Test Execution Tutorial: Detailed Guide With Best Practices
- Learning Hub
- Test Execution Tutorial: Detailed Guide With Best Practices
CHAPTERS
- Overview
- What is Test Execution
- Importance of Test Execution
- Activities of Test Execution
- Ways to perform Test Execution
- Guidelines for Test Execution
- What aspects to consider during Test Execution
- Test Execution States
- Test Execution Priorities
- Test Execution Cycle
- Test Execution Report
- How to Achieve Faster Test Execution Cycles
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
OVERVIEW
Test Execution involves verifying the functionality of each feature in the software application, which is placed in different scenarios to validate its response in those situations. It plays a crucial role in the testing process to help teams create robust software applications that meet the end-user requirements.
As testing software is a complex process, Test Execution helps development team ensure efficiency, reliability, and compliance with industry standards. It is the final step in the testing process and is usually performed after the test cases have been created and reviewed.
What is Test Execution?
Test Execution refers to the execution of test cases of software applications to ensure they meet the pre-defined requirements and specifications. In this case, it compares the intended results with the actual results. The Test Execution phase is an essential part of the Software Testing Life Cycle (STLC) and Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC). It begins with the completion of the Test Planning phase.
Once the test script is ready, it is shared with the development and business analyst team for review. Then the QA incorporates the necessary changes. This marks the completion of the test design process. After getting the test cases ready, we need to have the application prepared to initiate the Test Execution process.
Besides test cases, the software build and test environment are also essential aspects of the Test Execution phase.
Listed below are the pointers that ensure the effective execution of test cases.
- Ensure that the test design (i.e., defining the test cases) is complete.
- Test management tools must be available to use.
- A proper workflow to track test results and metrics.
- Every folk should know what data to be tracked.
- Team members must know the criteria for logging tests and reporting bugs.
Importance of Test Execution
Test Execution allows software teams to reach the next level of development and ensures your projects run efficiently and smoothly. It’s also responsible for ensuring the application’s competency in the global market. When the Test Execution intended result is the same as the actual results, the software is ready to go live in the market.
Test Execution evaluates the efforts of all team members involved in the development process and answers some of the below questions:
- If the requirements are collected and correctly interpreted?
- Are the requirements correctly incorporated in designs and architecture?
- Is the development team's software application built in accord with these requirements?
Activities of Test Execution
This phase aims to validate the application under test before moving on to production. To complete this phase, the testing team conducts different types of testing to ensure product quality. In addition, bug reporting and retesting are carried out during this process.
Following are the important activities of the Test Execution phase.
- System Integration testing: This is the phase where the actual validation of the application under test begins. System integration testing is a black box testing technique that validates the system's compatibility with specified requirements and test cases.
- Defect reporting: Defect Reporting is the process of identifying flaws in an application under test by testing or collecting customer feedback and developing new versions of the product that address the problems highlighted by the customer. Hundreds of flaws exist in complex and business-critical systems; monitoring, analyzing, and prioritizing these defects is difficult. The defects increase with time, and the defect monitoring system is utilized to help manage them effectively.
- Defect mapping: Once an issue has been identified and logged, it should be mapped to the appropriate failed or blocked test cases and requirements in the requirement traceability matrix. The defect reporter is in charge of this mapping. After mapping the test cases and requirements to the defect, stakeholders can analyze and decide whether to fix or reschedule the defect based on priority and severity.
- Re-testing: Re-testing is the constant practice of testing individual test cases to ensure that bugs are fixed, and the functionality of the software applications functions appropriately in the final execution. Re-testing uses the same set of unit tests to ensure the code's functionality. In other words, Re-testing is the process of repeating the same manual or automated tests to ensure that the new build works flawlessly.
- Regression testing: Regression testing is a technique to validate the new build after a code commit. A tester's responsibility in this process is to ensure that no new bugs are introduced into the code due to software modifications and adjustments. After creating the Regression test suite, you may automate it with an automation testing tool. However, it does not apply to Re-testing.
Ways to perform Test Execution
This Test Execution tutorial section focuses on multiple ways to execute tests. Testers can choose the preferred method based on their needs.
- Run test cases: It is a simple approach for running test cases and typically runs on the local machine. Other test artifacts, such as test plans, test scripts, test environments, test case execution records, and test suites, can be coupled with the test case.
- Run test suites: A test suite is a collection of test cases (both manual and automated). When launching suites, you can select whether to execute the test cases sequentially or parallel. When using sequential suite execution, you can opt to stop the execution of the suite if a single test case fails. This is helpful if the success of the last test case is dependent on the success of the current test case.
- Run test case execution and test suite execution records: Test Execution can be automated and manually executed. Recording Test Execution is a key activity in the test process and helps to identify Test case execution and test suite execution. It is very important to follow Test Execution procedures since they help to keep things organized, reduce errors, and make the testing process more efficient.
- Generate test results without execution: Test results are significant to the software development process for tracking the project progress and identifying and resolving problems. However, executing all test cases is not always feasible due to limited time and resources. In such cases, generating sufficient test results from non-executed test cases can be an effective alternative strategy for obtaining comprehensive Code Coverage vs Test Coverage.
- Modify execution variables: In your test scripts, you can modify variables for particular test runs using execution variables.
- Run manual and automated tests: There are many ways to perform Test Execution. Manual, Automated, and Continuous Testing are some of the most common ways to test software.
- Schedule test artifacts: Test artifacts are significant when performing Test Execution because they document the results of previous tests and provide information about what needs to be tested in future Test Executions. Test artifacts can include screenshots, video recordings, data reports, and more. Test artifacts should be stored securely so they can be accessed whenever needed.
- Defect tracking: Test Execution and defect tracking are inseparable. Without defect tracking, test execution becomes difficult at best and impossible at worst. If you can't adequately track defects that arise during testing, you'll have no way to identify what went wrong and why which makes it impossible to improve your process.
Guidelines for Test Execution
Upon satisfying the entry criteria and delivering the test objective, the next phase is to execute the test. Listed below are some critical points of the Test Execution process to help you better understand.
- Execution of test cases means verifying and validating the pre-decided requirements.
- The build (a standalone application) is one of the most critical aspects that must be available to start the Test Execution.
- Test Execution consists of three phases: the creation of test strategy and cases, execution of test cases, and validation of test results.
- As Test Execution occurs in the QA test environment, creating a dedicated development and QA environment is recommended to ensure that the development team's work on the code does not occur within the same location.
- As the project progresses, the size of the test team may change. During the Test Execution phase, the team reaches its maximum size.
- Select the test suites based on the potential defects and business requirements. Further, they are shared with the development and business team for their reviews and feedback.
- A group of highly-skilled software testers typically performs Test Execution.
- A Test Execution cycle consists of two rounds. All test suites or cases are executed in the first cycle to identify any blockers or high-critical defects. In the second cycle, testers identify medium-sized bugs, correct script gaps, and get test results.
- There is also one phase - Test Readiness Review occurs before the Test Execution phase and after build deployment( AUT). It is the type of transitional step that ends the Test design phase and initiates the Test Execution phase.
- Exploratory testing is performed once the build is ready for testing to eliminate any critical defects before starting the next level of testing.
- After the deployment phase, smoke and sanity testing are performed to ensure that the current build is working correctly.
- The output of the execution of test cases is in the form of test reports, i.e., bug report or Test Execution status report.
- Teams can execute tests manually or by leveraging automation tools.
What aspects to consider during Test Execution
The Test Execution tutorial section will look at some prerequisites for executing test cases. Before starting the testing process, the QA team must consider a few factors that can impact the test results. A few of them are as follows.
- Make sure the test design and test case creation are completed.
- Select a subset of the test suite for this cycle based on risk.
- For each test suite, assign test cases to testers.
- Track test status, execute tests, and report bugs continuously.
- Identify and resolve blocking issues as they arise.
- Report daily statuses, adjust assignments, and reevaluate priorities.
- Analyze and report findings from the test cycle.
Test Execution States
Test Execution states help teams in determining test completion and success. The test completion rate allows the team to manage the remaining portion of the test effort, including the risk of potentially undiscovered quality issues. The test success rate helps the team determine whether the software or system is functioning correctly. It is essential to classify various states of Test Execution.
The following are some of the most critical execution states and their classifications.
- Pass: The test procedure is run and satisfies the intended result.
- Fail: The test procedure is run but does not satisfy the intended result.
- Inconclusive: Further analysis is needed to determine the results of the test.
- Block: This test procedure cannot be run since one of the test case requirements has not been met.
- Deferred: The test procedure is not yet executed and will be scheduled for a future test release for execution.
- In progress: A test procedure is currently being executed.
- Not run: No test has been run yet.
Test Execution Priorities
When it comes to software testing, many factors need to be considered when deciding on Test Execution priorities. To successfully choose the right tests and prioritize them effectively, we need to know what they are and how they affect the testing process.
Test execution priority is a complex, multi-dimensional function that considers numerous factors. While there are formal schemes in some industries (e.g., the FDA), I believe that the priorities of any software test organization cannot be formalized due to the flexibility and differences between systems, data, and business objectives. The following is a list of variables that have been found to influence Test Execution priority:
- Risks covered
- Platforms covered
- Test complexity
- Test case depth
- Test case breadth
Test Execution Cycle
A Software testing life cycle is an iterative, cyclical process that aims to prevent software errors. Testing activities include analysis, planning, designing, setting up, executing, and closing tests. Similarly, Test Execution is also part of the Software testing life cycle and plays a vital role in the testing life cycle.
The Software testing life cycle consists of six different phases.
- Requirement analysis: The Software testing life cycle begins with requirement analysis. As part of this phase, functional and non-functional requirements are examined from a testing perspective to identify testable requirements. customers' Quality Assurance team works with customers, solution architects, technical leads, business analysts, and other stakeholders to comprehend the client's needs and tailor tests accordingly.
- Test planning: With the data collected in the requirement analysis, the QA team goes one step closer to planning the testing process. Test planning or test strategy is the most critical phase of the Software testing life cycle. All the testing strategies employed to test the software during this phase are defined.
The test lead determines the project's cost estimates and efforts at this stage. A range of test activities is planned and strategized here, along with resource analysis, which boosts the effectiveness of the planning phase and helps in accomplishing the testing target. Software testing cannot be valued without effective tools, primarily when you perform test automation.
This phase includes the selection of the appropriate software testing platforms. There are numerous software testing platforms available on the market. Regarding testing at scale, cloud-based automation testing platforms like LambdaTest are the way to go.
- Test case designing and development: The requirements have been reviewed, and a test plan has been developed in response. It's time to be creative and mold this test method into test cases. Test cases are created and refined based on a test strategy and particular specifications to examine and validate each test plan.
Business analysts can create this requirement document, which should contain all potential user scenarios for the software application. You can design the test cases after getting the requirement document.
Designing test cases includes two steps: identification and analysis of test cases. The first stage is to discover all of the feasible test cases that can cover all user scenarios. Then, after reviewing them, you need to remove the test cases that are not fit for execution, have a low priority, or may not be able to find any flaws. When the test design process is completed, the quality assurance team begins designing effective test cases.
- Test environment setup: Following the design and development of the test cases, the software testing process requires an adequate platform and environment that includes the essential and necessary hardware and software to establish and replicate the ideal conditions and environmental factors to conduct actual testing activities.
The testing environment is set up at this phase. The test environment defines the parameters that will be used to evaluate the software. Since this is a separate activity, it can run alongside the test case development process.
The testing environment varies from one organization to the next. Sometimes, the developer or tester creates the testing environment; in others, the clients create the testing environment depending on their needs and expectations.
While the customer or developer sets the test environment, the testing team prepares for Smoke testing. Smoke testing aims to verify the testing environment by identifying its readiness and stability.
- Test execution: The QA team can now conduct some proper testing activities because they have the test cases, test data, and testing environment. In this phase, the testing team performs the test cases based on the test cases and test planning prepared in the previous phases, like test planning and test case design.
A score is assigned to each test case that passes. The development team receives the notification of a defect or issue when a test case fails. For future reference, these bugs can be linked to test cases.
Ideally, every failed test case would be associated with a defect. Identical test cases are rerun after the development team has addressed the bug to ensure that it is indeed fixed and working as expected. The report shows the number of test cases passed, blocked, failed, or not run.
- Test closure: The test closure phase begins with the completion of the Test Execution phase and the software product delivery. This is the stage at which the entire cycle is reviewed. In addition to the test results, other testing-related aspects like quality attained, test coverage, test metrics, cost of the project, adherence to deadlines, and so on are considered and analyzed.
The team also reviews which components of the Software testing life cycle process performed well and which may be improved. The test case report is generated to determine the severity of the issues. After the test cycle is completed, the test metrics and closure reports are generated.
Explore our Analytical Test Strategy Guide. Understand its importance, roles, tools, defects management, metrics, automation, and more. Master analytical testing confidently.
Test Execution Report
The software Test Execution report is one of the important deliverables offered to the client after completing the software testing and development process. It provides a comprehensive testing process summary with accurate details and information. The report should be well-organized, concisely providing all essential information.
It usually follows a set of templates that contains an overview, summary, and analysis of the test plan, test cases, issues encountered during validation tests, defects list, and defect tracking information. The report also includes detailed information on the various tools used for testing and their effectiveness in finding critical defects in the developed software product.
A typical test report has the following template:
- Test Summary Report Identifier
- Summary
- Variances
- Comprehensive Assessment
- Summary of Results
- Evaluation
- Summary of Activities
- Approval
How to Achieve Faster Test Execution Cycles?
The duration of release cycles has become a crucial factor for software application development. Time To Market (TTM) becomes critical in a dynamically changing business environment since you always want to keep up with your competitors. Being sluggish in releasing items, offering updates, or engaging customers erodes the market.
Startups and major businesses are looking for tools and approaches to help them accelerate their development and testing workflows. Regarding on-premise testing, you'd probably agree that complicated, scalable infrastructure setup and maintenance costs can significantly raise your burn rate. If you have a small QA team with everyone sitting in the same room or a large distributed team scattered over multiple places, cloud-based testing has something for everyone. It even helps in the resolution of the most complex remote testing challenges.
Cloud testing is most typically used to simulate testing environments over the cloud. LambdaTest is one such cloud-based cross browser testing platform that lets you test your web and mobile applications across 3000+ browser, device, and OS combinations. By leveraging parallel Test Execution on LambdaTest’s online Selenium Grid, organizations and enterprises can accelerate their testing efforts and improve their product’s quality. To test your websites and applications in real-user conditions, you can harness LambdaTest real device cloud.
There are numerous benefits of cloud testing. However, users often come up with a question - A cloud infrastructure isn't as fast as a local one. On the other hand, local setups lack the features of cloud-based setups.
In the next section of this Test Execution tutorial, we will see how you can overcome the slow Test Execution challenges and faster your release cycles with LambdaTest’s HyperExecute and Test At Scale.
Faster Test Execution with LambdaTest ‘s HyperExecute
HyperExecute by LambdaTest is a next-gen smart testing platform to help businesses run end-to-end automated tests at the fastest speed possible. Therefore, it enables you to achieve blazing fast Test Execution up to 70% faster than any traditional cloud grids.
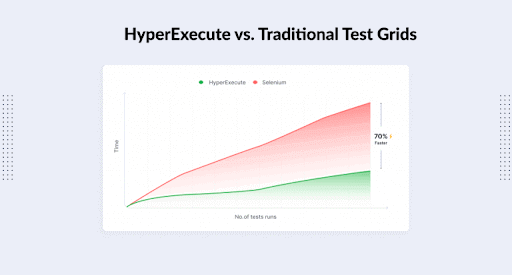
These are some of the reasons why you should use HyperExecute.
- Ensure that powerful tooling is available to both developers and testers.
- Lack of a unified testing environment.
- The cloud platform requires speed compromises, which is unfair.
In a nutshell, HyperExecute combines the speed of a local configuration with the finest cloud capabilities – speed + best-in-class intelligence + zero maintenance + autoscaling.
By executing tests at breakneck speed, HyperExecute significantly reduces feedback time for developers. Instead of testers updating their code every time, the tooling does the heavy work.
Accelerate Testing with LambdaTest’s Test At Scale
Development teams are unaware of which test cases were impacted by their most recent code changes. As a result, teams continue to run all of the tests in every job, which is unnecessary and only leads to:
- Clogged pipelines
- Expensive resources
- Low productivity
- Slow release cycles
LambdaTest’s Test At Scale is a platform for test intelligence and observability that reduces testing time and gives faster feedback. It enables developers to gain early insights into flaky tests and boosts their productivity, allowing them to ship code frequently and confidently.
Subscribe to the LambdaTest YouTube Channel and get the latest tutorials around Selenium testing, Cypress E2E testing, Responsive testing, and more.
Conclusion
In the software development life cycle, Test Execution plays a critical role in identifying defects, bugs, and issues in the system. It is also a part of all test activities. With Test Execution, teams can create a product that meets the end-user requirements and offer different types of services.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is a Test Execution and Report?
Test Execution report shows the ratio of passed tests to all tests executed. This report shows the number of Test Case templates created, their executions, and the number of executions with the given status.
Why is Test Execution important?
Test Execution allows software teams to move on to the next development phase and ensures that your projects function quickly and successfully. It is also responsible for ensuring the application's competency in the global market. When the expected Test Execution results match the actual results, the software is ready to go live in the market.
Author's Profile

Harish Rajora
Harish Rajora, He is a computer science engineer. He loves to keep growing as the technological world grows. He feels there is no powerful tool than a computer to change the world in any way. Apart from his field of study, he likes reading books a lot and write sometimes on Twitter.
Reviewer's Profile

Salman Khan
Salman works as a Digital Marketing Manager at LambdaTest. With over four years in the software testing domain, he brings a wealth of experience to his role of reviewing blogs, learning hubs, product updates, and documentation write-ups. Holding a Master's degree (M.Tech) in Computer Science, Salman's expertise extends to various areas including web development, software testing (including automation testing and mobile app testing), CSS, and more.
Try LambdaTest Now !!
Get 100 minutes of automation test minutes FREE!!
 Christmas Deal is on: Save 25% off on select annual plans for 1st year.
Christmas Deal is on: Save 25% off on select annual plans for 1st year.