- Automation
- Home
- /
- Learning Hub
- /
- Mocha Tutorial
- -
- June 17 2023
Mocha Tutorial – A Detailed Guide On Mocha Testing
Master Mocha Testing with our detailed tutorial! Learn essential techniques, tips, and tricks for robust code quality. Start your Mocha journey now
OVERVIEW
Mocha is a versatile and high-performing JavaScript testing framework. It simplifies test creation, freeing developers from infrastructure concerns. Being open-source, it offers customization options. Mocha supports JavaScript and TypeScript, integrates well with frameworks and libraries, and synchronizes test actions with UI. It enables testing of native and hybrid views, including black-box and component testing, and provides annotations and assertions. Mocha ensures efficient and effective quality assurance for JavaScript applications.
What is Mocha.js?
The Mocha testing framework provided as a NodeJs module and a browser script makes asynchronous testing simple and fun. In addition, the framework's ability to run tests serially allows tests to be flexible and accurate without sacrificing speed or accuracy.
Mocha provides a way to write a structured code for testing the applications thoroughly, classifying them into test suites and test cases. Mapping errors to corresponding test cases allows us to produce a test report after the run.
Mocha supports any number of test interfaces, including TSS, Exports, QUnit, and Require. The default interface is a behavior-driven development (BDD), which aims to help developers build software that is predictable, resilient to changes, and not error-prone.
Note: You can also run your Mocha.js test scripts on LambdaTest cloud.
Why Use Mocha.js Framework?
Mocha.js, a widely adopted JavaScript testing framework, is highly regarded among developers for its versatility in testing applications across the front and back ends. Its numerous advantages contribute to its popularity in the development community. Below are some notable benefits offered by the Mocha.js framework:
- Number of installation options: It can be installed globally, as a development dependency for your project, or set up to run test cases directly on the web browser.
- Multiple browser support: Mocha makes it easy to create test cases that run seamlessly on all major web browsers. It can be extended with plugins, and each revision of Mocha provides upgraded JavaScript and CSS builds for different web browsers.
- Various ways to offer test reports: It provides users with a variety of reporting options, such as the list reporter, the progress reporter and the JSON reporter, which allows you to choose the one that best suits your needs.
- Supports JS assertion libraries: With Mocha, you can reduce testing costs and speed up the process by having compatibility for various JavaScript assertion libraries—Express.js, Should.js, Chai. This multiple library support makes it easier for you to write lengthy and complex test cases, so if everything works fine, you won't have to rewrite them again.
- Supports both BDD and TDD environments: Mocha supports both behavior-driven development (BDD) and test-driven development (TDD), making it easy to write high-quality tests and enhance coverage.
- Supports both synchronous and asynchronous testing: Mocha is designed to fortify asynchronous testing with features that invoke the callback once the test is finished. It enables synchronous testing by omitting the callback.
Browsers Supported by Mocha.js
Mocha.js is compatible with a wide range of popular web browsers, ensuring seamless functionality across platforms. Here are the browser versions supported by Mocha.js:
- Google Chrome (27 and above)
- Mozilla Firefox (10 and above)
- Internet Explorer (10 and above)
- Opera (69 and above)
- Safari (7.1 and above)
- Microsoft Edge (15 and above)
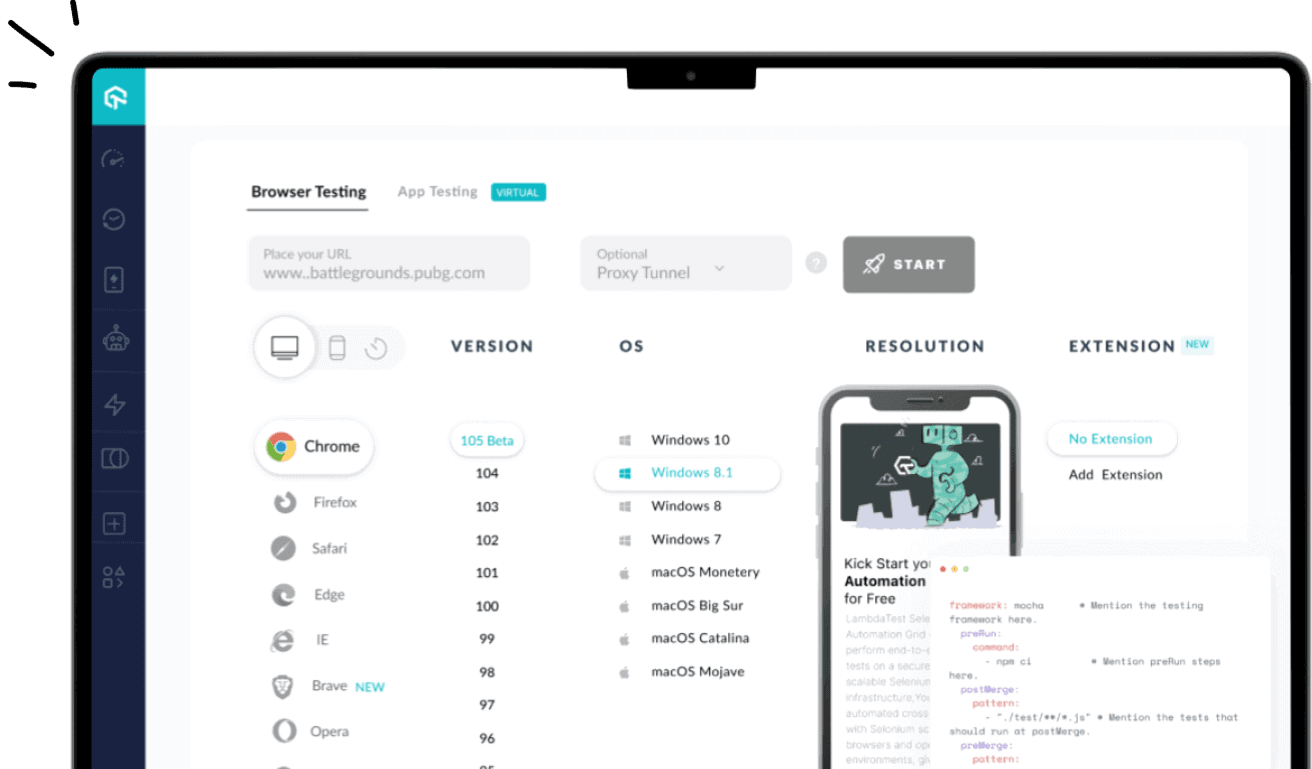
Run Your First Mocha.js Tests
Mocha.js cloud grids like LambdaTest offer the convenience of scaling Mocha.js testing. With these cloud grids you can automate cross-browser testing on a diverse range of browsers and operating systems. This allows for efficient test execution and enhances overall test coverage, resulting in improved product quality.
To run your first Mocha.js automation testing script online, refer to our GitHub repository. No need to worry about the challenges with Mocha.js infrastructure.
Our detailed Mocha.js tutorials will help you develop a better functional understanding of the Mocha.js framework. Finally, kick-start your Mocha.js automation journey by running your first Mocha.js test script on the LambdaTest cloud.
Prerequisites for Executing Mocha Test Automation Scripts
Prior to executing Mocha test automation scripts utilizing Selenium, the following prerequisites need to be fulfilled:
- Acquire and implement NodeJS from the official NodeJS documentation, ensuring a minimum version of NodeJS v6 or above.
- Verify that the latest iteration of JavaScript is being utilized.
- Install npm from the designated source, the official npm website.
- Procure the Selenium JavaScript bindings from the authorized website. Optimal performance can be achieved by utilizing the most recent editions of the Selenium Client and WebDriver when executing your JavaScript automation testing script within LambdaTest's Selenium Grid.
Installing Selenium Dependencies and tutorial repo
Step 1: Clone the LambdaTest’s mocha-selenium-sample repository and navigate to the code directory as shown below:
git clone https://github.com/LambdaTest/mocha-selenium-sample
cd mocha-selenium-sampleStep 2: Install the required project dependencies using the command below:
npm i
npm install selenium-webdriverSetting up Your Authentication
Make sure you have your LambdaTest credentials with you to run test automation scripts on LambdaTest Selenium Grid. You can obtain these credentials from the LambdaTest Automation Dashboard or through LambdaTest Profile.
Step 3: Set LambdaTest Username and Access Key in environment variables.
- For Linux/macOS:
export LT_USERNAME= "YOUR_LAMBDATEST_USERNAME"
export LT_ACCESS_KEY= "YOUR_LAMBDATEST_ACCESS_KEY"set LT_USERNAME= "YOUR_LAMBDATEST_USERNAME"
set LT_ACCESS_KEY= "YOUR_LAMBDATEST_ACCESS_KEY"Run Your First Test
Sample Test with MochaJS
When conducting a sample test with MochaJS, it is essential to adhere to a structured approach. Set up the test environment by initializing Mocha and configuring settings. Define test cases using Mocha's syntax and assertions to verify expected outcomes.
//single_test.js
var assert = require("assert"),
webdriver = require("selenium-webdriver"),
conf_file = process.argv[3] || "conf/single.conf.js";
var caps = require("../" + conf_file).capabilities;
var buildDriver = function(caps) {
return new webdriver.Builder()
.usingServer(
"http://" +
LT_USERNAME +
":" +
LT_ACCESS_KEY +
"@hub.lambdatest.com/wd/hub"
)
.withCapabilities(caps)
.build();
};
describe("Google's Search Functionality for " + caps.browserName, function() {
var driver;
this.timeout(0);
beforeEach(function(done) {
caps.name = this.currentTest.title;
driver = buildDriver(caps);
done();
});
it("can find search results", function(done) {
driver.get("https://www.lambdatest.com").then(function() {
driver.getTitle().then(function(title) {
setTimeout(function() {
console.log(title);
assert(
title.match(
"Cross Browser Testing Tools | Test Your Website on Different Browsers | LambdaTest"
) != null
);
done();
}, 10000);
});
});
});
afterEach(function(done) {
if (this.currentTest.isPassed()) {
driver.executeScript("lambda-status=passed");
} else {
driver.executeScript("lambda-status=failed");
}
driver.quit().then(function() {
done();
});
});
});
Configuration of Your Test Capabilities
Step 4: In conf/single.conf.js file, you need to update your capabilities. In this code, we are passing browser, browser version, and operating system information, along with LambdaTest Selenium grid capabilities via capabilities object. The capabilities object in the above code are defined as:
exports.capabilities = {
'build': 'Mocha-Selenium-Sample', //Build name
'name': 'Your Test Name', // Test name
'platform':'Windows 10', // OS name
'browserName': 'chrome', // Browser name
'version': 'latest', // Browser version
'visual': false, // To take step by step screenshot
'network':false, // To capture network Logs
'console':false, // To capture console logs.
'tunnel': false // If you want to run the localhost than change it to true
};
Executing the Test
Step 5: The tests can be executed in the terminal using the following command.
npm run singleYour test results would be displayed on the test console (or command-line interface if you are using terminal/cmd) and on LambdaTest automation dashboard.
LambdaTest Automation Dashboard will help you view all your text logs, screenshots and video recording for your entire automation tests.
Running Your Parallel Tests Using Mocha Framework
Setting up the Parallel Environment
Here is the parallel_test.js file which would help you to run a single test on various browsers at the same time.
//parallel_test.js
var assert = require("assert"),
webdriver = require("selenium-webdriver"),
conf_file = process.argv[3] || "conf/single.conf.js";
var capabilities = require("../" + conf_file).capabilities;
var buildDriver = function(caps) {
return new webdriver.Builder()
.usingServer(
"http://" +
LT_USERNAME +
":" +
LT_ACCESS_KEY +
"@hub.lambdatest.com/wd/hub"
)
.withCapabilities(caps)
.build();
};
capabilities.forEach(function(caps) {
describe("Google's Search Functionality for " + caps.browserName, function() {
var driver;
this.timeout(0);
beforeEach(function(done) {
caps.name = this.currentTest.title;
driver = buildDriver(caps);
done();
});
it("can find search results" + caps.browserName, function(done) {
driver.get("https://www.lambdatest.com").then(function() {
driver.getTitle().then(function(title) {
setTimeout(function() {
console.log(title);
assert(
title.match(
"Cross Browser Testing Tools | Test Your Website on Different Browsers | LambdaTest"
) != null
);
done();
}, 10000);
});
});
});
afterEach(function(done) {
if (this.currentTest.isPassed()) {
driver.executeScript("lambda-status=passed");
} else {
driver.executeScript("lambda-status=failed");
}
driver.quit().then(function() {
done();
});
});
});
});
Executing Parallel Tests using Mocha
To run parallel tests using Mocha, we would have to execute the below command in the terminal:
npm run parallelYour test results would be displayed on the test console (or command-line interface if you are using terminal/cmd) and on LambdaTest automation dashboard.
Testing Locally Hosted or Privately Hosted Projects
You can test your locally hosted or privately hosted projects with LambdaTest Selenium grid cloud using LambdaTest Tunnel app. All you would have to do is set up an SSH tunnel using LambdaTest Tunnel app and pass toggle tunnel = True via desired capabilities. LambdaTest Tunnel establishes a secure SSH protocol based tunnel that allows you in testing your locally hosted or privately hosted pages, even before they are made live.
Refer our LambdaTest Tunnel documentation for more information.
Here’s how you can establish a LambdaTest Tunnel.
Download the binary file of:
Open command prompt and navigate to the binary folder.
Run the following command:
LT -user {user’s login email} -key {user’s access key}
So if your user name is lambdatest@example.com and key is 123456, the command would be:
LT -user lambdatest@example.com -key 123456
Once you are able to connect LambdaTest Tunnel successfully, you would just have to pass on tunnel capabilities in the code shown below :
Tunnel Capability
const capabilities = {
tunnel: true,
}
Why Choose LambdaTest
LambdaTest is a leading test execution and orchestration platform that is fast, reliable, scalable, and secure. It allows users to run both manual and automated testing of web and mobile apps across 3000+ different browsers, operating systems, and real device combinations. Using LambdaTest, businesses can ensure quicker developer feedback and hence achieve faster go to market. Over 500 enterprises and 2 Million + users across 130+ countries rely on LambdaTest for their testing needs.
What does LambdaTest offer?
- Run Selenium, Cypress, Puppeteer, Playwright, and Appium tests over scalable automation testing cloud with 3000+ real desktop and mobile environments.
- Live interactive cross browser testing in different environments.
- Perform Mobile App testing on Real Device cloud.
- Perform 70% faster test execution with HyperExecute.
- Mitigate test flakiness, shorten job times and get faster feedback on code changes with TAS (Test At Scale).
- Smart Visual Regression Testing on cloud.
- LT Browser - for responsive testing across 50+ pre-installed mobile, tablets, desktop, and laptop viewports.
- Capture a full page automated screenshot across multiple browsers in a single click.
- Test your locally hosted web and mobile apps with LambdaTest tunnel.
- Test for online Accessibility testing.
- Test across multiple geographies with Geolocation testing feature.
- 120+ third-party integrations with your favorite tool for CI/CD, Project Management, Codeless Automation, and more.
The Landscape of Mocha.js Framework
JavaScript's prominence as the most popular programming language, as highlighted in Stack Overflow insights 2021, is further amplified by the growing influence of web and mobile technologies. Consequently, JavaScript frameworks have evolved, enabling testers to develop comprehensive end-to-end automation test suites. Mocha, a widely favored JavaScript testing framework since 2016, has gained significant traction according to The State of JS 2021.
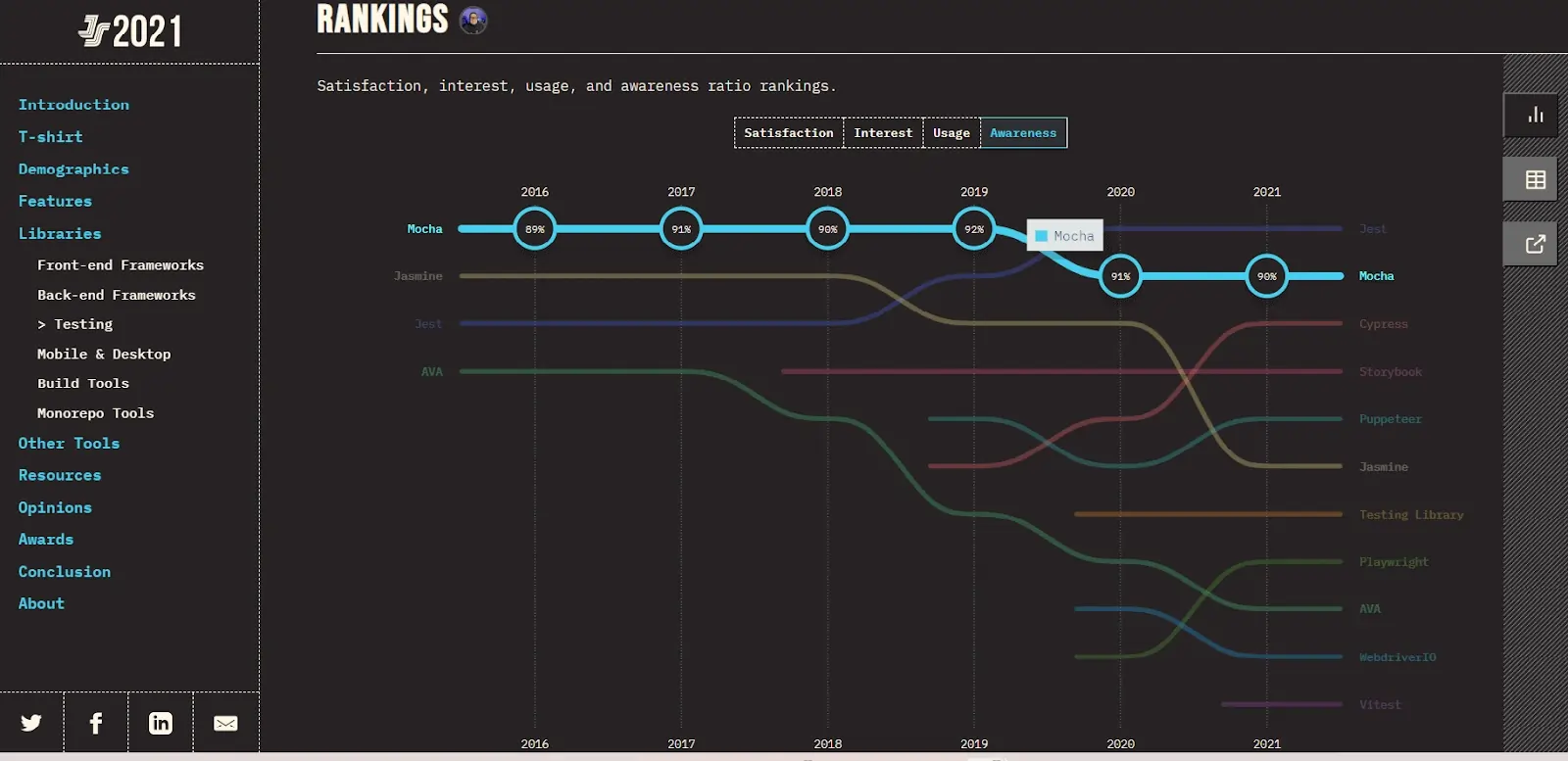
Check out The State of JS 2021 Mocha.js testing data on the basis of developer Usage and Awareness.
Usage:
The change in the level of usage of Mocha among testers hasn’t shown a significant change since its inception. The percentage varies from 49% in 2016 to 50% in 2021.
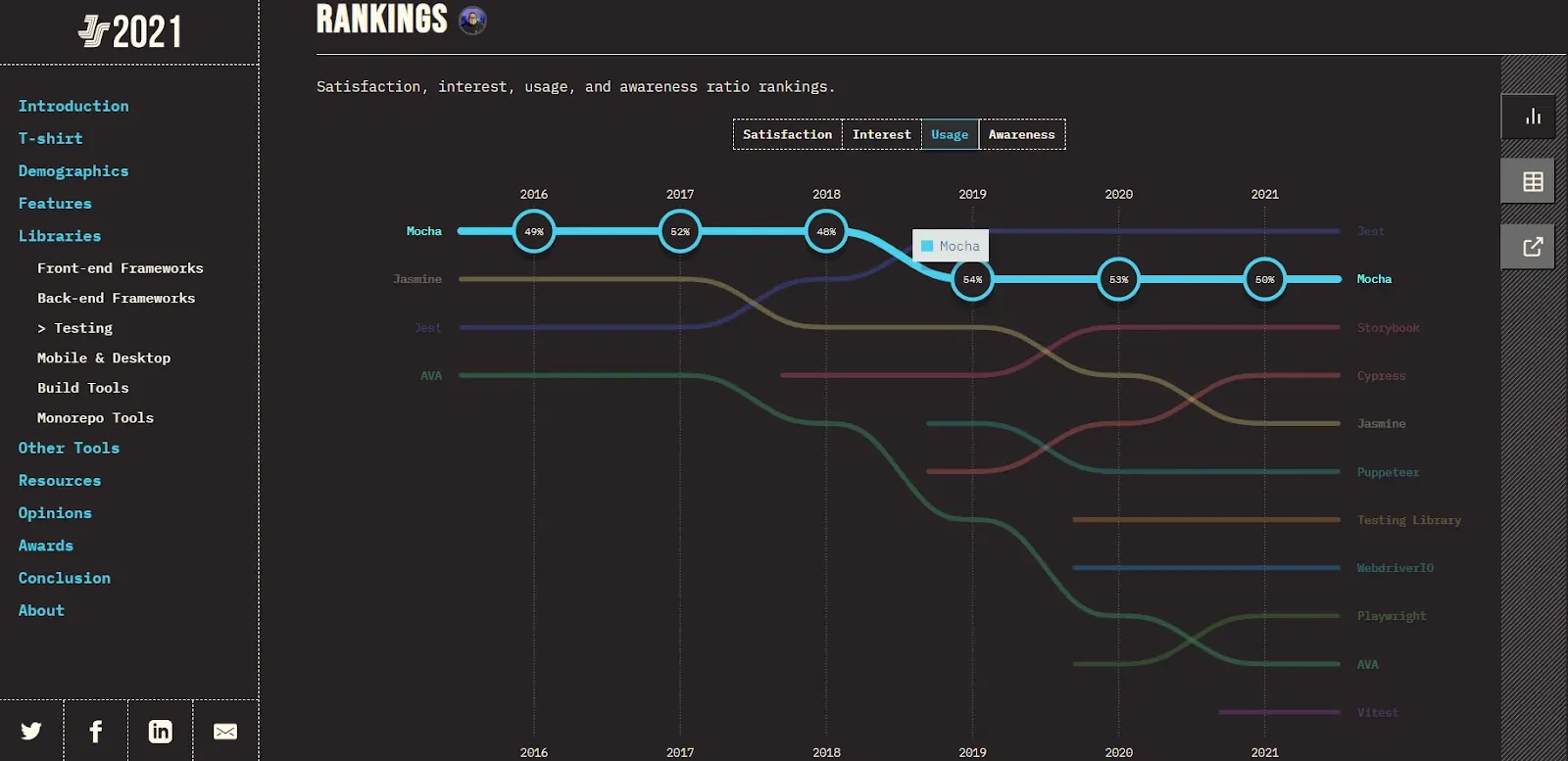
Awareness:
The percentage of awareness about Mocha among the tester community has seen a slight increase, indicating growth potential i.e., from 89% in 2016 to 90% in 2021.
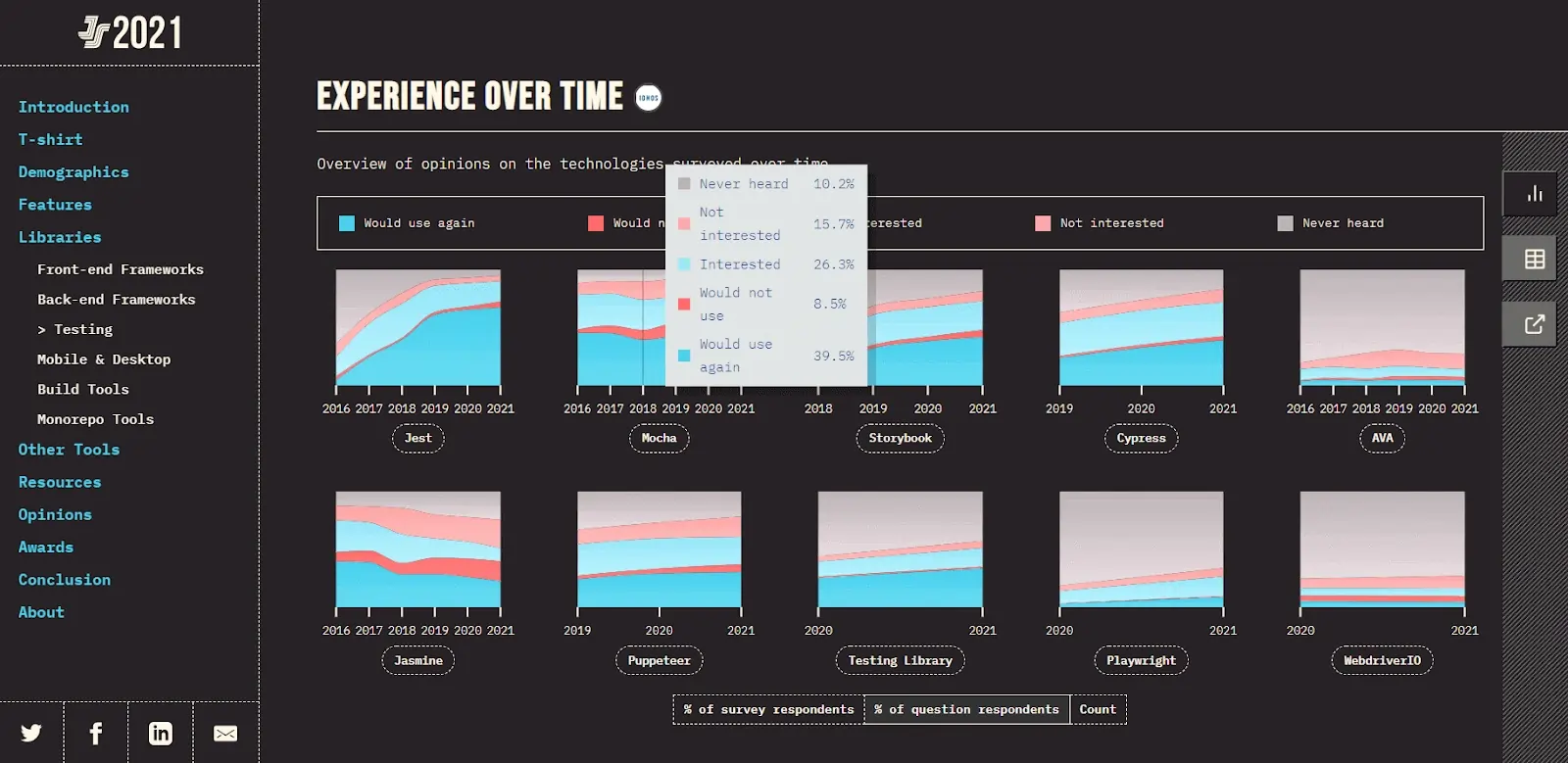
As per the experience over time section, the overall interest among the tester community to use Mocha has seen a constant downfall in the last 5 years. There is also a decrease in the percentage of testers who would like to use Mocha again, from 45.6% in 2016 to 34.6% in 2021.
Limitations of Mocha.js Testing
- Compared to other frameworks, Mocha requires more configuration, making it less flexible.
- In the case of Mocha, if you are unable to afford flexibility, then you must choose an assertion library explicitly.
- Mocha snapshot testing can be tricky. To do it well, you'll need to work with the chai-jest-snapshot library.
If you are looking to run unit tests, You can refer to our guide on Mocha unit testing
Mocha.js vs Jasmine: A Detailed Comparison
Jasmine is a JavaScript testing framework that was created around 2008 and has been updated regularly since. The documentation describes it as “batteries included,” meaning that it attempts to provide everything a developer needs in a testing framework. Mocha, created in 2011, is a younger framework than Jasmine. It is not a “complete” framework; instead, it covers the basics and allows developers to extend it with other frameworks.
Assertions:
Assertions are Boolean functions that test behavior. A true result from an assertion indicates that the expected behavior occurred when the test ran. Jasmine includes a library of assertions that use expect-style syntax. While Mocha does not have a built-in assertion library, developers can use the popular Chai assertion library, which uses a syntax similar to Jasmine.
Test Doubles/Spies:
Test double frameworks, such as Jasmine, create test doubles. A test double, or spy, is like a clone of an object. It has the same functions as the original object. However, those functions are "stubbed out," meaning they don't do anything. The "stubbed" functions exist so the test double framework can "watch" the double in action, tracking calls to its functions. Mocha does not include a spy framework, but SinonJS is a popular choice for creating spies.
In conclusion, Jasmine comes with assertions and spies, but it doesn’t necessarily make it a better option than Mocha. Mocha focuses on BDD test definitions and does so very well, but other best-of-breed frameworks combine with Mocha to extend its functionality.
To make an informed choice, try both Mocha and Jasmine. Your particular application, and the needs of the test suite will make one option clear as you experiment. You can use either library on its own, but to keep your tests consistent and readable, we recommend combining Mocha or Jasmine with Chai and Sinon within an application.
Conclusion
Mocha.js is a powerful testing framework that empowers developers to create and execute tests efficiently. Its intuitive interface, comprehensive reporting, and real-time feedback make it easy to identify and fix bugs swiftly, ensuring optimal performance and reliability. With support for multiple test interfaces, assertion libraries, and both synchronous and asynchronous testing, Mocha offers flexibility and compatibility.
Additionally, by integrating with LambdaTest, developers can leverage the cloud grids for seamless cross-browser testing and enhance overall test coverage. Start your Mocha.js automation journey today with LambdaTest to achieve faster and more reliable testing results. Sign up for LambdaTest and receive 100 minutes of free testing along with 2 parallel web+mobile automation testing.
On this page
- What is Mocha.js?
- Why Use Mocha.js Framework?
- Browsers Supported by Mocha.js
- Run Mocha.js Tests
- Run Your First Test
- Running Your Parallel Tests Using Mocha Framework
- Testing Locally Hosted or Privately Hosted Projects
- Why Choose LambdaTest
- The Landscape of Mocha.js Framework
- Limitations of Mocha.js Testing
- Mocha.js vs Jasmine
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Frequently asked questions
- General →
Did you find this page helpful?
More Hubs
Try LambdaTest Now !!
Get 100 minutes of automation test minutes FREE!!
 Christmas Deal is on: Save 25% off on select annual plans for 1st year.
Christmas Deal is on: Save 25% off on select annual plans for 1st year.