- Web development
- Home
- /
- Learning Hub
- /
- Software Development Life Cycle Tutorial
- -
- March 23 2023
What Is SDLC: Complete Guide
Step up your software development game! In this tutorial, learn about the Software Development Life Cycle, its benefits, models, stages, and more.
OVERVIEW
The Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) is a well-structured and systematic approach to developing high-quality, bug-free software applications that meet the end user's expectations. It is a series of phases, from planning to maintenance of a software application before being released in the market.
It acts as a framework that includes specific activities for developing and improving software applications. Its primary purpose is to develop high-quality software applications that could stand out in a highly competitive market.
When looking at the high competition in the global market, the total revenue of the software market in 2023 is $165.3 billion and is expected to rise to $217 billion by 2027.
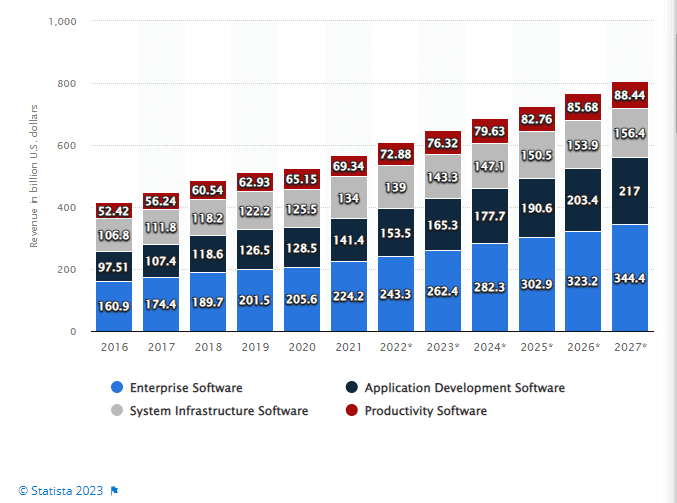
The high competition puts huge pressure on the software organization to develop bug-free applications. Most organizations are turning towards Software Development Life Cycle as it offers a systematic process for developing software applications. This eventually helps them to be informed about the development progress of the application and its standard as per competition in the market.
What is the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC)?
Software Development Life Cycle is the step-wise approach to design, develop and test software applications and ensure their quality and functionality. It involves different activities to deliver bug-free software applications in less time and with minimal effort. Technically, you can understand SDLC as an optimized strategy for developing software applications.
For every software application development, its completion in a pre-defined time and budget is equally important as ensuring its quality. To achieve this, you should work in an organized and structured manner to keep track of the progress in software development.
Here comes Software Development Life Cycle as the solution. It is a framework that defines the stages and activities of the software development process. You can follow this process to design, develop, test, and deploy software.
SDLC includes a detailed plan about how to work, build and manage the quality of software applications. Each phase of the Software Development Life Cycle has its specific process and deliverables, which feed into the next phase. Thus, it allows the developers and testers to navigate a defined plan and outline based on the different stages of software development.
To explain why SDLC is crucial, you must know its features and aspects well. Let us see this in the below section.
Why Software Development Life Cycle?
With digitization, many organizations and individuals depend on software applications for crucial and simple tasks. However, developing high-quality software applications is a complex and challenging process requiring much effort and work.
Therefore, you need a structured and systematic approach, like Software Development Life Cycle, to build top-notch quality applications. Here are some briefly explained the need for the SDLC:
- To develop a software application, getting started without any proper plan is difficult. This can make the software project chaotic. The Software Development Life Cycle acts as a framework to give you a structured plan and schedule for software development.
- Following the Software Development Life Cycle helps you to identify bugs and mitigate any risk associated with design and programming. It provides a formalized process where all team members know what to be done at each step while developing software applications. This helps you create a software development plan, which can be improved and repeated.
- SDLC with its structured plan appropriately tests software applications from start to finish before their release. Thus any issue associated with the functionality and usability of the software application can be resolved in time.
- It supports collaboration between the QA team, project analysts, developers, and others to develop software applications. This makes them aware of the software project's requirements; thus, you will not miss any crucial steps in the development process.
- Changes and modification in the software application is part of the development process. However, ensuring that any such changes do not give rise to any further bugs is essential. Therefore, developing software applications according to the Software Development Life Cycle helps find any relevant errors in the early phases corresponding to changes.
- SDLC gives direction or a path to the developers and testers to develop applications that one can easily monitor. This is because it increases visibility on all aspects of phases of software application. With this, tracking and controlling the activities in each SDLC phase can be done quickly.
- It is easy to keep track of progress, find early bugs, and strengthen collaboration using the Software Development Life Cycle. Consequently, we can improve end-user relations, lower project risks, increase development speed, and lower the cost of software application development.
Features of Software Development Life Cycle
To develop highly functional and optimized software applications, it is essential to have a robust plan and design strategy. Post that, using the SDLC approach in development can be an appropriate option. However, you need to know its features to get started.
Here are some features of the Software Development Life Cycle:
- Structured approach: It is structured with defined stages and processes to develop the application systematically. You can also ensure that developed software is released on time and within budget.
- Iterative and incremental: It is iterative and incremental in its application development approach. This means that software applications are developed in manageable and small stages, in which each step is interdependent. With this, you can get continuous feedback from the end user, giving scope for improvement throughout the phases of software development.
- Focus on requirement: It focuses on user requirements and Software Requirements Specifications (SRS) to develop any application. In other words, when you follow Software Development Life Cycle, the process is driven by the identification, analysis, and documentation of the requirements of the software. With this, you can ensure that the software is designed to meet the needs of the end-users, is delivered on time, and is within budget.
- Flexibility: The SDLC can be flexible: This indicates that the development process can be easily adapted to meet the needs of the software application and organization. If there are any changes in the feature of the application in the middle of its development, you can tailor the process to their specific needs.
- Focus on testing: The SDLC strongly focuses on testing software applications, which is the major approach to ensure bug-free applications. This involves different testing types, like functional testing, performance testing, usability testing, etc.
Benefits of the Software Development Life Cycle
The significance of the Software Development Life Cycle cannot be overstated in this modern era of software development. It offers developers and testers an easy approach to developing software applications.
Here are some key benefits of the SDLC, making it highly popular among developers and testers:
- Provide structure to the steps and activities involved in the software development process.
- Provide control of the software development activities in each phase of the Software Development Life Cycle by ensuring that it complies with all SRS.
- Offers a clear and concise framework for managing software applications, ensuring their completion within the planned budget, schedule, and scope.
- Help to ensure that the developed software application is aligned with the end user's objectives and goals, thus giving them maximum value.
- Gives transparency and visibility of all the processes in developing highly featured applications.
- Following the Software Development Life Cycle, you are more towards getting high-quality software applications quickly. SDLC would have given you a clear idea of its basic concepts.
Software Development Life Cycle vs. Software Testing Life Cycle
Testers or developers often consider Software Development Life Cycle and Software Testing Life Cycle (STLC) similar. Even though they sound similar, the two have a huge difference.
Software Development Life Cycle and Software Testing Life Cycle are two crucial concepts in software development. However, they are distinct from each other. The SDLC defines different phases of software application development. In contrast, Software Testing Life Cycle specifically describes the activities taken to ensure quality and bug-free software applications.
The following table shows the key differences between Software Development Life Cycle and Software Testing Life Cycle.
| Parameters | Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) | Software Testing Life Cycle(STLC) |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Both development and testing process. | Only on the testing process. |
| Definition | It is defined as the series of phases to develop high-quality software applications according to end-user expectations. | It is defined as a series of phases to test the developed software application systematically. |
| Relationship | Regarded as the predecessor. | Regarded as successor. |
| Phases |
|
|
| Requirement Gathering Phase | It involves business analyst to collect requirements and structure development plan | "It involves QA team to collect requirements and structure System Test Plan. |
| Design Phase | It consists of the development team structuring and developing levels of designs of software applications based on requirements. | The test lead or test architect plans the test strategy. |
| Deployment Phase | Support and release updates are given by the development team. | Checking of maintenance code deployed is done through regression suites, performed by the QA team. |
| Execution | It is performed before the Software Testing Life Cycle. | On completion of the Software Development Life Cycle, it is done to check for any errors or bugs. |
Models of Software Development Life Cycle
There are many different models of the Software Development Life Cycle through which software development can be done.
The Model of the SDLC is defined as the framework that outlines software development methods or approaches. Many different models of the SDLC detail essential steps to develop high-quality software. Based on the need and preference of software projects, the Software Development Life Cycle model can be chosen.
Let us look at the most popular models to understand this better.
Waterfall Model
The Waterfall Model is one of the most crucial and widely accepted SDLC models. In this method, software development is done in small phases with specific goals that the team requires to achieve. The phases of the Waterfall Model include requirement analysis, design, development, testing, deployment, and maintenance.
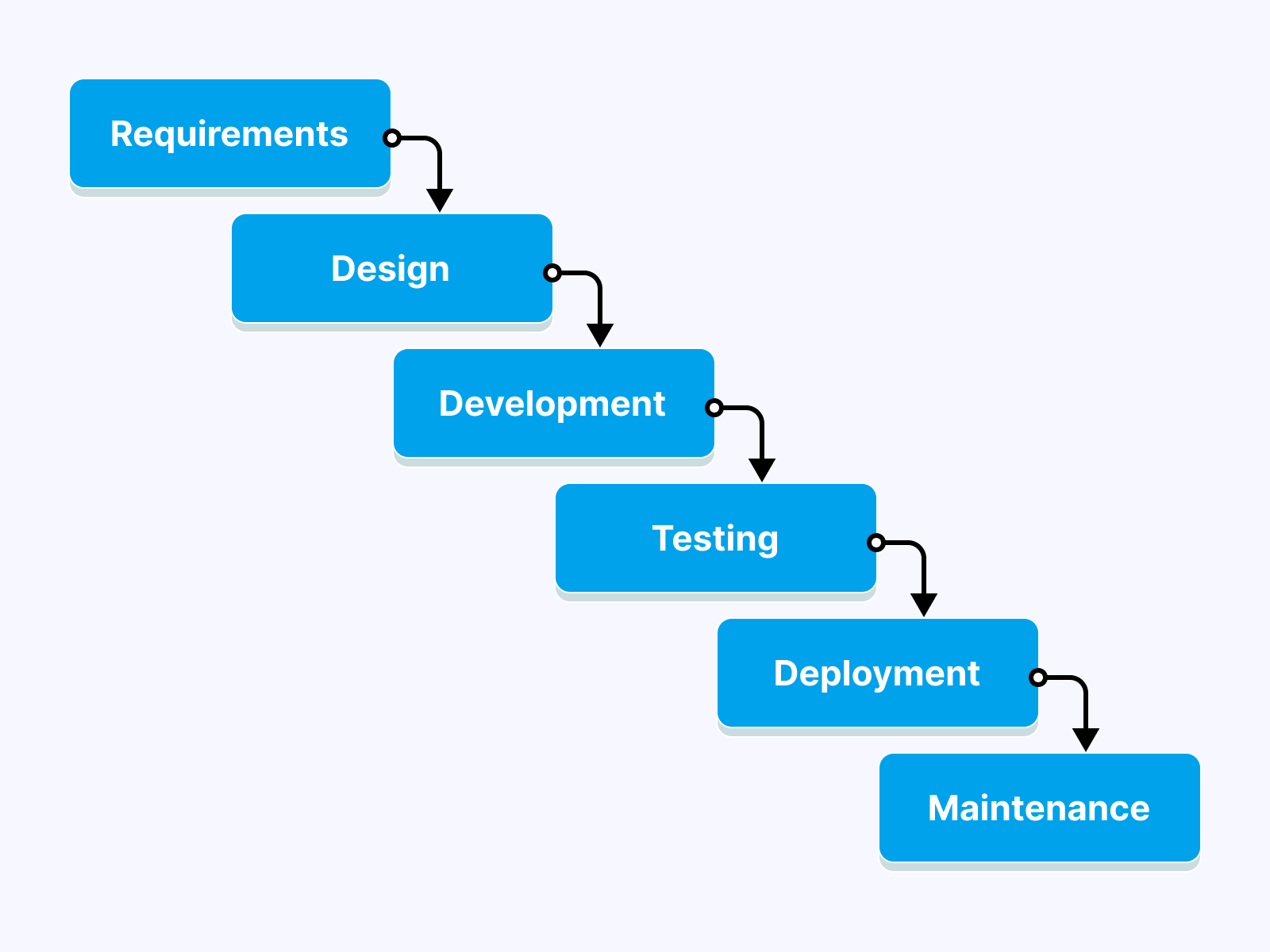
Each phase involved here must be completed before moving to the next incremental approach. This is because the outcome of previous phases functions as input for the next and is thus regarded as a sequential-linear model. Therefore, you can easily monitor the feasibility through each step of the development of software development.
Advantages:
- It is easy to understand and follow, making it suitable for small software application projects having clear Software Requirement Specifications and limited budgets.
- It gives a complete set of requirements upfront, allowing you to plan and estimate the project timeline and budget easily
- It has clear and well-defined milestones, and you can monitor the software project's progress and ensure that it stays on track.
Disadvantages:
- The Waterfall Model is a linear and sequential approach, so there is a lack of flexibility. This means you cannot return to the previous phase to make the new changes. Thus it can be a problem if the software requirements change or new issues arise during development.
- It can be time-consuming because each phase of software development must be completed before moving on to the next. Consequently, this gives rise to a long lead time between the software’s start and release phases.
- The testing phase in the Waterfall Model usually occurs at the end of the development process. This means errors and defects can go undetected until late in the SDLC. Hence, one can face difficulty fixing those errors and defects, which can be expensive too.
Suitability: You can choose the Waterfall Model if complex software projects have constant requirements and regulations, little changes, and predictable outcomes.
V Model
It is similar to the Waterfall Model with slight changes as each phase involved in software development is planned in parallel. In other words, there is a verification phase and a validation phase executed opposite to each other. Thus, two interdependent processes help eliminate any risk or error in applications, thus improving quality.
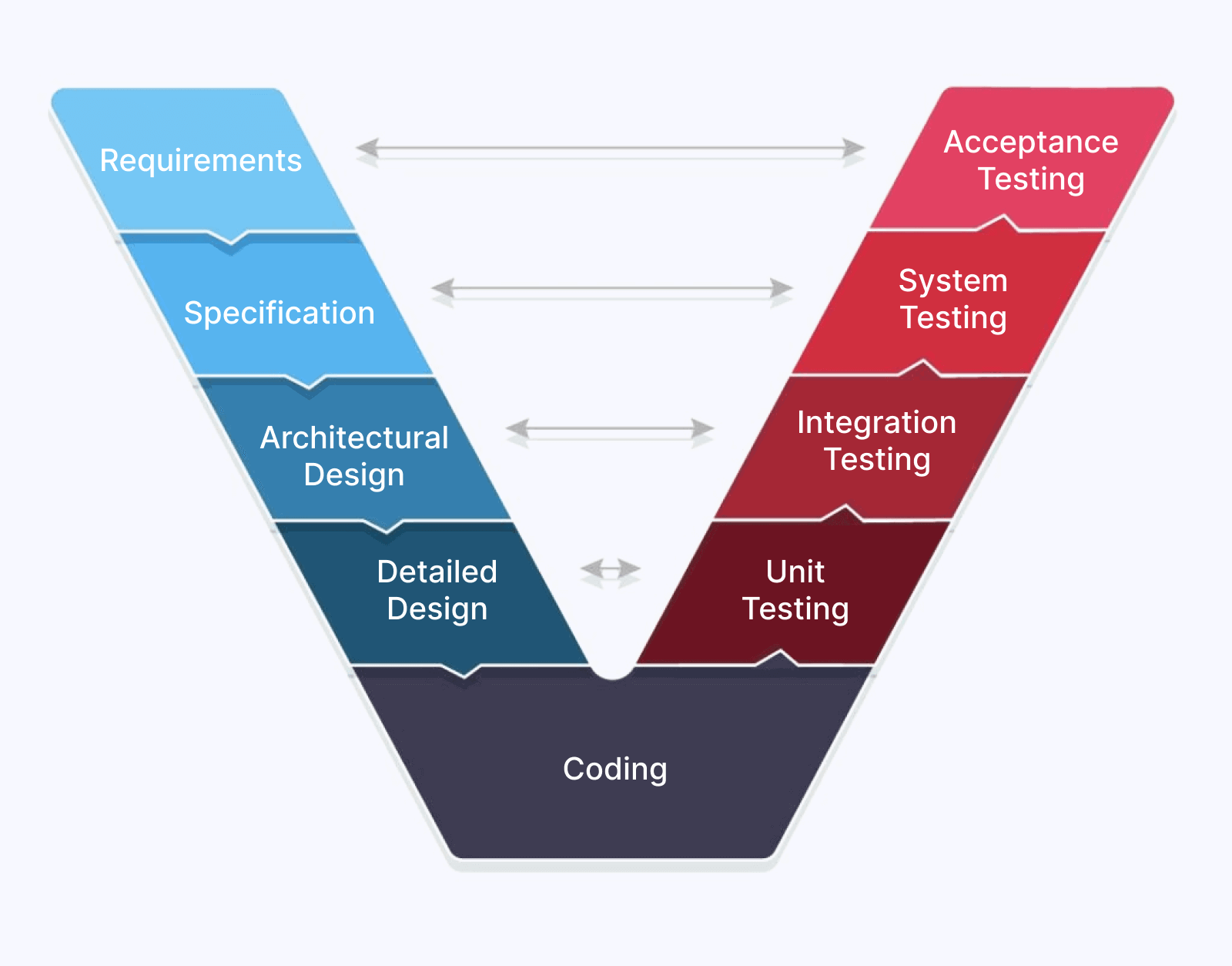
Advantages:
- Focuses on testing and verification at every phase of development, which ensures that defects and bugs are detected early on, reducing the cost and time needed to fix them.
- It demands that testing be done at every stage, which helps to ensure that the system being developed aligns with the end-users requirements.
- It has clear deliverables associated with each stage, which helps to ensure that the software development stays on track and its progress can be monitored.
Disadvantages:
- The V-Model, like the Waterfall Model, is a linear approach, which makes it problematic to accommodate changes in requirements or fix new issues that may arise during the development of software applications.
- It is more expensive than other models because of its primary focus on testing and verification at each stage, which can require additional resources and specialized testing tools.
Suitability: When the software development requirement is well defined with a clear plan, we can choose the V-Model of the Software Development Life Cycle. It suits medium-size software development projects where the end-users requirement is fixed.
Iterative Model
Iterative Model comprises small repetitive iterations, which involve repeating a series of steps until the expected software application is developed. In other words, the entire development of software applications is broken into small application builds, known as iterations.
Such iteration undergoes different stages of SDLC. Further, each cycle of respective iteration develops on others and easily deploys when the software build is completed.
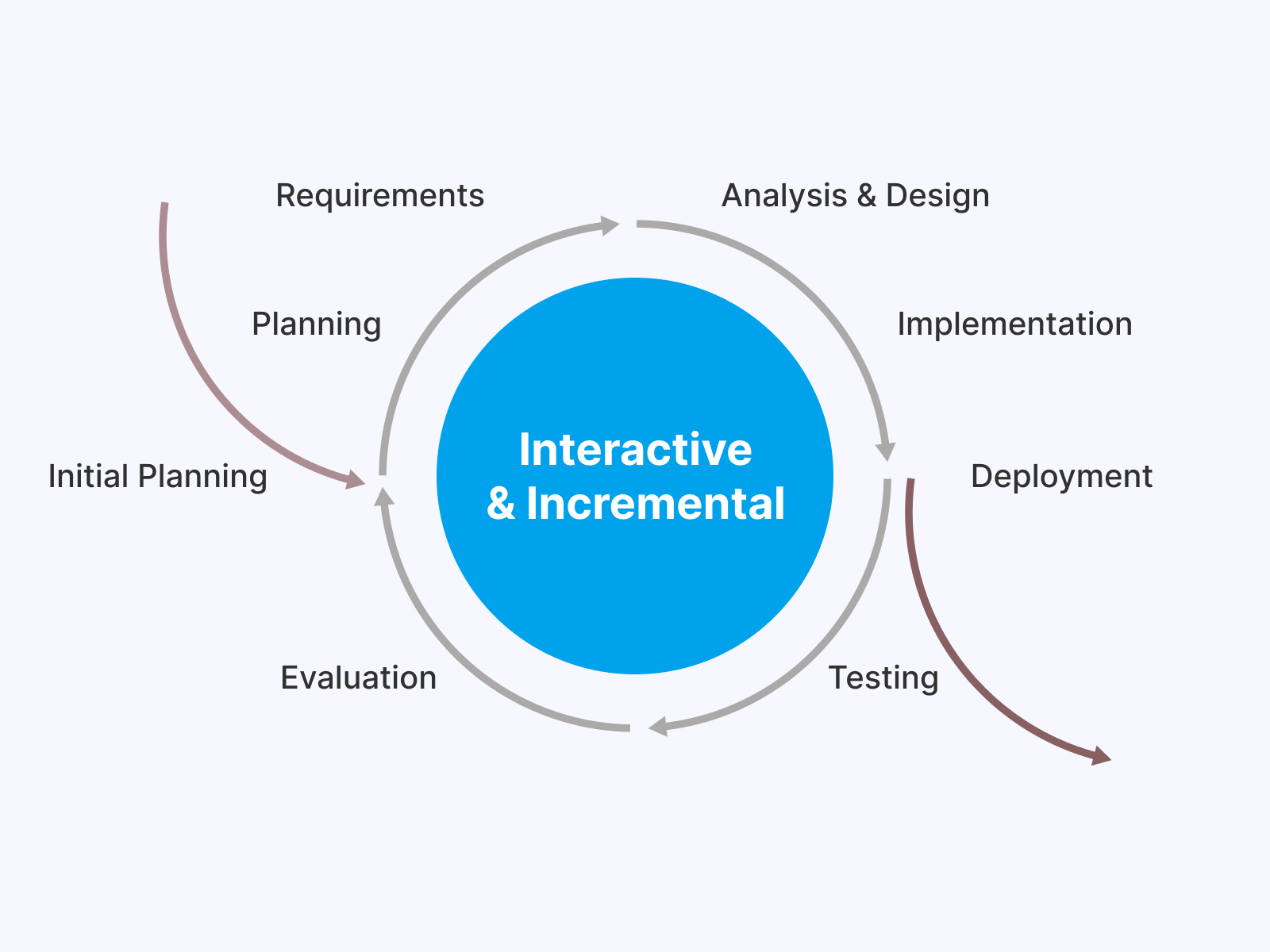
Advantages:
- It is more flexible than the Waterfall Model, as you can make changes throughout the development process based on end-user feedback.
- Seek regular feedback from end-users, which helps ensure that the developed software system aligns with the user’s requirements.
- It delivers working software early in the development process, which allows for early testing and feedback and helps to ensure that the final software application meets the end-users' needs.
Disadvantages:
- It is more complex than the Waterfall Model, as it requires additional planning and coordination to manage and maintain the iterative process.
- More expensive because managing the iterative process requires additional resources and time.
- It is time-consuming, particularly for large or complex software development projects.
Suitability: You can choose an Iterative Model under three conditions. First, if the requirement is clear and easy to comprehend. Second, when the software application is large size. Third, when changes or modifications could be made in the future.
Spiral Model
The Spiral Model is risk-driven and based on the Iterative Model. This method involves the development of software applications where the process is divided into small and manageable sub-phases. Each phase involves planning, requirements, gathering, designing, implementation, testing, and review. You will get a working prototype that end users can test and evaluate.
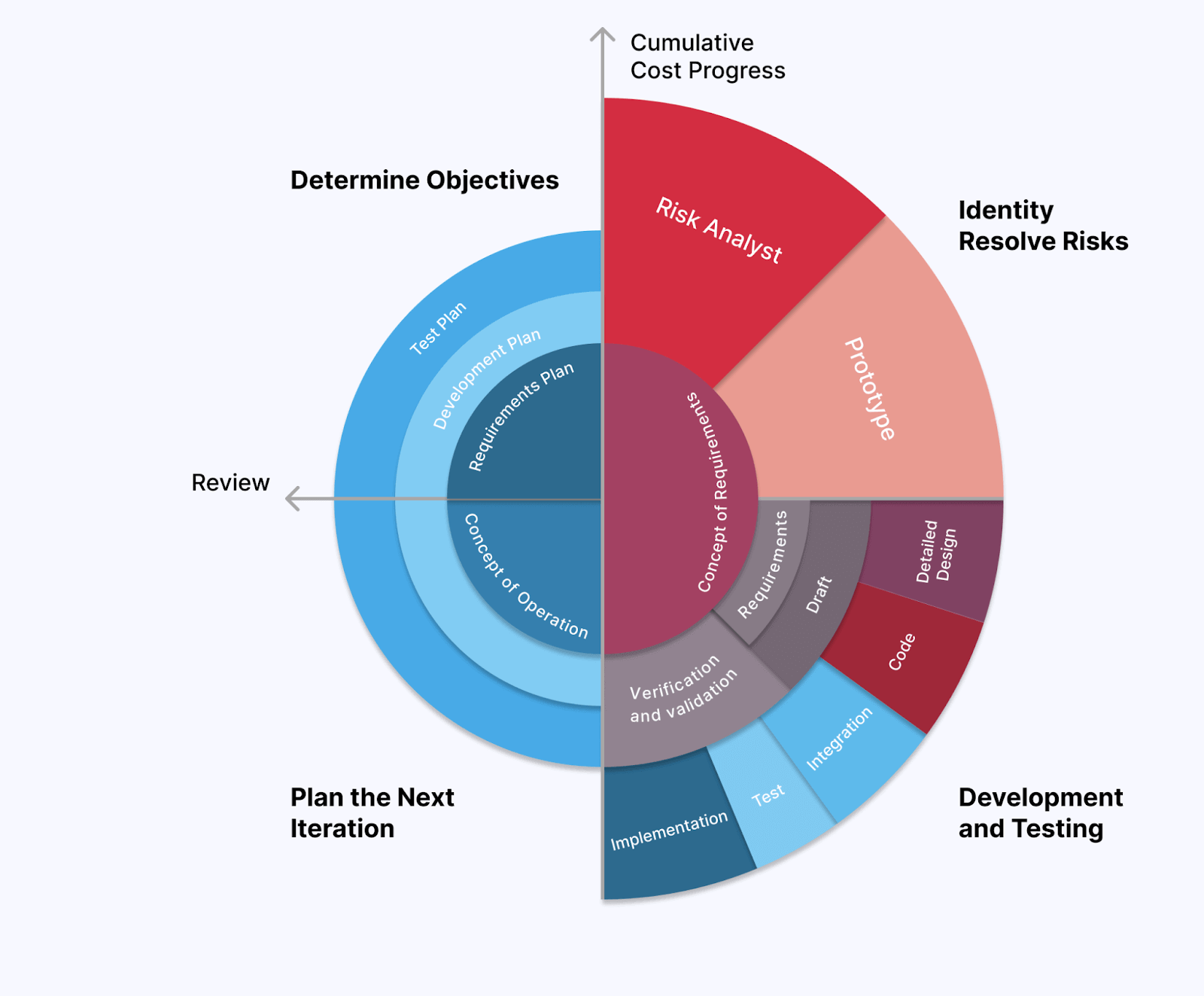
The Spiral Model is called so because the development process spirals through repeated cycles, each building on the previous cycle's results. The spiral starts with identifying objectives and constraints, followed by evaluating risks and changes, and finally, the development and testing of the software application begins.
Advantages:
- It is highly flexible and adaptable, making it appropriate for software development projects with changing or unclear requirements. It allows for incorporating changes and modifications at any phase of the development process.
- The Spiral Model strongly focuses on risk analysis and management, effectively identifying and mitigating potential errors or bugs early in the software application development.
- Provides a high level of visibility into the development phases, allowing end-users to track progress and provide feedback throughout the SDLC.
- It incorporates user feedback at every stage of the development process, ensuring the quality of the final software application.
Disadvantages:
- It is a complex process model, making it problematic to manage and implement, especially for small-size software applications or inexperienced development teams.
- The iterative nature of the Spiral Model can result in longer development cycles, as each cycle involves a complete set of software development activities.
- Can be expensive to implement, as it requires a higher level of expertise and software tools than other Software Development Life Cycle models.
Suitability: The spiral model is appropriate for large, expensive, and complicated software application projects. If the release is required to be frequent and the end-user requirement is not clear or complex, the spiral model can be a good option to get started with software development.
Big Bang Model
As the name suggests, there is no fixed structure in the Big Bang Model for developing software applications. You can understand this as a method that does not require planning and testing for developing software applications. Its primary focus is on fulfilling the requirements of the end users without any deadline.
In this model, all the phases of the software development process are executed simultaneously, without any specific order.
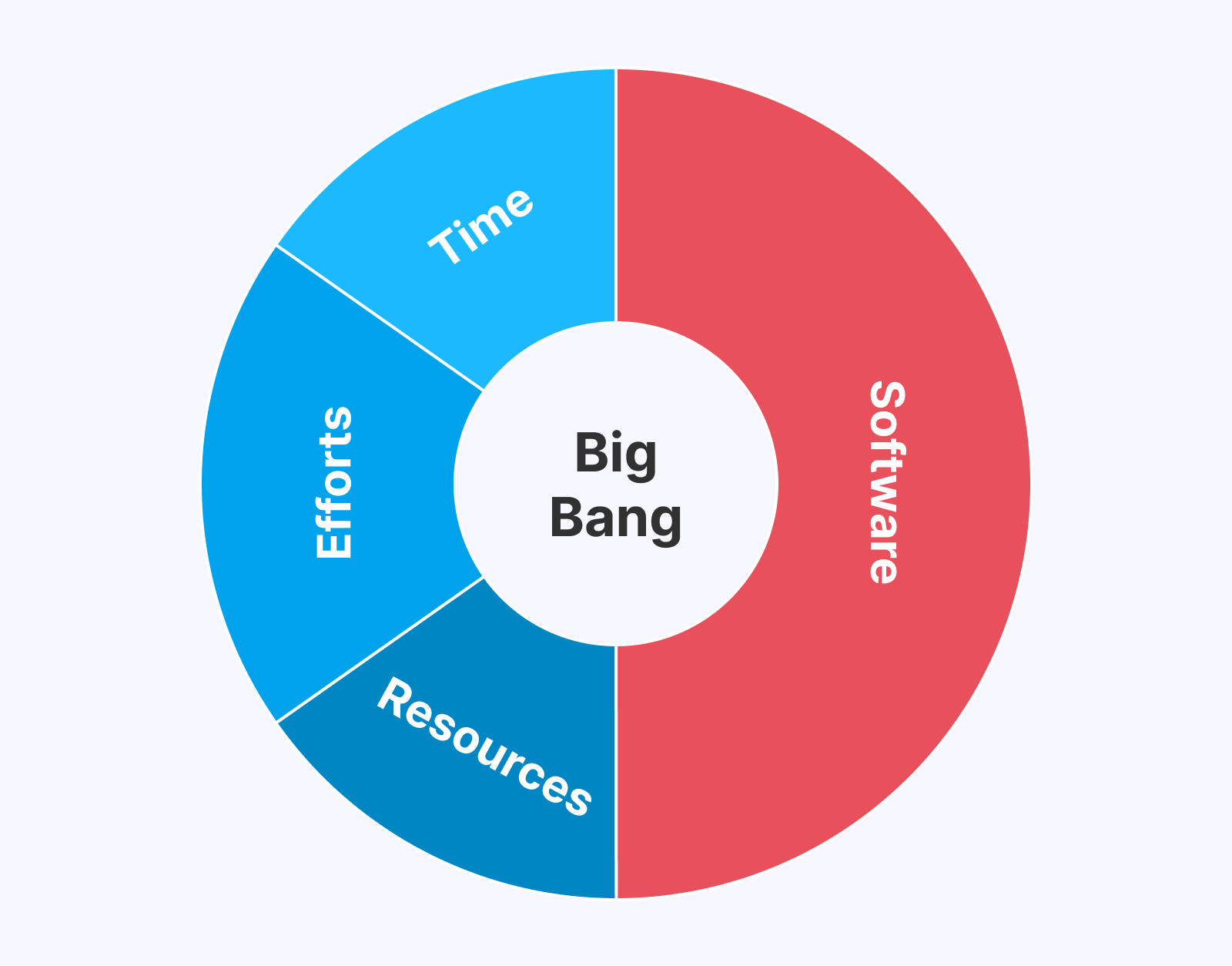
Advantages:
- In this model, each phase of the development cycle is completed simultaneously; therefore, we get user feedback quickly. With this, you can easily identify issues early on and resolve them faster, resulting in a high-quality software application.
- It is well-suited for prototyping. You can experiment with different ideas on the working model and quickly implement feedback-based changes.
Disadvantages:
- It is a high-risk approach because there is no proper planning and designing phase in software application development. This can lead to problems in the software development process with no progress tracking.
- It is unsuitable for large and complex software applications because of its unplanned structure. This can make it challenging for developers and testers to manage and develop large-size software applications.
Suitability: If you have a small-size software application to create and wish to hop right into it that does not require any initial planning, choosing the big bang method can be a good option.
Prototype Model
In the software development method, a prototype is developed for the application before working into the actual application. In simple terms, it is an iterative approach to software development that focuses on building a working model of the software before creating the final software application.
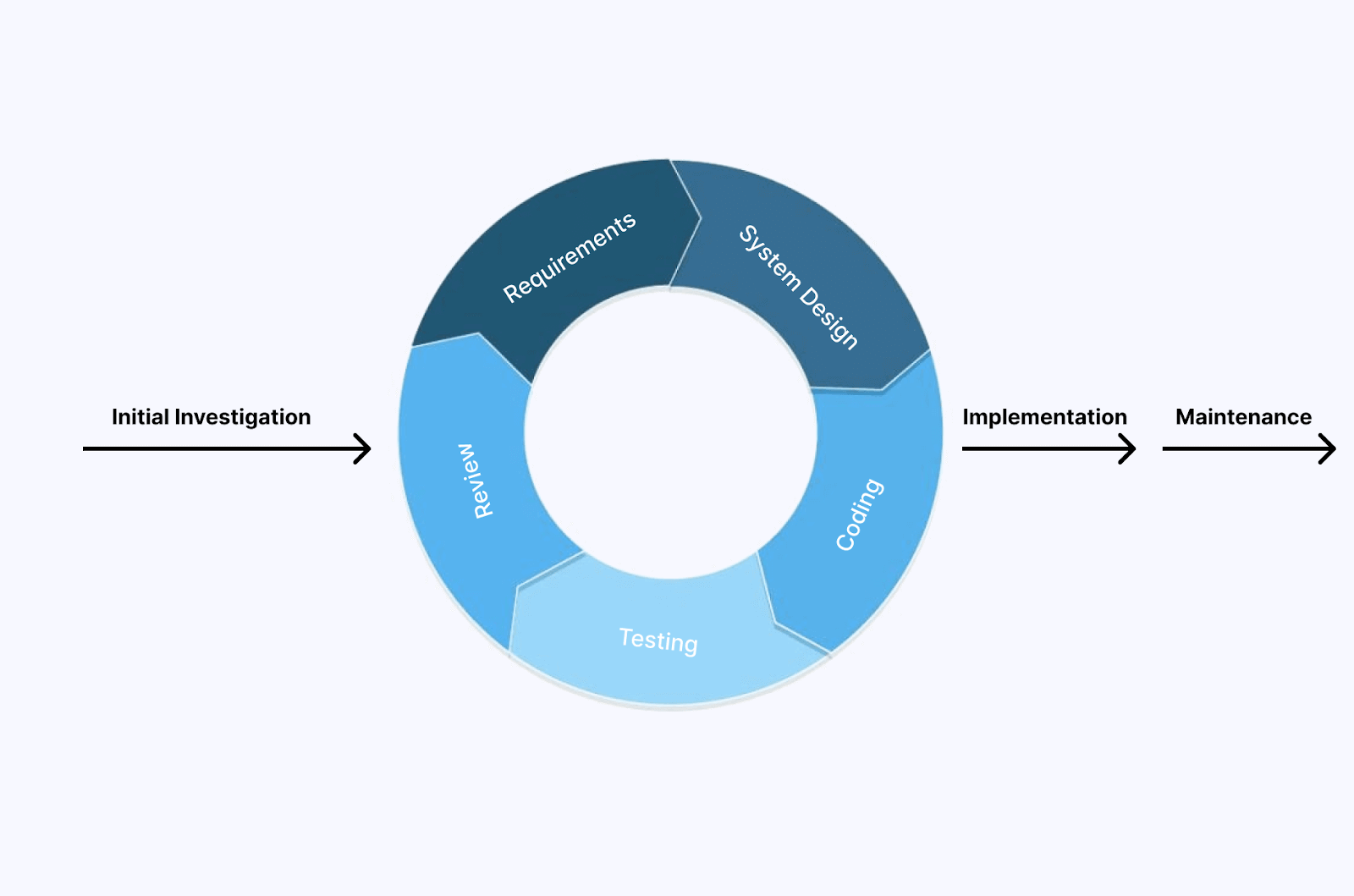
It consists of several phases, each built on the previous one. Feedback is sought from the end user, and based on this, changes are made to the working model of the software application.
Advantages:
- Using working software application models helps identify and implement end users' requirements. You can better understand the final software application design and functionality.
- You can detect and resolve errors before the development of software applications. Thus, this will reduce the overall cost and time required in the development process.
Disadvantages:
- In the initial phase of the software development, there will be a need to create multiple prototypes for testing. This can be a very time-consuming and exhaustive process.
- It can be very challenging to manage the prototype model. It is especially when the team and end users are not collaborative, and there are frequent changes in the requirement or design of the software application.
Suitability: Prototype Model is suitable for small software development projects with two or more developers working collaboratively. In such projects, the end-user requirement is not well understood, and the final software release date is not given.
Agile Model
Agile Model is the crucial software development method enabling the interaction of the testing and development phases of the SDLC. The development process is broken into small iterations called sprints.
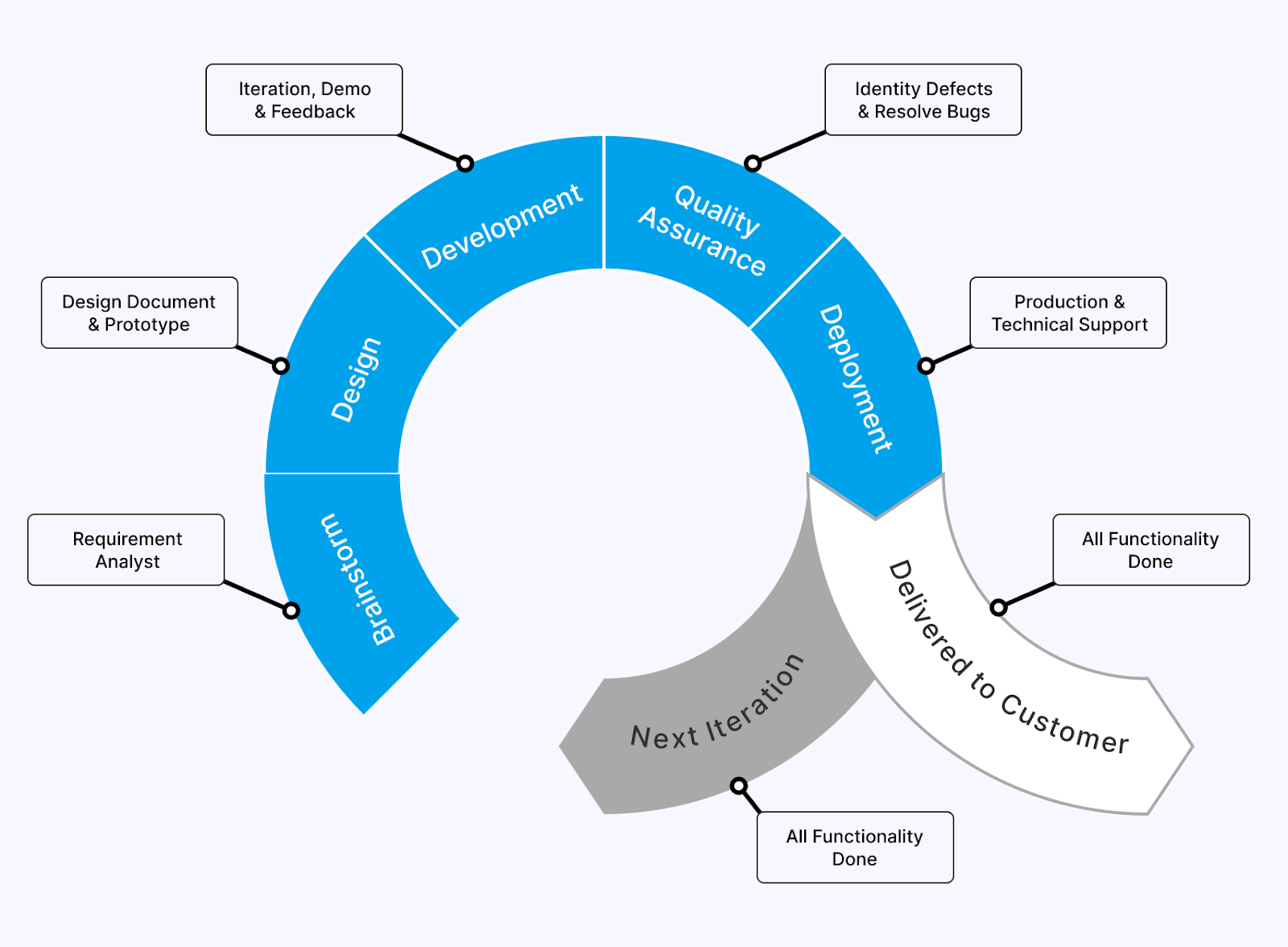
It values adaptability and responsiveness to change in the software application. It is designed to be used in software applications without fully defined requirements, or the end user’s needs may change over time.
Advantages:
- Focuses on the fast delivery of software applications in short iterations. This helps the development team to develop software applications with top-notch quality quickly.
- It can easily incorporate changes in the requirements of end users throughout the development process.
- Emphasis on continuous testing and integration is done and thus allows easy and early detection of bugs in software applications.
Disadvantages:
- It focuses on working software over comprehensive documentation. This can lead to a lack of documentation that creates problems in the maintenance and support of software application projects.
- More emphasizes is put on teamwork and collaboration. This can be challenging if the team members are inexperienced or unskilled in Agile development methodologies.
Suitability: Agile Model could be a good option when there is a need for quick software application release in the market. Such software application requires implementing new features or changes during the development process.
Which SDLC Model is right for you?
The above section has given you immense learning on different SDLC Models. However, the first thing that comes to your mind is how to choose the correct model. Before that, you have to consider the team size, software development projects, and their complexity. Further, it is also important to focus on the experience of developers, the types of software development tools you are using, and the user's requirements.
If you have a skilled team of developers and testers, you can save your software release time by outweighing documentation. This Agile Model can be a good option as it offers flexibility and helps to adapt to the changing environment.
However, if you have well-planned and structured requirements for software development projects, Waterfall and V Models can be chosen. It can run with novice developers as it has clear instructions on methods to develop a software application.
Further, you should consider that the Waterfall Model can be expensive and does not provide a way to make new changes. Therefore, it is always advisable to go through the requirements and complexity of the software application before choosing the SDLC model.
Stages of Software Development Life Cycle
The most critical aspect of the Software Development Life Cycle is to determine different phases and their underlying activities to develop a quality software application. Usually, the SDLC process is divided into several stages, which may vary according to the end-user requirement for the application. However, basic sets of stages are crucial to follow, beginning with analyzing the market.
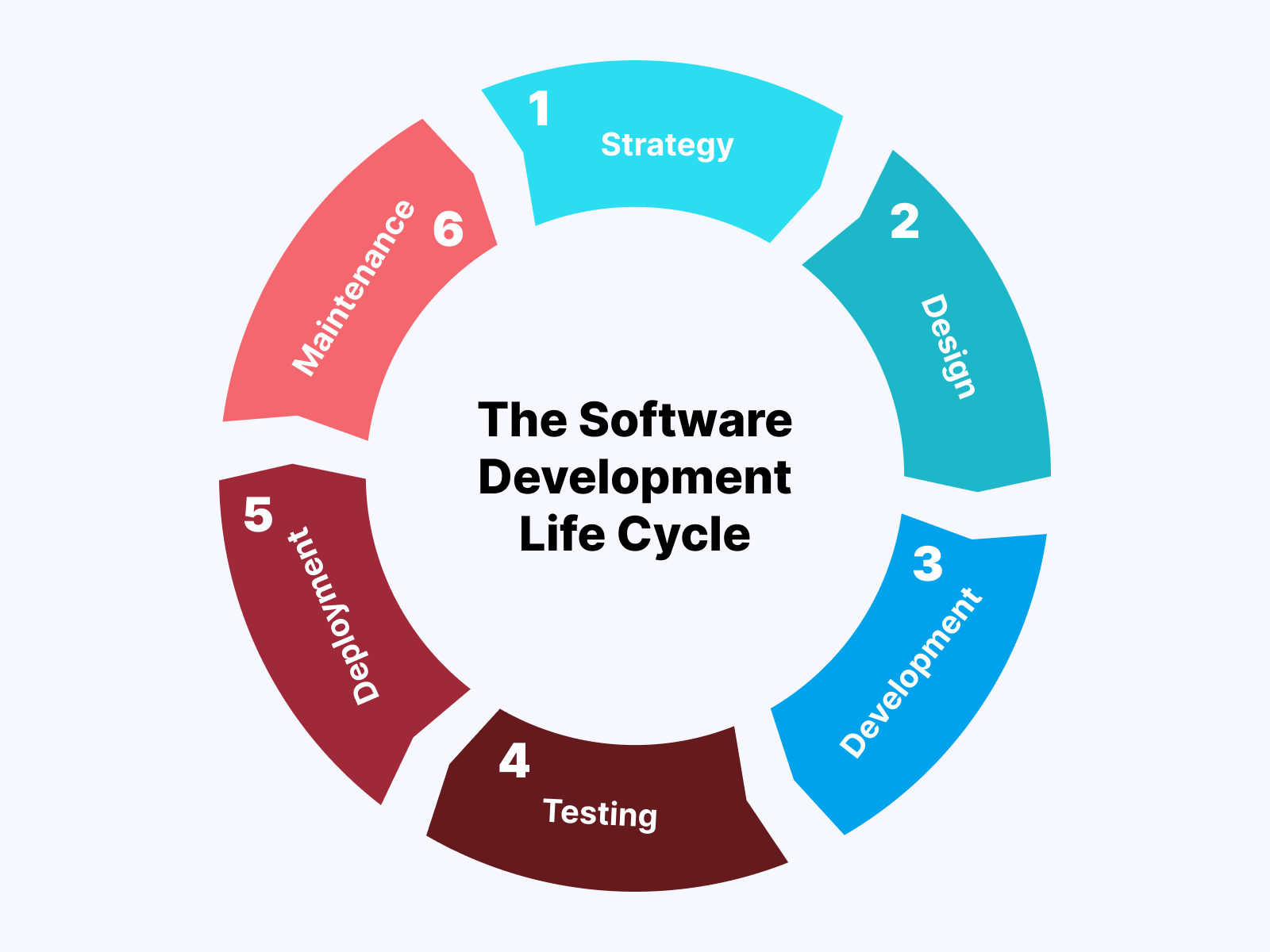
Market analysis and knowing the demand for the application are essential to creating a detailed plan for software application development.
Proceeding this, the primary development stages prevail, like designing, prototyping, and development. Then, evaluation and testing are done to check and test for any flaws and ensure their fixes before deployment is required to be done.
The SDLC and its stages are loop-structure and non-ending. As soon as one cycle is completed, new cycles take place.
Analysis
Before initiating the development of an application, it is important to find what exactly needs to be developed. This is where the analysis phase begins. It evaluates the current software applications in the market and identifies the need for new applications. This involves all software development teams deciding on new software applications and their features and functionality.
The end-user requirements, expectations, and specifications are analyzed related to the software applications. All such information is gathered by the business manager or project head of the organization before starting with the software application's actual development process.
The information may include how to use software applications, user information, features, and others. Based on this, processes or methods are determined for the successful development of the software application. All such actions are taken to create SRS (Software Requirement Specification) documents.
SRS includes information on the detailed features of applications, requirements, and related aspects. This is then presented to the end-users for deciding the anticipated issues, opportunities, and directives. It will also allow organizations to finalize the deadline for software application development.
Planning
On completion of the requirement analysis phase, now it's time to decide how the development process of the software application will take place. It includes planning an objective, the pathway to reach it, things to be done, etc. In simple terms, planning is all about deciding on the distribution of time, resources, and efforts.
Planning phases are conducted with the help of an SRS document with complete information on what will be designed and developed during the SDLC.
Following are the five types of planning checks that must be addressed in the planning phase:
- Economic:What is the budget of the software application?
- Legal:Is it possible to handle the application as per the cyber laws and adhere to different regulatory frameworks and compliances?
- Planning feasibility:Can we create plans as per the user’s expectation?
- Technical:Ensure whether the computer system can support the software application to be developed.
- Schedule:Ensure that software application projects can be developed successfully within the given timeframe.
Design
The next phase includes the design phase, which comprises detailed software application analysis as per SRS. Here, the logical design of the software application is converted into the physical design. You can understand this in simple terms as the requirement phase includes the features of the software application to be developed, and the design phase gives way to developing it.
Hence, once the purpose and specification of the application are created (Design Document Specification-DDS), the developer moves to create the project design.
This phase prepares an outline of the model's working and different design aspects. Some include:
- Programming: Identify the programming language for developing the software application.
- User Interface: Determine how the user interacts with the software application and related response to particular inputs from the user.
- Security: The measures like password protection, secure data storage, and SSL encryption are considered to ensure the security of the software application.
- Communication: Determine the medium for communication between the software and different assets like central servers.
- Platforms: Outline the platforms which can be used to host software applications like Linux, Windows, etc.
- Architecture: Define the templates that include design, specific programming languages, and other things required to develop software applications. This phase may also comprise designing prototypes as the software model to find its looks, function, and response.
The design phase includes two different types of design documents-high level design and low-level design.
The high-level design includes the following:
- Description and name of components or units of software application.
- Functionality of every component or unit.
- Interface relationship between the component or unit.
- Database tables with key elements.
- Architecture diagram with technology and tools to be used.
The low-level design includes the following:
- Functional logic of the component or unit of software application.
- Database tables with defined sizes and types.
- Information on the user interface.
- Dependency issues.
- Error message, if any.
- Output and input of every module.
Development
On completion of the design phase, the development phase is the main part of the SDLC. It is the phase where developers start to develop and build the complete software application by writing code based on the preferred programming language. To simplify things, the units and components of the software applications are divided and assigned to various developers for development.
The development phase is the most prolonged phase of the Software Development Life Cycle. The software application is developed based on the SRS and DDS. Here, the front-end developers are developing Graphical User Interface (GUI) and other essential interfaces to establish connections with back-end operations and developers. All such things are executed as per the plan and coding guidelines.
The use of programming tools like debuggers, interpreters, and compilers are used to generate and implement the code to develop software applications.
Testing
Once the software application's development is completed, the testing phase follows. The tester's role comes into existence in this phase, where they go through the codebase of the developed software application to find bugs and errors. They prepare a test plan that involves all the types of testing like integration testing, acceptance testing, unit testing, functional testing, and non-functional testing. Hence, the entire software application is tested for its functionality, features, and working ability as per the SRS.
During the testing phase, the bugs are reported to the developers for fixes. Testers perform manual testing and automation testing.
Manual testing involves testing the software application manually to identify any bugs or issues. However, automated testing consists in writing automated test cases to test the functionality of the software application and ensure that it meets the SRS.
Looking to boost your testing skills? Subscribe to the LambdaTest YouTube Channel and get in-depth tutorials on Selenium automation testing, Cypress testing, and more
Once the bug is fixed, it is again sent to the QA team for retesting. This process continues until a bug-free, functional, and stable software application is built according to the SRS
Tools involved in testing software applications
The availability of several automation testing frameworks has eased the identification of bugs and errors. Some of the most popular testing tools are explained below
- Selenium
- Cypress
- Playwright
- Appium
Selenium is an open-source automation testing framework for web testing. It supports multiple programming languages like Java, JavaScript, C#, Python, and others to create test scripts. Selenium testing can be done across various browsers like Chrome, Firefox, Edge, and Opera and operating systems like Windows, macOS, and others.
Cypress is a JavaScript automation testing framework for modern web applications. It can be used directly using DOM manipulation and creating automated test cases.
Playwright is a Node.js library designed for end-to-end automation testing of web applications. It allows you to test on Chromium, Firefox, and WebKit with a single API.
Appium is an open-source automation testing tool where testing can be done on different platforms like Windows,Android and iOS.
You can perform software testing using two techniques: on-premise and cloud-based testing.
On-premise testing involves running software applications on local machines, systems, or devices within the office. Consequently, it entails a great deal of responsibility. You'll need everyone on board to perform maintenance, monitor, and upgrade the machines and software. In addition, on-premise testing is time-consuming and expensive.
However, testing performed in a cloud-based platform offers scalability, reliability, flexibility, and security.
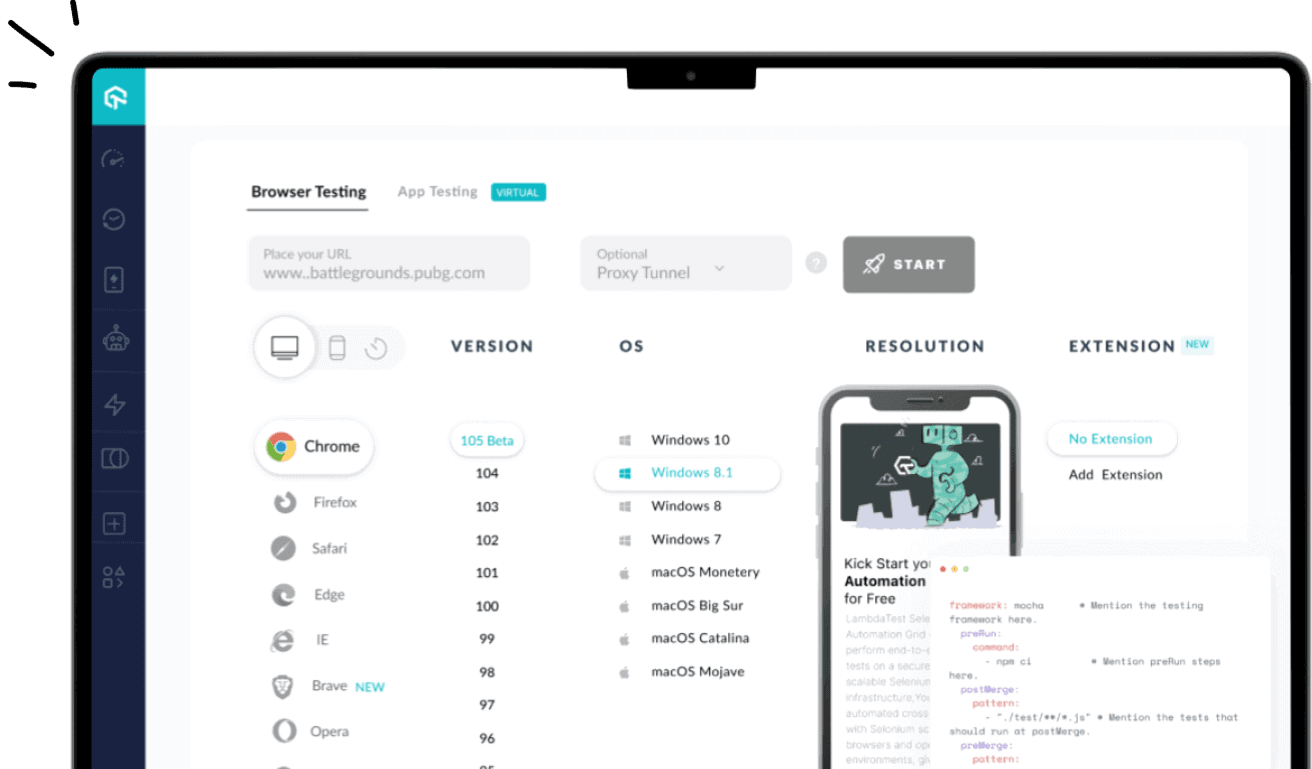
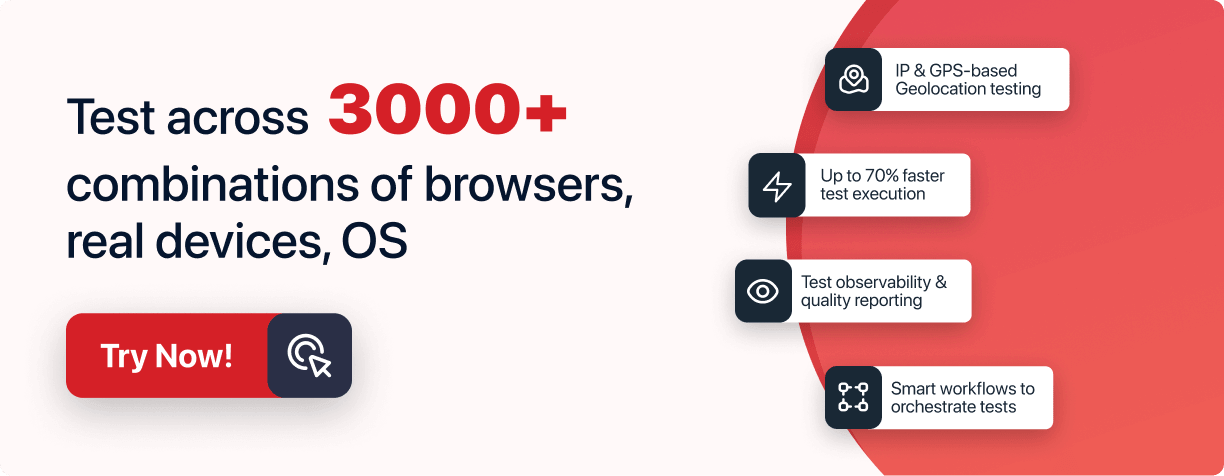
Cloud-based testing platforms like LambdaTest let you perform manual and automated testing of web and mobile applications across a wide range of browsers, devices, and operating systems. It allows you to automate test suites with popular frameworks like Selenium, Cypress, Playwright, Appium, and more. In addition, parallel test execution can accelerate your test cycle.
Run your test scripts across 3000+ real desktop and mobile browsers. Try LambdaTest Now!
Deployment
When the developed software application is tested and all the bugs or errors are removed, it is time to deploy the application. This involves preparing the software application for release and deploying it to the live environment. Therefore, feedback is sought from the end-users and incorporated into the software application to ensure its functionality as per the requirement.
The deployment phase comprises a series of steps to prepare the application for smooth and bug-free deployment. You have to prepare a release plan, including the release date, target audience, and deployment environment. Such information shall be communicated with the software development team. Then, you must conduct system testing in the live environment to ensure that application works per SRS.
On passing the test, deployment preparation is done by finalizing the installation package, setting up the production or live environment, and creating backup and recovery plans.
The main deployment occurs by installing the software application on the deployment environment. It is executed carefully to outweigh any downtime and issues from the end-users. On releasing the software application to the end-users, they are asked to perform beta testing. The end-user can ask to make changes in the application, which were mentioned in the SRS, to make it more user-friendly.
The software application is finally deployed to the end-user to resolve the issues by the development team.
Maintenance
It is the last and long-lasting phase of the SDLC. It tends to continue until the application development is completed. When the user starts using the application, the main issue begins, like compatibility issues, which must be solved at the earliest. Here, maintenance of the software application is needed, and all such issues are addressed.
The three main activities addressed to maintain the software application are as follows:
- Bug fixing: Errors and bugs are reported because some scenarios might not be tested thoroughly.
- Upgrade: The software application is upgraded to new versions.
- Enhancement: New features and functionality are added to the existing software application. The software testing and development team makes new changes to the software’s unit and hardware to maintain the working and improve performance.
Limitations of the Software Development Life Cycle
While the Software Development Life Cycle offers an effective framework for managing software development projects, it has limitations. It is important to know about some of its disadvantages so that they can be considered developing a high-quality software application following its underlying phases.
Some disadvantages of the SDLC are as follows:
- Rigidity of the Software Development Life Cycle is one of its major limitations. It follows a specific set of stages, and it is difficult to incorporate new changes or adapt to the new requirements that may arise during the development process.
- May not necessarily consider or address specific needs and constraints of distinct software projects or organizations in the application’s development process. This could lead to inefficiencies and missed opportunities.
- In some software application projects with strict deadlines for their release, following the Software Development Life Cycle may be time-consuming. The reason is that the initial phase of the SDLC involving planning and execution may slow the overall development process.
- As each phase of the Software Development Life Cycle depends on the previous one, indicating its linear process. This creates a challenge in receiving feedback on each stage and incorporating the changes. In other words, once a stage is completed, and the development team moves on to the next stage, it might not be possible to go back and make changes to earlier stages based on feedback or new requirements.
- While the SDLC may be a practical approach for many software application projects, it may not be best or suitable for all such projects. For example, some software application projects may require more iterative and Agile methods where flexibility and adaptation to new changes are essential. This may not be well-suited to the structured approach of the Software Development Life Cycle.
Best Practices of the Software Development Life Cycle
The execution of different phases of the Software Development Life Cycle should be enhanced and improved to develop high-quality software applications. For this, best practices of the Software Development Life Cycle should be incorporated while developing software applications.
Let us see some of those Software Development Life Cycle best practices.
- Focusing on the application's security early in the Software Development Life Cycle can eliminate future bugs or errors. However, the security aspect is tested at the last phase of the cycle. To address this, leverage DevSecOps which builds security in your code, and security risk is examined during code review, penetration test, and others. This saves the software application from future errors.
- Integration of security and developing secure code are crucial aspects to be followed in the Software Development Life Cycle. It could be done by updating the security requirement to eliminate new errors or flaws. You can also use threat modeling to find and eliminate risks quickly.
- Security audits should be performed to find errors before they create hurdles in the software development process. A tried-and-true checklist can be used to expedite the process, which is both cost and time effective.
- Implementing code reviews to ensure its quality and finding vulnerabilities, you can use SAST tools.
Conclusion
Software Development Life Cycle is crucial for developing quality and top-notch software applications. It allows the team to plan, design, develop, test, and deploy software applications. No matter how big or complex the software application project is, the SDLC can help start the development process.
However, it is important to note that Software Development Life Cycle may not be the one-size-fits-all approach. They require to be adapted to fit specific software application requirements. With the high demand for speed and agility in the development process, a shift from the older Software Development Life Cycle (Waterfall Model) to DevOps emerged. With this, security is now considered a critical component throughout the SDLC.
Frequently asked questions
- General
Author's Profile

Nazneen Ahmad
Nazneen Ahmad is an experienced technical writer with over five years of experience in the software development and testing field. As a freelancer, she has worked on various projects to create technical documentation, user manuals, training materials, and other SEO-optimized content in various domains, including IT, healthcare, finance, and education. You can also follow her on Twitter.
Reviewer's Profile

Salman Khan
Salman works as a Digital Marketing Manager at LambdaTest. With over four years in the software testing domain, he brings a wealth of experience to his role of reviewing blogs, learning hubs, product updates, and documentation write-ups. Holding a Master's degree (M.Tech) in Computer Science, Salman's expertise extends to various areas including web development, software testing (including automation testing and mobile app testing), CSS, and more.
Did you find this page helpful?
More Hubs
Try LambdaTest Now !!
Get 100 minutes of automation test minutes FREE!!
 Christmas Deal is on: Save 25% off on select annual plans for 1st year.
Christmas Deal is on: Save 25% off on select annual plans for 1st year.