enter the email "demo@example.com" and password "demo123," then identify and click the "LOGIN" button.
- Verify and read the visibility of the “Welcome - LambdaTest” on the main screen.
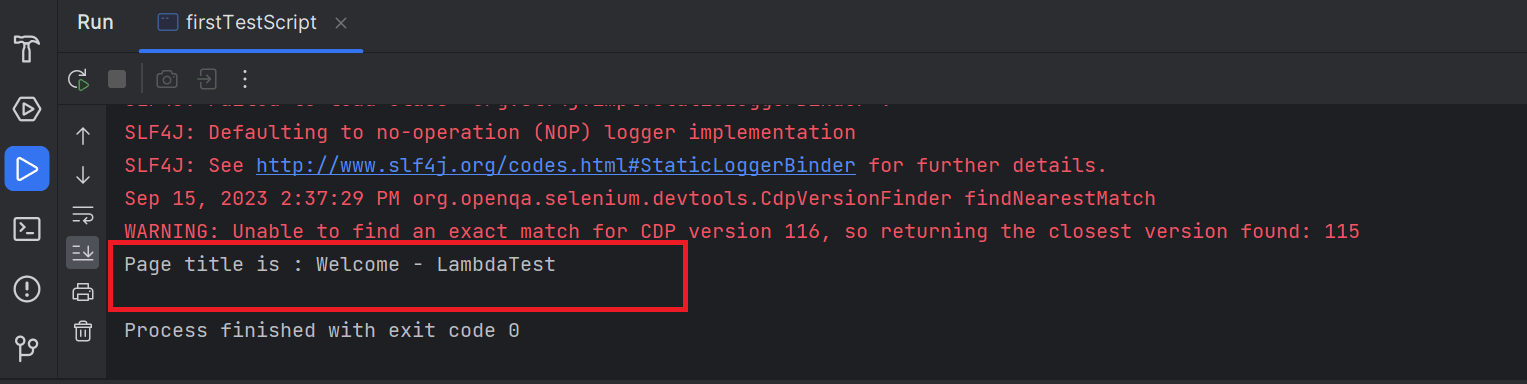
- Get the website's title “Welcome - LambdaTest” screen that appears after login, for example, using getTitle().
- Print the page title "Welcome - LambdaTest" on the console to verify that the login was successful.
- Record the test as passed if the title text matches the expected result. Otherwise, mark the test as failed.

Supercharge testing with LambdaTest! Choose the right tool, scale, and conquer. Try LambdaTest Now!
Supercharge testing with LambdaTest! Choose the right tool, scale, and conquer.
Identification of Test Script Failures
In automation testing, failure of test scripts is a common occurrence that may create hurdles in completing the test process. Knowing about those failures and their reasons will help you overcome such issues while performing software testing. Here are some of the reasons for test script failure.
- Element not found: This test script fails when it cannot locate the elements on the user interface it needs to interact with.
- Synchronization issues: When a software application's response time is slower than expected, there can be timing issues. For example, some scripts involve navigating from one page to another. If the application takes longer to load the new page, the test script might fail as it cannot find the expected elements on the new page.
- Incorrect data: Test data is crucial for the execution of a test script, which may include inputs and datasets to simulate real-world scenarios. However, when test data is incorrect, it may cause unexpected results or errors during the execution of the test. It may eventually lead to failure.
- Environment-related issues: Lead to failures in software testing when tests are executed in different environments due to varying configurations and dependencies.
- Flaky tests: This may happen in the test process where the test fails without any known or actual reasons. This makes it challenging to find any root cause of the failure. The occurrence of flaky tests in software testing also leads to the failure of the test scripts.
- Code defects: Errors in the test script's implementation can lead to incorrect interactions with the application.
Now, let’s learn some debugging methods that the testers can use to address the above test script failure.
Debugging Techniques for Test Scripts
Debugging techniques in case of test case failures is one of the most crucial skills for testers. Some methods that can be used to identify and fix issues may include the following:
- You may implement an approach of logging and reporting in the test scripts that allows easy tracking of the test execution flow and errors. When you analyze the logs, you can pinpoint the location of the failure.
- You may comment or remove parts of the scripts to find any specific features or code snippets leading to failure. With this, you can narrow down the issue and identify the root cause more effectively.
- You may leverage browser developers' tools and testing frameworks to learn more about specific elements of the software applications during the execution of the test to validate their correct identification.
- Debugging features of the integrated development environments can also help the software testers step through the code and evaluate the test execution flow.
Best Practices for Writing a Test Script
To improve the writing of test scripts, here are some of the standard best practices:
- The test script should be clear and requires communication with the project in charge to provide details on the software applications. However, to avoid this, consistently verify that each step in the test script is clear, concise, and coherent, facilitating a smooth testing process.
- To create a test script, you should contain one specific action for testers. It helps ensure that each function is tested accurately and does not lead to skipping any software testing steps.
- You should always define a clear objective for the test script to know what you want to achieve from the test and the functionality that requires testing.
- To the test cases, give descriptive names, as it will help you identify the main aim of the test without going through the entire script.
- Clearly define each test case's test data, input values, and expected results.
- You should ensure that each test case is independent and does not rely on the results of previous tests. It allows for easier debugging and isolation of issues.
- An excellent practice is to create reusable code that can be applied across multiple testing scenarios.
Future Advancements in Test Scripting
The future of test scripting holds tremendous excitement and dynamism as AI and ML get integrated into test script generation and Shift-Left Testing practices gain traction. These trends can revolutionize the testing landscape, ushering in a new era of faster, more intelligent test scripting closely intertwined with the software development process. Let us learn more about this:
AI and ML in Test Script Generation
As the software development landscape undergoes constant evolution, so does the field of software testing. Among the most promising and captivating future trends in test scripting lies the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) into test script generation. This convergence of AI and ML technologies can potentially revolutionize creating, maintaining, and executing test scripts.
Traditional test script creation heavily relies on manual efforts, where testers invest in particular design and writing to cover diverse test scenarios. This process can be time-consuming and resource-intensive, particularly for large-scale applications with intricate functionalities. However, with the infusion of AI and ML, test script generation can transcend into a more automated and intelligent domain.
AI-powered testing tools can analyze the application under test, adeptly learn from its behavior, and automatically generate scripts based on observed patterns and usage. Such tools can discern crucial test scenarios, prioritize test cases, and even identify potential edge cases that might escape human testers' attention. Consequently, test script generation attains swiftness, enhanced efficiency, and reduced error propensity.
Moreover, AI and ML are indispensable allies in test script maintenance. When the application undergoes changes or updates, AI-based tools demonstrate their intelligence by updating the testing procedures to accommodate the modifications, thereby minimizing the effort required for regression testing. This adaptive prowess ensures that the testing procedures remain relevant and practical throughout the software development lifecycle.
Shift-Left Testing and its Impact on Test Scripts
Another critical future trend with a significant impact on test scripting and the entire testing process is Shift-Left Testing. Traditionally, software testing was a phase that transpired toward the culmination of the development cycle. However, with the emergence of Agile and DevOps methodologies, testing has been integrated earlier in the development process.
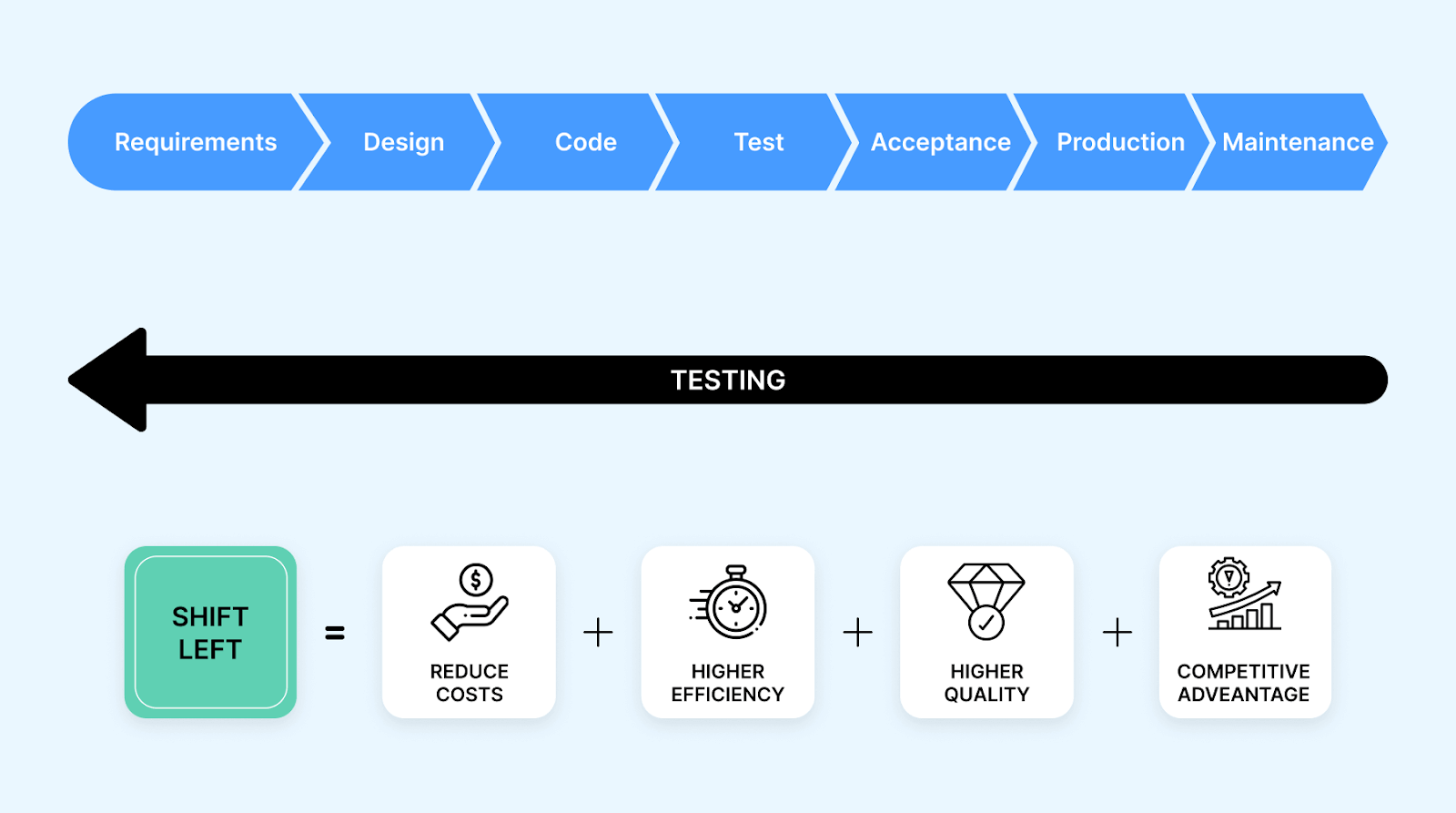
Shift-Left Testing advocates for the active involvement of testers right from the project's inception, enabling a close alignment with developers and other stakeholders. This paradigm shift emphasizes the early detection of defects and issues, ultimately reducing the cost and time involved in rectifying them later in the development cycle.
In software testing, Shift-Left Testing promotes the early creation of testing procedures right at the beginning of the development process, even before the actual coding begins. This proactive approach aids in defining precise testing requirements, identifying potential risks, and establishing a solid testing strategy from the outset.
By engaging testers in the early phases, Shift-Left Testing facilitates seamless collaboration between developers and testers, leading to swift feedback loops and improved software quality. Test scripts created with the Shift-Left approach serve as guiding beacons throughout the development journey, ensuring that the application adheres to the desired functionality and performance requirements from the outset.
Furthermore, testing scripts evolve into dynamic and adaptive assets as testers and developers embrace close collaboration. Feedback from the early testing phases continually improves the test scripts, rendering them more potent in detecting defects and preempting issues before propagating to later stages of development.
Now that you have learned about testing scripts, you must have analyzed how they differ from the test case. Let us get brief on this in the below section.
Conclusion
Test Scripts refer to detailed descriptions that outline the system transactions necessary for validating the application or system under test, guiding testers through the testing process. On the other hand, a Test Case is a step-by-step procedure used to test an application, while a Test Script provides instructions for automated application testing. There are three methods to create test scripts: record/playback, keyword/data-driven scripting, and writing code using a programming language.
Ensure your test script is clear and focuses on a specific action for testers to execute. Using a test script is the most reliable approach to ensure comprehensive testing, leaving no space for omissions and guaranteeing accurate results per the desired testing plan. A Test Script Template is a reusable, formatted document containing essential information for creating a practical test script.
On this page
- Overview
- What are Test Scripts?
- Why use Test Script?
- Type of Test Scripts
- Test Script vs. Test Case
- Understanding Test Script Template
- Information in Test Script
- Approaches for Writing a Test Script
- When to Use the Test Script Approach
- Test Scripting Tools
- Test Scripting Frameworks
- Test Script Development Process
- Test Script Example
- Identification of Test Script Failures
- Debugging Techniques for Test Scripts
- Best Practices for Writing a Test Script
- Future Advancements in Test Scripting
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
Frequently asked questions
- General
Author's Profile

Nazneen Ahmad
Nazneen Ahmad is an experienced technical writer with over five years of experience in the software development and testing field. As a freelancer, she has worked on various projects to create technical documentation, user manuals, training materials, and other SEO-optimized content in various domains, including IT, healthcare, finance, and education. You can also follow her on Twitter.
Reviewer's Profile

Saniya Gazala
Saniya Gazala, a Computer Science graduate, brings two years of hands-on experience in manual testing and delving into technical writing, showcasing her detail-oriented and systematic approach. As a technical reviewer, her key responsibilities involve spotting inconsistencies and factual errors in content. Leveraging her in-depth knowledge, she ensures the accuracy and coherence of the material under review.
Did you find this page helpful?
More Hubs
Try LambdaTest Now !!
Get 100 minutes of automation test minutes FREE!!
 Christmas Deal is on: Save 25% off on select annual plans for 1st year.
Christmas Deal is on: Save 25% off on select annual plans for 1st year.