What is Non-Functional Testing: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Learning Hub
- What is Non-Functional Testing: A Step-by-Step Guide
CHAPTERS
- Overview
- What is Non-Functional Testing
- Why do you need Non-Functional Testing
- Objectives of Non-Functional Testing
- Advantages of Non-Functional Testing
- Disadvantages of Non-Functional Testing
- Difference between Functional and Non-Functional Testing
- What are the types of Non-Functional Testing
- How do you capture Non-Functional requirements
- Non-Functional Testing Best Practices
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
OVERVIEW
Non-functional testing involves validating the performance, reliability, utility, and other non-functional aspects of a software application. Further, this testing assesses a system's readiness for non-functional parameters that aren't typically addressed in functional testing.
Every software has its own functionality. You would expect a food delivery app to deliver your favorite dishes when you click on “Order food.” The job of a non-functional tester will be to test if you can easily navigate to the “Order food” button. They would also test if more than the ‘n’ number of users could place an order simultaneously from any browser/OS/device configuration.
What is Non-Functional Testing?
Non-Functional Testing is a type of software testing that verifies the non-functional aspects of a software application. It is designed to assess the readiness of a system according to several criteria not covered by functional testing. Non-functional testing includes evaluating a system's performance, reliability, usability, efficiency, maintainability, and scalability.
Non-functional testing is crucial because it deals with aspects that impact the user experience and the application's effectiveness in the real world. It helps ensure that the software meets the established standards and provides a high-quality experience to the end-users.
Factors such as performance, stress resistance, and reliability aren’t related to functionality, in other words, how you perform the operations of a system. Yet, they determine how your users would feel when they are working on your software system.
They can be deal-breakers or deal-makers for software testers. Hence they deserve equal importance as functional testing.
Does it come under Black Box testing or White Box Testing? Obviously, non-functional testing is one of the black box testing methods since it covers the system’s external behavior instead of the system's internal workings.
Why do you need Non-Functional Testing?
We need non-functional testing to increase the product's efficiency, portability, usability, and maintainability. This way, you can reduce production risk, which can hamper the release velocity of your product. You can also increase the ROI of your sales and marketing efforts while you reduce the cost directly proportional to the non-functional product aspects.
Objectives of Non-Functional Testing
The objective of non-functional testing is to verify the requirement specifying the criteria you can use to judge any system operation, such as maintainability, accessibility, performance, security, and availability. Some objectives include:
- Verification of the quality attributes judging the system’s operations.
- Detection of product behavior problems under simulation of different operations.
- Determination of system compliance under certain use conditions.
- Optimization of how you install, set up, manage, execute and monitor the product.
- Collection and production of metrics and measurements to cater to internal research and development.
- Create awareness of the product behavior and technologies we need to use.
Advantages of Non-Functional Testing
Non-functional testing is the backbone of user experience for any software product. Here is why you can gain the upper hand over end-user experience if you involve non-functional testing:
- Get end-to-end, top-level security features. Security is a fundamental feature through which you can protect your system from malware or cyber-attacks.
- Make sure that the loading capability of the system is intact when the ‘n’ number of users leverage it simultaneously.
- Improve the system performance.
- You don’t change the test cases. Hence all you need to do is write them only once.
- You consume less time comparing it with different testing processes throughout the software testing life cycle.
Disadvantages of Non-Functional Testing
In spite of the advantages that you get with non-functional testing, there are a few challenges as well:
- Every time you update the software, you have to perform non-functional testing
- Owing to software updates, every person must pay extra when they want to re-examine their software. Hence their software expenses rise.
- When the performance of a product is as per the expectations of a consumer with the needed efficiency under different circumstances, you can term it a reliable product. You carry out non-functional testing under the terms and conditions of what the customer would expect. It plays a crucial role when you want to satisfy a client's expectations. Since feasibility issues might arise when you manually manage non-functional testing, we use a few special automation testing tools to manage these testing types
Difference between Functional and Non-Functional Testing
With functional testing, you can perform mobile app testing or web application testing against different functional specifications and requirements. Here, the tester needn’t worry about the application’s source code. When you provide the test input, you must ensure that the output you received is right and compare both
Through non-functional testing, you test the system's behavior. This type of testing concerns testing the system readiness per different non-functional parameters unaddressed by functional testing.
Here is the difference between functional testing and non-functional testing:
| Functional Testing | Non-functional Testing |
|---|---|
| You can verify the actions and operations of an application. | You can verify how the application behaves. |
| Customer requirements play a huge role in this type of testing. | Customer expectations play a huge role in this type of testing. |
| You can easily enhance the application behavior. | You can easily improve the application performance. |
| You can easily execute manual functional testing. | It’s tough to perform non-functional testing manually. |
| You get to test what the product does. | You get to test how the product does what it does. |
| Functional testing helps assess business requirements. | Non-functional testing helps assess the performance requirement. |
| Functional testing is performed before your application goes live. | Non-functional testing includes tests such as maintainability and documentation, which happen after testing. |
Do you want to know what’s beyond functional testing? Here is what Devender Sharma has to say in TestMu 2022:
Subscribe to the LambdaTest YouTube channel to learn more about TestNG with Selenium, Shift left testing, real time testing, and much more
What are the types of Non-Functional Testing?
There are many types of non-functional testing. The most important ones are listed below:
- Security:This parameter tells us how to protect a system from unintentional and intentional threats from external and internal sources. We use security testing to validate its efficiency.
- Survivability:This parameter ensures that the computing system runs smoothly. This also restores the system when there is a system malfunction. We perform recovery testing to verify this.
- Reliability: We use this parameter to test how your software system can consistently execute the needed tasks without errors. This is done through reliability testing.
- Availability: We use this parameter to specify how much you can rely upon the running machine. We use stability testing to verify this.
- Usability: This parameter checks how conveniently the user can perform, read and plan different inputs and outputs by contacting a specific machine. We use usability testing to verify this.
- Scalability: This parameter refers to checking how expandable the software application’s computing power is to satisfy the never-ending demands and needs. We can use scalability to validate this factor.
- Efficiency:This parameter can check how much the software product can manage volume, power, duration, and reply variations.
- Responsiveness: It is a technique for making web pages automatically adjust to different viewports. In simpler terms, it means making web pages that look great on all devices. Responsiveness test ensures all users accessing your website using different devices will have a seamless experience.
- Test for visual deviations: With visual regression testing, you can ensure that each element on a web page has the correct size, shape, and placement. A visual test compares a system's visible output to its intended output.
- Interoperability:This non-functional parameter validates the interactions of a software system with other software systems. Interoperability testing verifies this factor.
- Portability: We use this parameter to check the software's capability to switch from the current software or hardware application setting.
- Flexibility: We can use this parameter to check how quickly and easily your program can run across different hardware and software setups.
- Reusability:This means the software which you can adapt to use in a different program.
- Documentation:Documentation refers to visual and written material describing, defining, specifying, and guiding users in their product operation. With clear, well-written documentation, you can get most of the answers to different user questions, which is a must for product success. Before you go live, ensure that documentation requirements are covered with documentation testing.
- Endurance: Through Endurance, you can verify if the system can handle the load beyond a certain limit. It’s done to ensure that the system doesn’t experience a breakdown. You can sort it out through endurance testing.
- Load: Load is a parameter used to perform system testing under different amounts of load on any software, website, or app. This is to design the system's response to normal and peak conditions. You can then analyze the results to identify if there are any troubling areas causing degradation. Load testing can take care of this parameter.
- Scalability: This parameter is used to check if the machine can cope with many transactions, different load conditions, and a hike in the data volume. Scalability testing can help you check this parameter under test design.
- Volume: Volume can check if there are variations of data load at different time points. It helps us analyze to what extent we need to expand our database with an increasing number of users. Volume testing can help you check this parameter.
- Stress: This parameter can determine if the system is stable after it reaches a breaking point. This is to check for availability, robustness, and error handling under a large amount of data that gets dumped into the system. We can make use of stress testing to handle this.
- Recovery: We can use this parameter to test the ability of the system to recover from any potential breakdown within a short time period. This is also known as the system’s recovery plan from forced failure. We can use recovery testing to get this done.
- Baseline: Through this parameter, we can validate if the required documents and specifications of the test case data are working right. We leverage baseline testing to check this parameter.
- Compliance: Compliance is used to validate how well the development procedure is as a whole entity. You need to check if everything matches the IT requirements. We use compliance testing to check it.
- Compatibility: Examine the compatibility of the software with many software and hardware configurations, be it browser versions, browsers, or operating systems along with third-party integrations and multiple versions. Compatibility testing would need access to devices, real browsers, and operating systems when you run tests to check the app's behavior in different environments.
Continuous quality cloud platform like LambdaTest lets you perform cross browser compatibility testing of your websites and web applications across 3000+ real browsers, devices, and operating systems. With its real device cloud, you can test applications in real-world scenarios and get accurate results.
How do you capture Non-Functional requirements?
When you perform testing, you focus more on functional testing to test the product functionality. But, we cannot forget how important non-functional testing is. We need to consider the testing requirements right from the start of the project.
We can use non-functional requirements such as the expected performance output from the software or the application under test. This can include the time the software takes to operate a unique system.
Non-functional requirements can also help you capture the user behavior when many people use the software or system simultaneously. Most of the time, the servers might be unavailable or busy, thanks to heavy load. The best example is a college website where exam results are obtained.
Hence you need to document the non-functional requirement properly. When you perform the test properly, you can also get high-end satisfaction in terms of potential customer usability.
Even though this testing doesn’t impact the business directly on the functionality aspects, you can amplify the user-friendliness and user experience to the next level. This will lead to high-end software quality.
In agile, you can capture the non-functional requirement using different inputs. These are a few ways through which you can capture it:
- User /Technical Stories
- In Artifact
- In Acceptance criteria
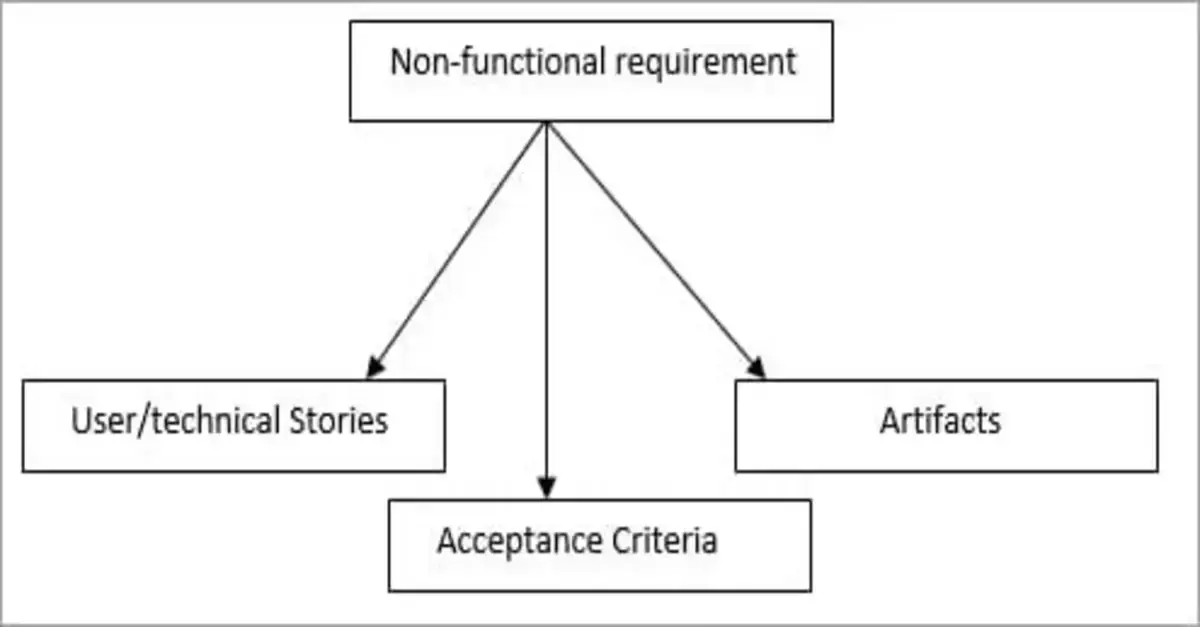
- User or Technical Stories
- Acceptance Criteria
- Through Artifacts
You can capture the non-functional requirement with technical or user stories. Whether you capture non-functional requirements in the form of a user story or any other requirement, both remain the same. The major difference between a technical story and the user is that the user story would require discussion and consist of visibility.
Acceptance Criteria is the point at which your customer can accept your product through user acceptance testing (UAT). You might also be unable to test the non-functional requirements in each story when you perform every iteration. Hence you need to add or test the requirements with only the relevant iteration.
You need to prepare a separate artifact to manage the non-functional requirements. This can help you develop a better idea of what you need to test and how you can do it in different iterations.
How to perform Non-Functional Testing
Performing non-functional testing is easy and simple. Here is a detailed step-by-step method to perform non-functional tests:
- Initially, you need to examine the system specifications and requirements
- The tester would choose all the needed valid inputs in a positive testing scenario. This is done to check if the SUT can process them correctly. Also, we can choose a few invalid inputs and negative test scenarios to verify if the SUT can detect them.
- Tester would determine the expected outputs for every input
- Tester can also construct different test cases with your selected inputs.
- The tester would then execute the test cases
- They would then compare the actual outputs against the expected outputs.
- They would also check if the defects are fixed after re-testing them.
Non-Functional Testing Best Practices
There are a few points you must remember to make non-functional testing memorable and productive. Here they are:
- Don’t wait until the last moment to get non-functional testing covered.
- The approach document before you conduct non-functional testing has to cover the test scope, test metrics, testing tools, important dates, and deliverables.
- Stick to your requirements. Locate every NFRs and map them accordingly
- Prioritize which tests need to be done first and last.
- Ensure that your test environment consists of the same production environment setup, be it configuration, mentoring, or physical architecture.
- Note down the run state to know if it’s at normal, failure, peak load, or latency stage.
- Repeat the steps involved in the dataset, configuration, request load, and scenario.
- Ensure that your NFR tests reflect real-time use cases.
- Record everything that’s needed, be it response time or throughput.
- Use graphs and other visual representations as evidence.
- Summarize the test results for your TL;DR crew.
- Take lessons from what you learned and fix those bugs and errors
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is Non-functional testing?
Non-functional testing is how we test the properties of the application that doesn’t form a critical base for functionality. Instead, it must add power to the end-user experience.
What is functional and non-functional testing with examples?
The goal of functional testing is to validate different software actions. On the other hand, Non Functional testing can validate how the software performs. The best functional testing example is checking how the payment page functionality works. Non Functional testers would check if the dashboard can load within 2 seconds.
Is black box a non-functional test?
Black Box Testing, under the definition of the International Software Testing Qualifications Board (ISTQB), comes either under non-functional or functional testing, with no reference to the system or component’s internal structure.
What are the benefits of non-functional testing?
Non-functional testing enhances user satisfaction, safeguards data, and improves system reliability, ultimately leading to higher quality software.
What is the significance of non-functional testing in ensuring software quality?
Non-functional testing ensures that software not only meets functional requirements but also delivers optimal performance, security, and usability, meeting user expectations and business needs.
What are the challenges in non-functional testing?
Challenges include varying device configurations, network conditions, and platform-specific behaviors, necessitating comprehensive testing across different scenarios.
What is the future of non-functional testing in terms of emerging technologies?
Non-functional testing will continue to evolve to address challenges posed by technologies like AI, IoT, and cloud computing, ensuring that applications deliver optimal performance and user experience.
Can non-functional testing uncover hidden performance bottlenecks?
Yes, non-functional testing, particularly performance testing, helps identify hidden bottlenecks, such as memory leaks and inefficient algorithms, which can impact application speed and responsiveness.
What is the role of usability testing in non-functional testing?
Usability testing assesses user interaction, navigation, and overall user experience, ensuring that the application is intuitive and user-friendly.
What is the importance of performance testing in non-functional testing?
Performance testing helps ensure the application's responsiveness, scalability, and stability under various loads, preventing bottlenecks and slowdowns that could affect user experience.
Author's Profile
Reviewer's Profile

Shahzeb Hoda
Shahzeb currently holds the position of Senior Product Marketing Manager at LambdaTest and brings a wealth of experience spanning over a decade in Quality Engineering, Security, and E-Learning domains. Over the course of his 3-year tenure at LambdaTest, he actively contributes to the review process of blogs, learning hubs, and product updates. With a Master's degree (M.Tech) in Computer Science and a seasoned expert in the technology domain, he possesses extensive knowledge spanning diverse areas of web development and software testing, including automation testing, DevOps, continuous testing, and beyond.
 Christmas Deal is on: Save 25% off on select annual plans for 1st year.
Christmas Deal is on: Save 25% off on select annual plans for 1st year.
