Test Execution: Its Features And Tools With Examples
- Learning Hub
- Test Execution: Its Features And Tools With Examples
CHAPTERS
- Overview
- What is a Test execution tool?
- Why use a Test execution tool?
- Features of Test execution tools
- Advantages of Test Execution Tool
- Disadvantages of Test execution tool
- Scripting and Comparison techniques of Test Execution tools
- How does a Test execution tool help in Test planning ?
- How to pick the right Test execution tool?
- How to use a Test execution tool?
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
OVERVIEW
A Test execution tool can be characterized as a product that helps in one or more test activities, including test planning, gathering requirements, building, running tests, recording defects, and analyzing results.
It is crucial in the software development life cycle to find any gaps, flaws, or missing requirements against the actual customer requirements. Along with the software development life cycle, the Test execution tool plays a crucial role in the software testing life cycle.
Test execution tools require scripting languages to run. Scripting languages are basically programming languages. Software testers who wish to run a test execution tool directly must have programming skills to create and modify scripts.
What is a Test execution tool?
A testing tool in software testing refers to a Test execution tool or simply a tool that can run tests. A Test execution tool is also known as a test running tool. Since they can record or capture manual tests, therefore, referred to as capture/playback tools, "capture/replay" tools, or "record/playback" tools.
A test execution tool tests the developed software application against a specific test case scenario and compares the results to the expected results and post conditions. Test execution helps to ensure that the generated software application satisfies the pre-defined criteria and end-user specifications. Also, it links the performance of test cases or test plans on software applications.
Test execution tools can be classified based on different parameters like,
- The function of the tool
- Kind of operations that the tool can perform
- Different testing types and levels it supports
- Type of license (open source, free, commercial)
- The technology used in the tool
Why use a Test execution tool?
The majority of testers use Test execution tools for running test automation. This statement is somewhat ambiguous because it alternatively refers to test running, capture, or replay tools. It falls under the category of software testing tools most frequently. These tools initially automate regression tests since they quickly and effectively execute test scripts and shorten test execution times.
A high-skilled tester or professional with solid expertise in programming languages can design and modify test scripts with the Test execution tool to execute test cases and scripts correctly.
Features of Test execution tools
The testers already run most of the tests using Test execution tools. One of the most significant advantages of utilizing this Test execution tool is the ability to run all previous tests whenever an existing system is upgraded or modified.
For example, to address a defect or add new functionality. It ensures that the newly added modifications or functionality didn’t affect the existing system.
Following are some of the features of Test execution tools -
- Record (capture) test inputs while running tests manually.
- Run tests using scripts that have been stored and possibly data files that the end-user may have accessed (whether data-driven or keyword driven testing is employed).
- To dynamically compare screens, items, links, controls, objects, and values during the test run.
- To start the comparison after test execution.
- Record test results (pass/fail, variations between expected and actual results).
- Hide or filter the subsets of actual and expected test results, like filtering out the screen's current time and date, which are irrelevant to a specific test.
- To synchronize test inputs with the application under test.
- To send the test summary to a test management platform.
Advantages of Test Execution Tool
Until now, we have covered the basics of the Test execution tool; let’s have a look at the advantages of using the Test execution tool.
- Automation testing is a valuable and effective method for carrying out tests, especially regression tests that must be run repeatedly during each cycle of an iterative development model.
- These tools are essential in the development cycle since they involve numerous builds and follow-up smoke tests to validate those builds.
- Test scripts in automation require configuration management to monitor the many test objects and pieces, including test data and test scripts, which has a similar benefit to automation.
Disadvantages of Test execution tool
To make the most out of any tool, you should always have a clear idea about its pros and cons. This will help you to know the conditions where implementation of the tool will give the best possible results.
- Since it only keeps test inputs that have been recorded and not test cases, the script does not know the expected results until you code it.
- Several or hundreds of test scripts could be rendered invalid by a bit of modification to the software.
- Unrealistic expectations are one of the biggest challenges to success with tools.
- People usually make mistakes while underestimating the time, cost, and effort required for introducing a Test execution tool.
- Underestimating the time and effort required to achieve high ROI on automation.
- Anticipating 100% automation is not the right approach. You can not automate all test cases, and a scenario may require manual intervention.
Scripting and Comparison techniques of Test Execution tools
A scripting language is required to run the Test execution tools. The scripting language is a programming language; therefore, every software tester who wants to use a Test execution tool must use programming knowledge to create and modify the scripts.
The main benefit of programmable scripting is that tests can take different paths depending on test results. For example, if a test fails, go to a different set of tests. They can repeat actions (in loops) for additional data values (i.e., test inputs) and from other scripts giving the location of tests.
Nevertheless, during testing, the tests are not merely replayed for someone to observe how they interact with the system. Remember that the system may respond slightly differently when the tests repeat in a loop. However, the Test execution tools use various more effective methods that enable them to function correctly and provide the advantages of performing unattended automated tests.
The following list of at least five levels of scripting includes descriptions of them and several comparison methods.
- Linear scripts: They can be created manually or recorded by capturing a manual test.
- Structured scripts: They are organized and use programming constructs like iteration and selection.
- Shared scripts: A script can be reused by calling other scripts. A shared script requires a formal script library as part of configuration management.
- Data-driven scripts: Data-driven scripts read a control script's input from a file or spreadsheet containing test data.
- Keyword-driven scripts: It stores all test data in a file or spreadsheet with several control scripts to execute the tests described in the file.
How does a Test execution tool help in Test planning ?
Test planning incorporates defining the scope of the testing, describing the product, and strategic objectives. Further, it includes the layout to perform the testing, identifying the resources required (including people, hardware, software, and tools), planning the test environment, allocating the resources to the tasks, defining the schedule, and identifying and managing any risks as shown in the flow-chart below.
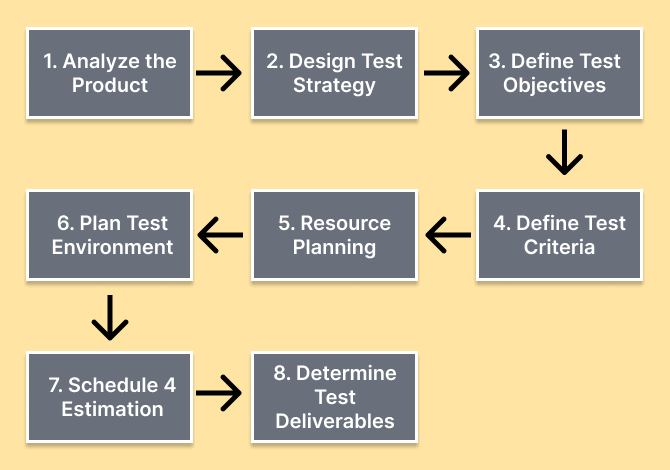
Testers need to monitor the progress and take action when it deviates from expectations. Re-planning takes place when the testing's scope has altered. Managing risks and issues, managing change requests during the project, reporting project status to the various stakeholders with test reports to give visibility into the testing performed, taking corrective action to ensure quality, and providing a detailed description, form an integral part of test planning.
Only an efficient Test execution tool will enable the test planning process seamlessly.
Following are some of the arenas where a coherent Test execution tool will be beneficial.
- Managing defects: The tester’s execution of the test cases can provide results different from those anticipated, which typically leads to a not-so-perfect report. Each flaw (bug) should provide a thorough description that includes:
- Defect number
- Severity
- Tester
- Date raised
- Status
- Description of defect and steps to reproduce it
- Impacts of the defect
- Responses to the defect
- Implementation and verification
- Managing change requests: The primary focus of the change control mechanism is the proper management of changes made throughout the project.
- Test monitoring and control: Performance testing aims to ascertain the system's response to a specific degree of usage, with users possibly being located worldwide and utilizing various networks, browsers, and devices. The goal is to ascertain how the system responds to expected and demanding loads, how many concurrent users the website can support, and how quickly it replies to those users.
- Risk Management: It aims to manage any undesirable test results. Risk-taking must be appropriately recognized, assessed, and organized for effective testing. These actions take place throughout the project lifecycle.
- Test Reporting:Test reporting aims to keep project stakeholders informed of the testing's progress. Throughout the project, the test manager will regularly generate test reports for the project's main stakeholders.
- A correct analysis of test status, schedule, effort, budget, and quality reduces the significant risks and difficulties.
- You are achieving the milestone status by scheduling your activities and deliverables (next period).
- The test manager reviews the test report with management and provides an update on the testing's progress and an overview of the main risks and problems.
It would be best if a tester fixed defects in a subsequent software release. The correction process entails investigation by the developers to identify the root of the issue and relevant software updates to fix it. A tester must test the upgraded application to confirm resolving bugs without adding new ones.
For instance, it is essential to limit modification as the project nears completion since changes to requirements typically impact other project deliverables, including design, code modules, and test papers.
The project manager may approve small change requests, but larger change requests need evaluation and approval by the change control board (CCB). The project's exposure to new risks is due to changes to the requirements, and the CCB must take these risks into account to ensure management.
In other words, the change control board evaluates the effects of a formal request to change the criteria after you log in. The CCB chooses whether to approve or disapprove the proposed modification. If you receive approval, developers implement the solution, and testers ensure that there is no introduction of new faults and that it is correct.
You can do performance testing with several agencies, including HP LoadRunner, Borland Silk Performer, IBM Rational performance tester, and Apache JMeter. You can replay the recorded test scripts by the performance test tools. You can control and save the test data. Therefore a test control language is used.
The test manager must identify the initial testing risks, which you must examine to ascertain their impact and propensity. The test manager must proactively identify and manage additional risks that may surface throughout the testing. A contingency plan deals with the scenario of the risk occurring, and countermeasures lessen the possibility of occurrence and impact of the risks.
Risk management activities include identifying risks, figuring out how likely they are to happen and what will happen if they do, coming up with solutions, monitoring, and reporting. During the testing process, reporting of risks must be regular.
The test manager will keep a risk repository (which could be a tool or a risk log as part of the project risk repository) to keep track of each risk's specifics, including its type and description, likelihood, impact, and suitable response.
The reports include a summary of the testing done so far. Typically, it will consist of essential project details like - Test deliverables that have been completed (during the period) - New risks, difficulties, etc.
A clear summary of the number of open issues by severity reveals the project's quality status. The test manager will present the main concerns and issues affecting testing and outline the solutions to address them. After hearing about the additional risks and difficulties, the project board will carefully assess how the test manager wants to cope with them and offer the necessary support.
How to pick the right Test execution tool?
With so many options available in the market, there is a high possibility that you might get confused when it comes to picking the right tool for test execution. The following tips will help you get your hands on the right product.
- The Test execution tool should boost your productivity: The requirement to test across various platforms and the fast pace of technology development provide significant hurdles for testing teams (both browsers and devices). One solution to this problem is to increase automation, as manual testing takes up most testing time.
- Granularity in terms of test information: The testing process should be well documented in the form of informative reports provided by the Test execution tool. For instance, in case of a test case failure, it is always beneficial to know which step the test failed rather than the test case as a whole. Any little adjustments made during testing should be communicated to the appropriate team members. It should also preserve a record of all changes, including complete versioning of test cases, for rapid follow-up and action.
- Tracking release management (DevOps): Software releases are complicated because several simultaneous actions (such as build version tracking, team collaboration, and release transparency) take place.
- Agile assistance: There is an ever-increasing demand for agile in the present market. Your Test execution tool has to support the agile process. Your tool should be able to support needs that are changeable in agile and finished gradually. Your chosen agile test execution tool should encourage strong collaboration between developers, testers, and other stakeholders (the basic principle of agile).
- Creation of stories.
- Estimation.
- Backlog planning for sprints.
- Charts showing speed and other information, etc.
- Kanban and scrum.
- Outside Integrations: Executing test cases automatically can relieve test engineers. The Test execution tool you choose should be simple to combine with other automation testing tools. Look for the capability to plan and run tests both locally and on the remote host, as well as to manage test scripts. Additionally, it would be ideal if the test management solution could save the results of automated tests.
- Your test execution tool must be compatible with tablets and mobiles: Teams working away from their desks at client sites or supervisors managing teams in various locations will find mobile assistance.
- The test execution tool's support staff should be dedicated to providing their clients with the best assistance available: Many Test execution tools are more concerned with producing glitzy websites and advertisements to attract additional clients.
However, additional ways to boost a tool's effectiveness include smart reporting, efficient test lab/data administration, and release management. Making a reasonable choice for the right test execution tool may significantly help to improve these characteristics.
Let's examine what a Test execution tool needs in terms of productivity.
The Test execution tool should also be able to compare test run outcomes and record test results as a session. Other functions anticipated from a typical test management solution include test planning execution, creating defects, connecting stories, and documenting test strategy. The cherry on top would be API support and a video upload feature.
To avoid conflicts with other test artifacts, a decent test execution platform has to have powerful release management tracking capabilities that maintain track of the list of the software being tested and published. Additionally, it must be able to manage every project asset in a single environment.
The tool needs to identify connections between requirements and other development assets. All stakeholders must access a single view of requirements via the test execution mechanism. Working together with stakeholders ensures that the proper requirements are recorded.
An agile Test execution tool should provide:
If you are examining changes in defect rates each iteration in an Agile context, a test run comparison by the Test execution tool might be beneficial. Another need for Agile is that the Test execution tool maintains a record of the product release for each iteration and backlog.
Incorporating a bug tracking tool simplifies the testing process for any QA team. The tool would be more valuable if it included a standard Test execution tool integrated with SDLC apps or other bug tracking tools. Users should be able to attach issues to specific test case execution instances for centralized software testing process execution. Additionally, it needs to make it possible for the complete project team to collaborate on a single issue simultaneously.
The test execution tool must be mobile-compatible with the whole feature set. Support for various devices and mobile operating systems is crucial since more devices have additional complexity, such as location, gesture, accelerometer, and orientation concerns. You never purchase a mobile phone intending to use it with your test management application.
To assist their clients, the finest Test execution tool should include features like live chat, phone calls, FAQs and online user manuals, product documentation details, knowledge base, the ability to raise help desk tickets, etc.
Several test execution tools now provide live video conferences with tool specialists to address client concerns. Demos or recorded videos connected to the test management tool should always be available on-site and accessible anytime. Developers require a sample script and detailed documentation if the product supports API or custom integration.
The following factors should be taken into account while choosing your Test execution tool provider:
- The tool should have an intuitive user interface and custom integration capabilities.
- It should support many time zones and languages.
- It needs to have extensive search capabilities.
How to use a Test execution tool?
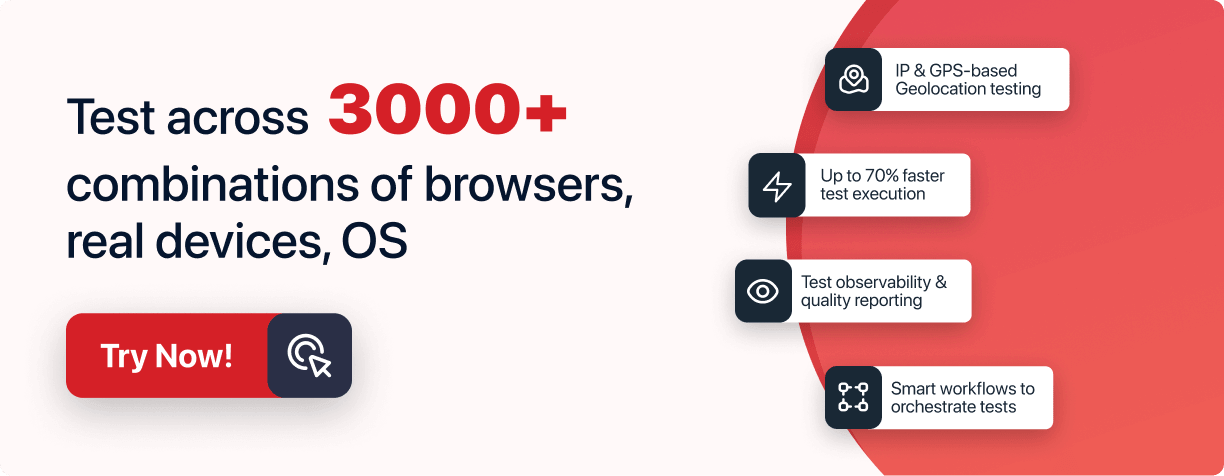
Startups and major organizations are looking for a Test execution tool to expedite their development workflow and test automation workflow. Generally, we test our websites and apps on desktop or mobile devices. On-premise testing involves significant infrastructure challenges and high maintenance costs and often comes with scalability issues. Therefore to avoid the hassle of test infrastructure, an ideal option is to choose a cloud-based Test execution tool like LambdaTest.
LambdaTest is a cloud-based cross browser testing platform that lets you perform live and automated testing of your websites and mobile applications across 3000+ real browsers, devices, and operating system combinations.
Check out some of the top-notch features of the LambdaTest platform.
- Run automated tests with Selenium, Cypress, Playwright, and Puppeteer.
- Automated app testing with Appium, Espresso, and XCUITest.
- Achieve faster test execution with HyperExecute and Test at Scale.
- Geolocation and localization testing of websites and mobile apps.
- Myriad of LambdaTest integrations with third-party tools
Shown below is the demonstration of performing live-interactive testing on the LambdaTest platform.
- Sign in to your LambdaTest account. If you don’t have an account, sign up for free.
- Once you are in the user Dashboard, navigate to Real Time Testing > Browser Testing.
- Enter your test URL, select testing type (Desktop/Mobile), VERSION, OS, RESOLUTION. Then click START.
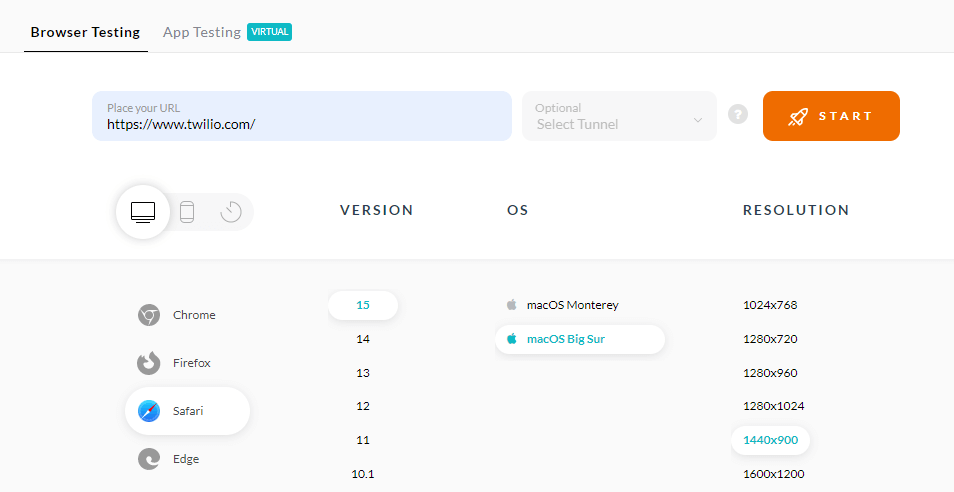
A cloud-based virtual machine will launch where you can perform testing of your web applications.
Check out the video tutorial below to get started with real-time testing on LambdaTest.
Now let’s look at how to perform automated testing using the LambdaTest platform.
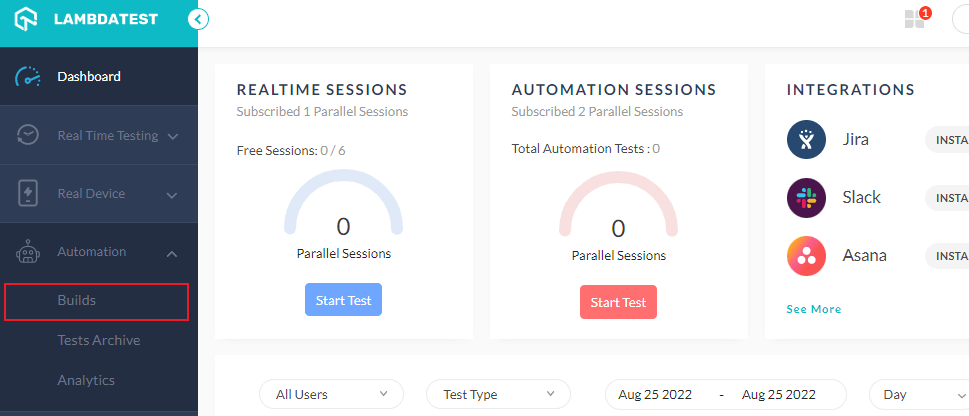
- Login to your LambdaTest account.
- Go to Automation > Build.
- Now you can select your favorite programming language and framework to kick start your web browser automation.

Also, you can easily migrate your test scripts or test suites from BrowserStack and Sauce Labs to the LambdaTest platform.
Summing up
Testing has evolved into a brand-new stage because of the availability of numerous sophisticated software testing technologies. In the past, testers would test a specific functionality for hours with inconsistent findings. The results are more accurate, decreasing manual errors and testing time.
The fundamentals of test automation involve a set of advantages and drawbacks, which are the same whether you are testing web and mobile apps. There are numerous software testing solutions on the market, each with unique benefits and capabilities.
We hope this post will help you look for the finest test management software. Always choose a tool wisely based on your project before making your choice.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the primary purpose of a Test execution tool?
The primary purpose of Test execution tools is to run the test scripts or the test suites. It can also record or capture manual tests, therefore known as capture or playback tools.
What are different types of testing tools
The different types of testing tools are test management tools, configuration management tools, static analysis tools, test execution tools, etc.
Author's Profile

Anupam Pal Singh
Anupam Pal Singh is a Product Specialist at LambdaTest, bringing a year of dedicated expertise to the team. With a passion for driving innovation in testing and automation, He is committed to ensuring seamless browser compatibility. His professional journey reflects a deep understanding of quality assurance and product development. He is actively contributing insights through blogs and webinars. With a strong foundation in the field, he continues to elevate LambdaTest's impact in the world of testing.
Reviewer's Profile

Salman Khan
Salman works as a Digital Marketing Manager at LambdaTest. With over four years in the software testing domain, he brings a wealth of experience to his role of reviewing blogs, learning hubs, product updates, and documentation write-ups. Holding a Master's degree (M.Tech) in Computer Science, Salman's expertise extends to various areas including web development, software testing (including automation testing and mobile app testing), CSS, and more.
 Christmas Deal is on: Save 25% off on select annual plans for 1st year.
Christmas Deal is on: Save 25% off on select annual plans for 1st year.