- Testing Basics
- Home
- /
- Learning Hub
- /
- Test Monitoring and Test Control Tutorial
- -
- October 6 2023
Test Monitoring and Test Control: A comprehensive Guide
Explore key aspects of test monitoring and control, covering definitions, significance, necessity, methods, and best practices.
OVERVIEW
Test Monitoring and Test Control are essential components of any successful project or product development process. In simple terms, they are like the navigational tools that help you stay on course while building something new.
Test Monitoring involves keeping a close eye on the various testing activities, tracking progress, and identifying potential issues or roadblocks early on. On the other hand, Test Control is all about making necessary adjustments and decisions based on the monitoring data to ensure that the testing process stays on track and meets its goals.
Together, they form the dynamic duo that ensures the quality and reliability of your project or product, making them indispensable practices for anyone aiming for success in the world of testing and development.
What is Test Monitoring?
Test Monitoring is like having a watchful guardian for your project's testing phase. It involves continuously keeping an eye on the testing activities, progress, and outcomes to make sure everything is going as planned. Think of it as a checkpoint system that helps you spot potential problems early on.
Test Monitoring keeps track of who is doing what, how much testing has been completed, and whether any issues have popped up during the process. It's like having a dashboard that shows you all the vital signs of your testing efforts, helping you make informed decisions and ensuring that your project stays on the right path to success.
What does test monitoring involve?
Test monitoring involves overseeing and tracking the progress and performance of a testing process to ensure its effectiveness and efficiency in achieving the testing objectives. It is a critical aspect of software testing and quality assurance, aimed at ensuring that testing activities align with the defined goals and requirements.
Here are the key components and aspects of test monitoring:
- Progress Tracking: Keeping tabs on the testing progress compared to the planned timeline and milestones.
- Test Execution Monitoring: Supervising the actual execution of test cases to ensure they follow the test plan.
- Resource Management: Efficiently assigning and using testing resources like tools and personnel.
- Risk Assessment and Mitigation: Identifying potential risks and planning to minimize their impact on testing goals.
- Adherence to Testing Standards and Processes: Making sure that testing activities comply with established standards and procedures.
- Communication and Reporting: Providing regular updates and reports to keep stakeholders informed about the testing progress.
- Feedback Incorporation: Gathering feedback from testing activities and using it to improve the testing process.
- Performance Metrics Monitoring: Tracking key metrics to evaluate the quality and effectiveness of testing efforts.
- Documentation and Record-Keeping: Thoroughly documenting all testing activities for future reference and traceability.
Key Metrics in Test Monitoring?
Key metrics in test monitoring are crucial for assessing the quality and progress of the testing process. These metrics include:
- Test Coverage: Percentage of the application or system that has been tested, ensuring comprehensive coverage.
- Defect Density: The number of defects identified per unit of code, indicating code quality.
- Pass/Fail Rates: The ratio of passed tests to failed tests, reflecting the stability and readiness of the software.
- Defect Severity and Priority: Classification of defects based on severity (impact) and priority (urgency to fix), aiding in effective defect management.
- Execution Time and Speed: Time taken to execute test cases and the speed at which tests are completed, helping optimize testing efficiency.
- Test Case Effectiveness: The ratio of passed tests to total tests executed, indicating the effectiveness of test cases.
- Traceability: Mapping requirements to test cases, ensuring all requirements are covered by tests and aiding in impact analysis.
- Resource Utilization: Efficient usage of testing resources such as testers, tools, and environments.
- Customer/User Satisfaction: Feedback and satisfaction scores from end-users, reflecting the quality of the product.
- Regression Test Effectiveness: Measure of how well regression testing ensures that new changes do not adversely affect existing functionalities.
These metrics provide valuable insights into the testing process, enabling timely adjustments and improvements to enhance overall software quality.
What is Test control?
Test Control is a crucial aspect of the testing process that often goes undervalued but plays a vital role in ensuring the success of a project. In simple terms, Test Control can be thought of as the steering wheel of your testing efforts. It involves actively managing and adjusting the testing process to ensure it stays on course and aligns with the project's objectives. This means making informed decisions based on the data gathered during Test Monitoring, and taking corrective actions when necessary.
Test Control ensures that the testing process adapts to changing circumstances, addresses issues as they arise, and ultimately helps deliver a high-quality product or project. It's the hands-on approach that keeps your testing efforts on track and ensures they yield the desired results.
Why do we need Test Monitoring & Test Control
- Detecting Problems Early: Test Monitoring helps us catch issues in AI systems before they become big problems. It's like finding a crack in a dam while it's still small, before it leads to a catastrophic flood.
- Optimizing Performance: Test Monitoring allows us to fine-tune AI systems, making them work better and smarter. Think of it as constantly tweaking a recipe until it's perfect.
- Keeping Data in Check: AI relies on data, and Test Monitoring ensures that the data used is accurate and reliable. It's like making sure the ingredients in a recipe are fresh and of high quality.
- Adapting to Change: In the real world, things change all the time. Test Monitoring helps AI systems adapt to these changes, much like a GPS system recalculating your route when you take a wrong turn.
- Reproducible Results: Test Control ensures that tests are consistent and repeatable, which is essential for verifying the AI system's reliability. It's like making sure you can bake the same delicious cake every time you follow a recipe.
- Reducing Bias: Test Control helps identify and minimize biases in AI systems, making them fairer and more equitable. It's like ensuring that a judge's decisions are based on facts and not personal biases.
- Generalization Testing: It assesses how well AI systems can handle new, unseen situations. It's like checking if a student can apply what they've learned to different types of problems.
- Meeting Regulations: In some industries, there are strict rules about how AI systems must be tested and controlled. Test Control ensures compliance with these rules, much like following traffic laws while driving.
Test Monitoring and Test Control are like the guardians of AI, making sure it works well, is fair, and follows the rules. They are crucial for building AI systems that benefit everyone and can be trusted.
How do we Monitor and Control?
Monitoring
- Real-Time Observation: Continuously observe the AI system during testing to track its performance.
- Data Collection: Gather data on the AI's responses and behavior during testing.
- Metrics and Benchmarks: Define key performance metrics and benchmarks to assess the AI's behavior against expected standards.
- Anomaly Detection: Use automated testing toolsand algorithms to detect anomalies or deviations from expected results.
- Feedback Loops: Establish feedback mechanisms to report issues and irregularities to the development team promptly.
Control
- Test Environment Setup: Create a controlled testing environment that mimics real-world conditions as closely as possible.
- Test Case Design: Carefully design test cases that cover a wide range of scenarios, including edge cases and unusual inputs.
- Data Management: Ensure the quality and diversity of test data, and be mindful of potential biases in the data.
- Automation: Use test automation tools to execute test cases consistently and reduce human error.
- Version Control: Keep track of different versions of AI models and algorithms to ensure reproducibility of tests.
- Documentation: Maintain detailed documentation of test procedures, including inputs, expected outputs, and any issues encountered.
- Bias Detection and Mitigation: Implement techniques to detect and mitigate bias in the AI system's responses during testing.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensure that your testing process complies with industry regulations and standards, especially in fields with strict guidelines, such as healthcare or finance.
- Continuous Improvement: Regularly review and refine your testing processes based on feedback and emerging best practices.
By combining effective monitoring and control practices, you can optimize the testing of AI systems, making them more reliable, accurate, and ethical in their operations. This approach is crucial for building trust in AI technology and ensuring its successful deployment in various applications.
Best Practices for Test Monitoring and Test Control in Software Testing
Test monitoring and test control are critical aspects of the software testing process, ensuring that testing activities stay on track, deliver meaningful insights, and align with project goals. Implementing best practices in test monitoring and test control is vital to enhance testing efficiency and effectiveness. Here are some best practices:
Best Practices in Test Monitoring:
- Define Clear Objectives:
- Use Test Management Tools:
- Establish Key Performance Indicators (KPIs):
- Regular Reporting and Communication:
- Monitor Test Execution:
Clearly define the objectives of the testing phase, including what needs to be tested, the expected outcomes, and the criteria for success. This clarity guides the monitoring process effectively.
Employ test management tools to track and monitor test cases, test execution, progress, and results. These tools provide real-time insights and facilitate efficient monitoring.
Define relevant KPIs to measure testing progress and quality. Metrics such as defect density, test case execution rates, and defect closure rates are crucial indicators for monitoring.
Implement regular reporting mechanisms to keep stakeholders informed about testing progress, issues, and risks. Clear and concise reporting facilitates better decision-making.
Monitor the execution of test cases to ensure they are running correctly and generating the expected results. Address any discrepancies promptly to avoid delays.
Best Practices in Test Control:
- Adhere to Testing Standards:
Establish and adhere to testing standards and guidelines to maintain consistency and quality throughout the testing process. This ensures that tests are conducted uniformly and effectively.
- Conduct Reviews and Audits:
Regularly review and audit the testing process to identify areas for improvement and compliance with defined processes. Conduct peer reviews of test cases, scripts, and plans.
- Adapt to Changes:
Be flexible and adaptable to changes in project requirements, timelines, or resources. Modify the testing approach accordingly, ensuring that testing remains effective and aligned with project changes.
- Implement Version Control:
Employ version control systems to manage changes to test scripts and test assets. This ensures that the correct versions of scripts are used consistently during testing.
- Continuously Optimize Processes:
Continuously analyze the testing process and identify opportunities for optimization. Implement improvements to enhance efficiency, accuracy, and effectiveness in testing.
- Involve Stakeholders:
Engage stakeholders, including developers, product managers, and quality assurance teams, in the test control process. Collect feedback and insights to refine the testing approach and make necessary adjustments.
Conclusion
Test Monitoring and Test Control are indispensable components in the realm of software testing, playing vital roles in achieving favorable testing outcomes. Test Monitoring involves overseeing and observing testing activities to ensure adherence to predefined plans and to gain valuable insights into project progress. It entails diligent observation and oversight, ensuring that testing plans are executed as intended. This oversight provides critical insights into the progress of the project.
On the other hand, Test Control involves real-time adjustments and decision-making to keep the testing process on track. It addresses deviations from the established course and optimizes testing efforts. The seamless integration of these practices into the testing lifecycle enhances efficiency and effectiveness, aligning the testing process with project goals. Employing best practices and appropriate testing tools further empowers organizations, leading to improved software quality and success in software development projects.
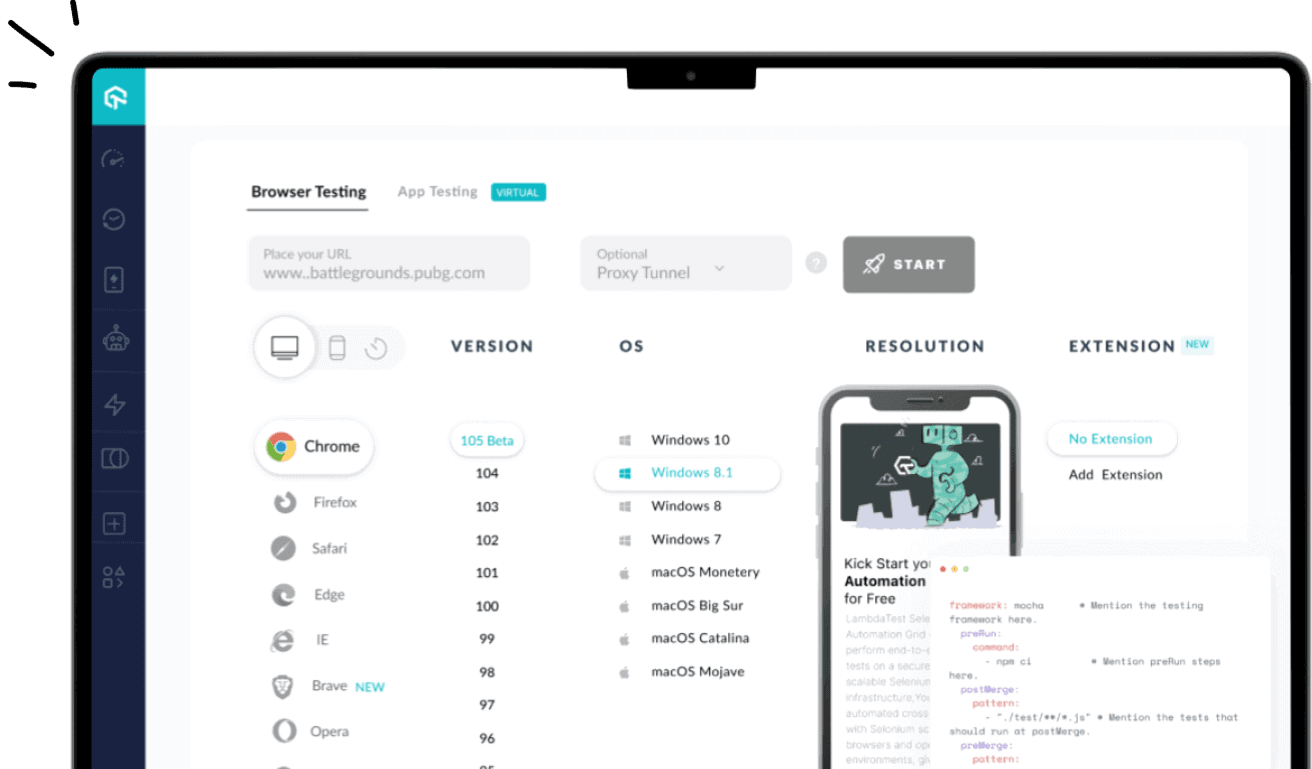
2M+ Devs and QAs rely on LambdaTest
Deliver immersive digital experiences with Next-Generation Mobile Apps and Cross Browser Testing Cloud
On this page
- Overview
- What is Test Monitoring?
- What does test monitoring involve?
- Key Metrics in Test Monitoring?
- What is Test control?
- Why do we need Test Monitoring & Test Control
- How do we Monitor and Control?
- Best Practices for Test Monitoring and Test Control in Software Testing
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
Frequently asked questions
- General
Author's Profile

Vishal kumar Sahu
Vishal, a tech enthusiast and Digital Marketer at LambdaTest, is on a continuous learning journey in the dynamic field of software testing. His passion for quality assurance is evident in his dedicated approach to mastering the intricacies of testing methodologies. Recently joining LambdaTest, Vishal is captivated by the fascinating world of QA and software testing. With a relentless pursuit of knowledge, he embraces challenges, contributing to LambdaTest's commitment to excellence in the ever-evolving landscape of technology.
Reviewer's Profile

Harshit Paul
Harshit is currently the Director of Product Marketing at LambdaTest. His professional experience spans over 7 years, with more than 5 years of experience with LambdaTest as a product specialist and 2 years at Wipro Technologies as a certified Salesforce developer. During his career, he has been actively contributing blogs, webinars as a subject expert around Selenium, browser compatibility, automation testing, DevOps, continuous testing, and more.
Did you find this page helpful?
More Hubs
Try LambdaTest Now !!
Get 100 minutes of automation test minutes FREE!!
 Christmas Deal is on: Save 25% off on select annual plans for 1st year.
Christmas Deal is on: Save 25% off on select annual plans for 1st year.