- Testing Basics
- Home
- /
- Learning Hub
- /
- Mobile Device Testing
- -
- October 23 2023
What is Mobile Device Testing: A Complete Tutorial
Learn mobile device testing, its types, processes, and how to test mobile apps on different devices.
OVERVIEW
Mobile device testing is a quality assurance process that ensure mobile devices, like smartphones, tablets, and wearables, works as expected. This process tests the device's functionality, performance, usability, and security to ensure that it meets specific requirements and standards.
In today's world, we're more connected than ever before. And mobile devices are at the center of it all. From smartphones and tablets to smartwatches and fitness trackers, these devices are not only powerful tools for communication but also connect us to the digital world.
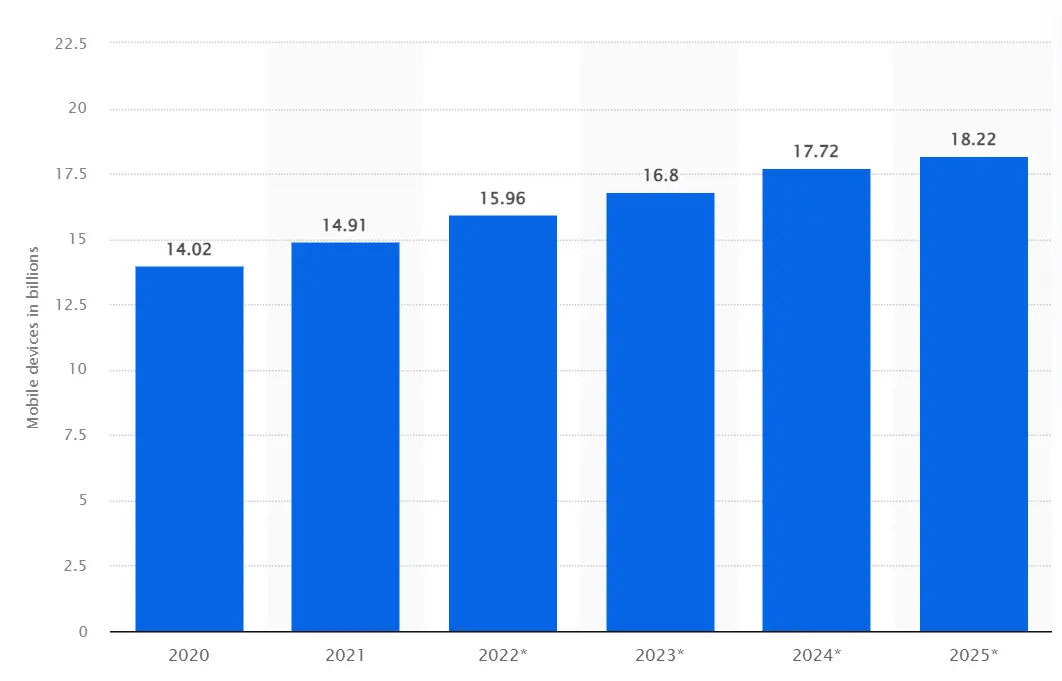
In the year 2021, the global count of mobile devices operating reached a staggering figure of nearly 15 billion, marking a significant growth from the previous year's total of just over 14 billion. It is projected that by the year 2025, this number will further surge to an astonishing 18.22 billion, signifying an impressive addition of 4.2 billion devices compared to the levels observed in 2020. This exponential rise highlights the ever-expanding presence and reliance on mobile technology worldwide.
With mobile devices playing such an integral role in our day-to-day lives, it's more important than ever to ensure that they work flawlessly. This is where mobile device testing comes in.
Mobile device testing is a complex and dynamic field that involves various approaches and strategies. It covers a wide range of factors, including mobile app functionality, performance, security, and user experience.
Whether you're a developer, QA engineer, business owner, or just someone interested in mobile devices, having a grasp of mobile device testing is crucial for informed decision-making, ensuring product integrity, and providing users with a smooth experience.
What is a Mobile Device?
Mobile devices are small, handheld (portable) devices that can be carried around and used wirelessly. The most common examples of mobile devices are smartphones, tablets, and e-readers.
In this tech-driven world, mobile devices have emerged as a way that serve multiple purposes for both individuals and businesses. These devices, such as smartphones and tablets, provide users with the convenience of accessing a plethora of software applications. From web browsing and sending emails to engaging in instant messaging and text conversations, these devices offer a seamless connection to the digital world.
Moreover, mobile devices often act as an alternative to PCs or laptops. In fact, in certain instances, these advanced mobile devices have enough capability to completely replace traditional PCs. Here, the beauty lies in their ability to synchronize with PCs when used together. This means that any task done on a mobile device remotely can be effortlessly updated on PCs, reflecting changes and incorporating new information even when one is away from their PC.
The first mobile device was the Personal Digital Assistant (PDA), which was popular in the 1990s and early 2000s. PDAs were like very small tablets, but they could not make phone calls. Most PDAs had a physical keyboard and limited software.
When designing a mobile device, there is a trade-off between making the UI larger to accommodate more features and making the device smaller and more portable. For example, phablets are larger than smartphones for ease of input, but they are still smaller than most tablets.
Mobile devices share a number of common characteristics, including:
- Wireless connectivity: They can connect to the Internet via Wi-Fi or cellular networks, and they can also connect to other devices via Bluetooth.
- Battery power: Mobile devices are powered by batteries, so they can be used on the go.
- User input: They typically have either a physical or a touchscreen keyboard for entering information.
- Portability: Mobile devices are small and lightweight, so they can be carried easily.
- Touchscreen interface: Most mobile devices now have touchscreen interfaces, making them easy to use.
- Virtual assistant: Many mobile devices have a virtual assistant, such as Siri, Cortana, or Google Assistant, which can be used to perform tasks such as setting alarms, making calls, and sending messages.
- App store: Mobile devices lets you download apps from an app store to use them for a variety of purposes, such as playing games, listening to music, and browsing the Internet
In addition to the above common characteristics, mobile devices can also have a variety of other features, such as cameras, GPS receivers, and fingerprint scanners.
Mobile devices are commonly referred to as portable devices that can access the Internet. However, there is a notion that digital cameras and MP3 players as mobile devices. In the next section, we will look at the types of mobile devices.
Types of Mobile Devices
Mobile devices come in a variety of screen sizes that run on different operating systems and perform a wide range of tasks, including
- Making and receiving voice calls
- Sending and receiving text messages
- Browsing the Internet
- Checking email
- Listening to music
- Watching videos
- Playing games
- Using apps and more
Major types of mobile devices include:
- Smartphones: Smartphones are more than just phones. They can also connect to the Internet, run a variety of apps, and connect to other devices, such as smart TVs, car music systems, and headsets.
- Tablets and iPads: Tablets and iPads are touchscreen devices that do not have separate keyboards or mice. They can be used for a variety of tasks, such as browsing the Internet, watching videos, playing games, and using apps.
- Personal Digital Assistants (PDAs): You might not see these around much these days, but they were pretty popular before tablets and iPads came along. PDAs could do things like making calls, browsing the Internet, and even sending faxes. They had a unique feature – you interacted with them using a stylus, like a pen, to input data.
But with the rise of touch screen technology, tablets and iPads have kind of taken over the PDA's role. They've become more versatile and user-friendly, making PDAs a thing of the past.
What is Mobile Device Testing?
At its core, mobile device testing involves examining a mobile device to ensure that everything, both its physical components (hardware) and the underlying functionalities (software), functions correctly and as intended.
From a technical standpoint, it can be thought of as a quality assurance process for mobile devices. This means making sure that the device meets specific criteria and standards concerning both its hardware and software before it's made available to the general public for use.
Mobile device testing is a thorough evaluation process where testers not only validate the device's hardware and software but also test the mobile applications that come pre-installed. This detailed testing process helps identify and rectify any issues or inconsistencies, ensuring that the mobile device is in prime condition and ready for a seamless experience once it's in the hands of real users.
Why is Mobile Device Testing Important?
The need for mobile device testing has never been more evident than in the present era, where mobile devices have become central to our interactions. These portable devices have reshaped the way folks engage with the digital world, offering unprecedented convenience and flexibility.
Over the past decade, their prevalence has surged, empowering us to accomplish an array of tasks without being tethered to a specific location. From online banking to shopping and bill payments, the list of what we can achieve with our mobile devices continues to expand.
However, this surge in mobile device usage has also ushered in a growing need for reliable and faultless devices. The convenience and efficiency that these devices provide are rooted in their ability to seamlessly execute various operations. As mobile devices become more and more like an all-in-one tool, the importance of ensuring their flawless functioning is super important. This is where mobile device testing comes into play.
By subjecting mobile devices to rigorous testing, developers and testers can identify and rectify issues in both hardware and software of a mobile device. This proactive approach significantly reduces the chances of devices malfunctioning or encountering issues problems that could disrupt the mobile experience.
Mobile device testing plays a pivotal role in preserving the trust and confidence that users place in their devices. When users can rely on their mobile devices to perform as expected, it bolsters their trust in the technology and enhances their overall satisfaction. Malfunctions, crashes, or security breaches not only undermine user confidence but can also have real-world consequences, particularly when sensitive data is involved.
Types of Mobile Device Testing
Mobile device testing involves a range of specific testing types that assess different aspects of a mobile device's functionality, performance, and security. Here are some of the key types of mobile device testing:
- Functional Testing: This testing verifies whether the device's basic features work correctly. For example, in the case of a mobile device, it involves ensuring that functions like making calls, sending text messages, and web browsing work as expected.
- Performance Testing: Performance testing examines how the device handles different scenarios. When testing a device, multiple apps running simultaneously or using a slow Internet connection can be evaluated to assess the device's performance under various conditions.
- Usability Testing: Usability testing focuses on how easily users can interact with the device. In the context of a device, it typically includes giving users tasks to complete and observing how they interact with the device.
- Compatibility Testing: Compatibility testing ensures that the device functions correctly with a variety of operating systems, networks, and other devices. In the case of a device, this testing can encompass connecting it to different Wi-Fi networks or Bluetooth devices to verify compatibility.
- Localization Testing: Localization testing validates that the device is adapted to different languages and cultures. In the context of a device, this entails checking if menus and text display correctly in the relevant language.
- Accessibility Testing: Accessibility testing make sure that the device can be effectively used by individuals with impairements. For a device, this may involve checking its compatibility with screen readers and other assistive technologies.
- Battery Testing: Battery testing assesses the device's battery life and performance. In the case of a device, this often involves running various applications to gauge their impact on battery consumption.
- Camera Testing: Camera testing appraises the quality and performance of the device's camera. For a device, this typically includes capturing photos and videos under different lighting conditions to evaluate the camera's capabilities.
- GPS Testing: GPS testing verifies the accuracy and performance of the device's GPS system. In the context of a phone, it can involve using the device for navigation and assessing the precision of the provided directions.
- Security Testing: Security testing aims to uncover and rectify security vulnerabilities in the device and its applications. For a device, this may involve attempts to breach the device's security or install malicious software to assess its resistance to such threats.
- Certification testing: It is a process of evaluating a mobile device to ensure that it meets certain standards and requirements. This type of testing is typically performed by a third-party organization and is necessary for the device to be launched in the market.
Role of Device Under Test (DUT)
A test device, also known as a Device Under Test (DUT), is a device that undergoes quality testing. When it comes to mobile devices, such as smartphones, the manufacturer assesses their quality before they reach the customers. This evaluation covers not only the software, the stuff that makes the device run but also the hardware, the physical parts like the screen and buttons, to make sure they meet the necessary requirements and work correctly.
For instance, if an organization plans to test the Samsung Galaxy A52s mobile device for its quality, this device becomes the test device or DUT. So, it's akin to putting this smartphone through a series of tests to ensure it functions as expected. The manufacturer wants to ensure that the phone can make voice calls, send messages, access the Internet, and run apps smoothly. Plus, they want to be certain that all the physical components, such as the screen and buttons, are in perfect working order.
Here, the aim is to catch any issues or glitches in the device before it's released to the public. By identifying and fixing any bugs or issues, an organization ensures that the customers receive a product that works well and meets their expectations.
Key Considerations for Mobile Device Testing
Since mobile devices have become an integral part of our daily lives, serving different purposes, ensuring comprehensive mobile device testing is essential. When testing mobile devices, there are a number of key considerations to keep in mind, including:
- Device fragmentation: The mobile device market is highly fragmented, with a wide range of devices running different operating systems and versions of those operating systems. It is crucial to test on a variety of devices to ensure that they work properly on all of the devices that they are expected to be used on.
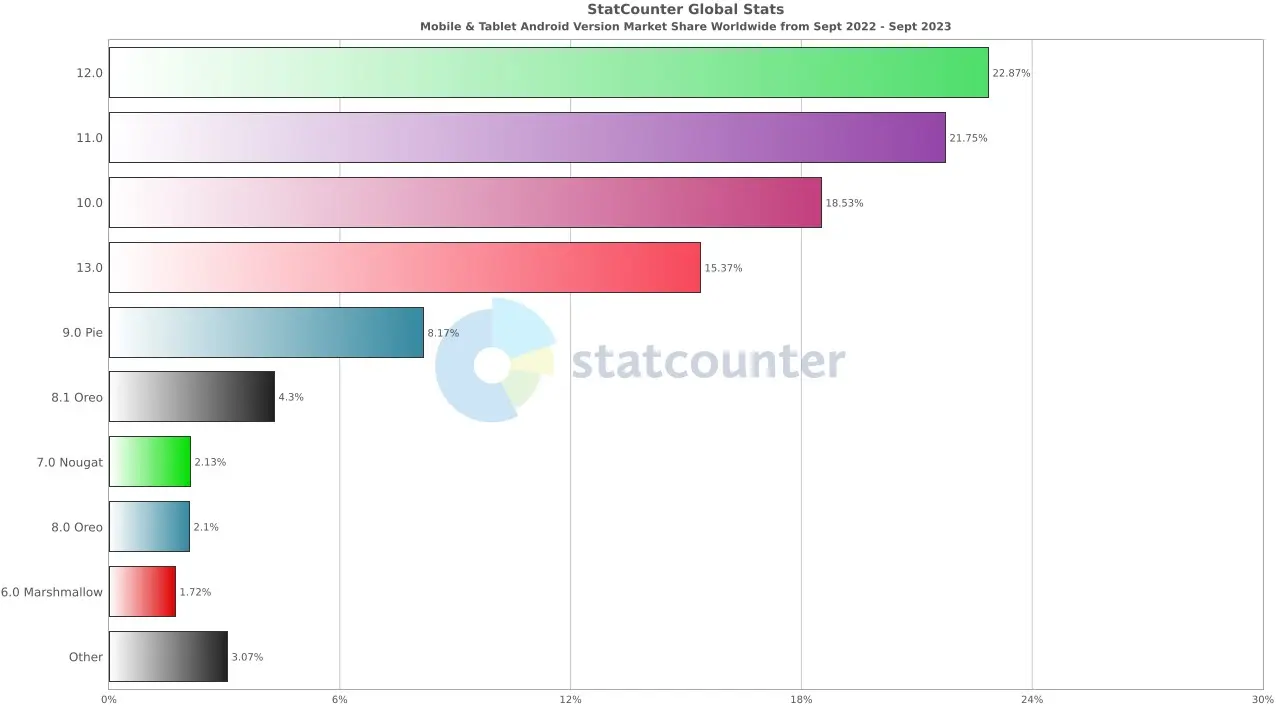
Android Version Market Share
iOS Version Market Share
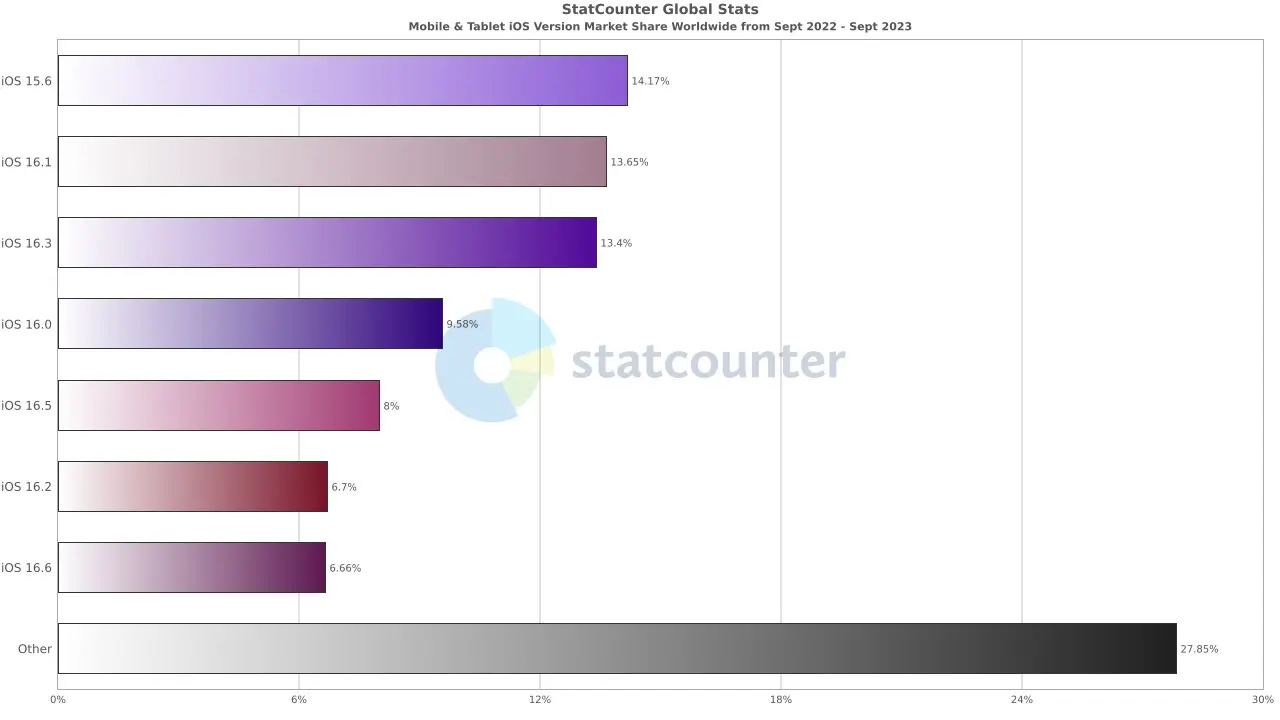
Device fragmentation can be a challenge for mobile app testing, but it also presents an opportunity to improve the quality and compatibility of apps. By testing apps on a wide range of Android and iOS devices and operating systems, testing teams can identify and fix potential compatibility issues early on, ensuring that users have a positive experience with their apps.
- Network connectivity: Mobile devices are often used in a variety of network environments, including Wi-Fi, cellular, and Bluetooth. It is crucial to test mobile devices on different network connections to ensure that they work properly in all of the environments that they are expected to be used in.
- Performance: Mobile devices are used to run a variety of apps, some of which can be quite demanding. It is essential to test the performance of mobile devices to ensure that they can meet the needs of users.
- Battery life: Mobile devices are often used on the go, so it is important to test their battery life to ensure that they can last for a reasonable amount of time on a single charge.
- Security: Mobile devices contain a lot of personal and sensitive data, so it is crucial to test their security to ensure that they are protected from unauthorized access. To ensure your mobile app follows best security practices, you should avoid testing it on rooted devices. Since rooted or jailbroken devices are not representative of the majority of devices that your mobile app will be used on, it is not recommended to test on them.
Other than these considerations, there are a number of other factors that may need to be considered when testing mobile devices, depending on the specific features and functionality of the device.
For example, if the device has a camera, it is important to test the camera's quality and performance. If the device has a GPS receiver, it is important to test the receiver's accuracy. By considering all of the relevant factors, testers can help to ensure that mobile devices are of high quality and meet the needs of users.
Mobile Device Testing Process
The mobile device testing process is a crucial step in ensuring the quality and reliability of mobile devices. It consists of several key phases:
- Test planning: The planning phase involves identifying the specific features and functionalities that need to be tested, as well as the devices and operating systems on which the testing will be performed. Testers also need to consider the target audience and usage scenarios to ensure comprehensive coverage.
- Test case development: Once the test plan is in place, the next step is to develop test cases. Test cases are step-by-step instructions for how to test a particular feature or functionality of the mobile device. They define the actions that testers need to take, the expected outcomes, and the criteria for success.
- Test execution: The test execution phase involves executing the test cases and verifying that the mobile device behaves as expected. Testers may use real devices or emulators/simulators, depending on the testing requirements.
- Defect reporting: If any defects or issues are identified during testing, they need to be reported to the development team promptly. This reporting phase ensures that the problems are addressed before the mobile device is released to users.
- Regression testing: Once the defects have been fixed, regression testing is performed to ensure that the affected features and functionality have been successfully fixed and that no new defects have been introduced.
The mobile device testing process is often iterative. It can be repeated as many times as necessary until all identified defects have been fixed, and the mobile device meets the predetermined quality standards. This iterative approach ensures that the mobile device is thoroughly tested.
Throughout the entire process, documentation is key. Testers maintain detailed records of test cases, test results, defect reports, and any other relevant information. Effective communication between testers and developers is essential to address issues and make necessary improvements.
By following a rigorous mobile device testing process, organizations can deliver reliable and user-friendly products to customers.
Note : Test your apps on real Android and iOS devices. Try LambdaTest Today
Mobile Device vs. Mobile Application Testing
In this section, we will list the difference between mobile device testing and mobile app testing.
| Aspect | Mobile Device Testing | Mobile Application Testing |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Evaluates the entire mobile device, including hardware and software components. | Concentrates on testing individual mobile applications. |
| Scope | Broader scope covering the device's functionality, hardware, and compatibility. | A narrower scope focused on the specific features and functions of a single application. |
| Objectives | Ensures the overall functionality, performance, and compatibility of the mobile device. | Verifies the functionality, usability, and performance of a single mobile application. |
| Tools and Equipment | Utilizes various testing equipment to assess hardware components like the camera, microphone, and sensors. | Uses emulators, simulators, real devices, and testing frameworks to evaluate the application's behavior on different devices. |
| Compatibility Testing | Ensures the mobile device is compatible with various mobile applications. | Check whether the application is compatible with different mobile devices and operating systems. |
| Hardware Testing | Focuses on evaluating hardware components like battery life, screen responsiveness, and network connectivity. | Typically, it is not concerned with hardware-specific testing as it concentrates on mobile app functionality. |
| Network and Connectivity | Tests the device's ability to connect to different networks, including Wi-Fi, cellular data, and Bluetooth. | Emphasizes the application's behavior with regard to network connections and data transfer. |
| Testing Complexity | Generally more complex due to the diverse range of hardware and software elements to be tested. | Often less complex as it focuses on a single application and its interactions. |
| Testing Phases | Typically performed in various stages, including factory testing, compatibility testing, and certification testing. | Mainly carried out during the development and quality assurance phases of the application's life cycle. |
Selecting the Right Mobile Devices for Testing
When testing mobile applications, it's crucial to use a diverse range of devices that cover various screen sizes, resolutions, and hardware specifications. This approach ensures that your app is compatible with as many devices as possible.
To make the best choices for mobile device testing, you need to consider factors like market share, screen size, resolution, and processing power. It's also a good idea to include devices from different manufacturers to ensure compatibility across various mobile interfaces.
Here's a list of some top mobile devices for app testing, along with their key parameters:
- Global traffic volume of website or app from device: Use analytics tools to determine which devices people use most when accessing your app or website. This will help you focus on testing those devices, so everyone has a great experience.
- OS versions: Test your app on different versions of mobile operating systems so that it will work adequately on many different devices. Consider testing on at least the two most recent versions of mobile OS, as well as any older versions that are still widely used.
- Screen sizes: Smartphones come in all sizes, so it is essential to check how your app looks and works on different screen sizes. Consider testing on a range of screen sizes, from small smartphones to large tablets.
- Keep track of upcoming mobile devices: Keep an eye on upcoming releases of mobile devices and consider including them in your testing matrix to ensure your app is compatible with the latest devices.
- Launch year of mobile device: It is vital to test your app on phones from different years to ensure it runs properly on older and newer models.
- Manufacturers: Testing your app on smartphones from different manufacturers can help ensure it works with all the different versions of mobile OS and their unique looks. Consider testing on devices from a variety of manufacturers, including Samsung, Google, and iPhones.
How to Test Apps on Multiple Mobile Devices?
Testing your mobile app on multiple devices is crucial to ensuring its quality, functionality, and compatibility. However, it can also be challenging, time-consuming, and expensive to acquire and manage a large fleet of physical devices.
Fortunately, several tools and platforms can help you test your mobile app on different platforms, screen sizes, and operating systems without breaking the bank.
- Emulators and Simulators: Emulators and simulators are software applications that mimic the behavior and appearance of real devices on your computer. They are a great way to test your app on a variety of devices without having to purchase them all. However, it is important to note that emulators and simulators cannot perfectly replicate the real-world experience, so testing your app on various physical devices is important.
- Device labs: Device labs are centers that house a large collection of physical devices, such as smartphones and tablets for testing mobile apps. These labs can be either owned and operated by the organization using them (on-premises device labs) or provided by a third-party organization or community (shared device labs).
While device labs offer several advantages, such as the ability to test apps on real devices in real environments, they also have some challenges, such as high cost, low efficiency, and high maintenance.
- Cloud-based testing platforms: Cloud-based testing platforms provide access to a large pool of real devices you can use to test an app. This can be a great way to test mobile apps on various devices without purchasing or managing them yourself. However, it is important to note that cloud-based testing platforms can be expensive, so it is important to compare pricing and features before choosing one.
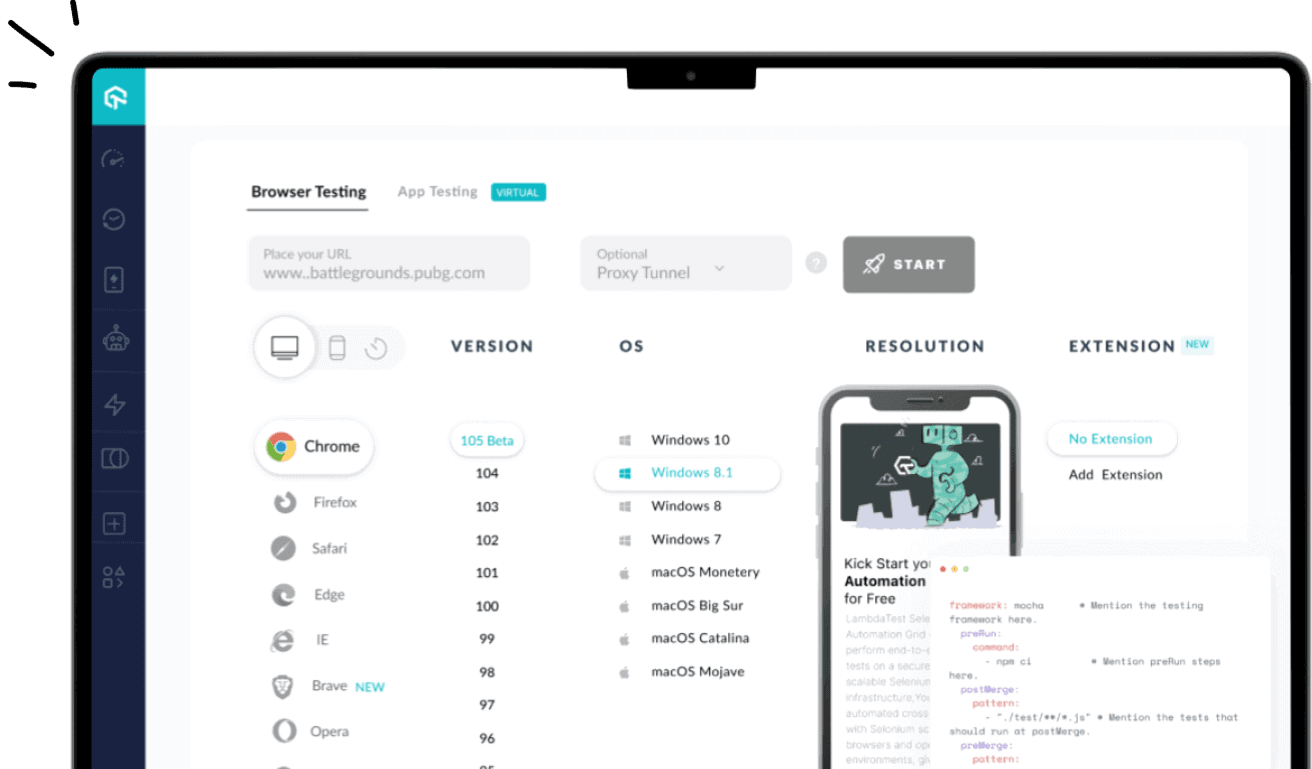
One cost-effective and affordable approach to testing your apps on different mobile devices is to use a mobile device testing lab offered by cloud-based testing platforms like LambdaTest.
LambdaTest is an AI-powered test orchestration and execution platform to perform mobile app testing on a real device cloud and a virtual device cloud of Android emulators and iOS simulators. You can choose from a wide array of the Android and iOS mobile devices from renowned manufacturers such as Apple, Samsung, OnePlus, Pixel, and more for instant website or app testing. This means that teams do not need to worry about maintaining expensive Android and iOS device labs.
Catch up on the latest mobile app testing tutorial around Appium automation, real-time app testing, and more. Subscribe to the LambdaTest YouTube Channel for quick updates.
Additionally, LambdaTest also offers integrations with popular test automation frameworks like Appium, Espresso, XCUITest, and others to facilitate comprehensive testing. LambdaTest online device cloud is consistently updated with the latest devices allowing you to test apps on the devices that your customers are most likely to use, which also includes the latest iPhone 15 and Google Pixel 8 Series.
We also recommend checking out this article - Android Device Statistics, to keep yourself updated with the latest Android device stats and popular Android devices to test your mobile apps.
Best Practices for Mobile Device Testing
Here are a few best practices for mobile device testing:
- Start with a plan: What exactly are you testing? What features and functionality are most important to your users? What devices and operating systems do you need to test on? Once you have a clear understanding of what you need to test, you can create a test plan that outlines your testing strategy.
- Test on real mobile devices: Emulators and simulators can be useful for some types of testing, but it's crucial to test your app on real devices as well. This is because emulators and simulators can't always accurately replicate the real-world experience.
- Use a variety of devices and operating systems: Don't just test your app on the latest devices. Test it on a variety of devices and operating systems that your users are likely to be using. This includes legacy devices as well.
- Test on different network conditions: Your app will be used on a variety of different networks, so it's important to test it under different network conditions. This includes testing on Wi-Fi, cellular networks, and slow networks.
- Test the user experience: It's not just about making sure your app works correctly. You also need to make sure that it's easy to use and enjoyable for your users. Test the user experience by having real users test your app and provide feedback.
- Test early and often: Don't wait until the last minute to start testing your app. Test it early and often throughout the development process. This will help you to identify and fix bugs early on.
- Use automation testing: Automation testing can help you to save time and money by automating the process of testing your app. There are a number of automation testing tools available, both free and paid.
- Continue testing after release: Don't stop testing your app once you released it. Continue to test it regularly to identify and fix any bugs that may be introduced in future updates.
Conclusion
In conclusion, mobile device testing is an indispensable part of the ever-evolving mobile technology landscape.
As our reliance on smartphones and tablets continues to grow, ensuring these devices function seamlessly becomes crucial. Through rigorous testing, we can guarantee not only the reliability of the devices themselves but also the quality of the apps and services that enrich our daily lives. Mobile device testing is a pivotal approach in mobile testing, enabling us to stay connected, productive, and entertained in our fast-paced digital world.
On this page
- Overview
- What is a Mobile Device?
- Types of Mobile Devices
- What is Mobile Device Testing?
- Why is Mobile Device Testing Important?
- Types of Mobile Device Testing
- Role of Device Under Test (DUT)
- Key Considerations for Mobile Device Testing
- Mobile Device Testing Process
- Mobile Device vs. Mobile Application Testing
- Selecting Right Mobile Devices
- How to Test Apps on Multiple Devices?
- Best Practices for Mobile Device Testing
- Frequently Asked Questions
Frequently asked questions
- General
Author's Profile

Salman Khan
Salman works as a Digital Marketing Manager at LambdaTest. With over four years in the software testing domain, he brings a wealth of experience to his role of reviewing blogs, learning hubs, product updates, and documentation write-ups. Holding a Master's degree (M.Tech) in Computer Science, Salman's expertise extends to various areas including web development, software testing (including automation testing and mobile app testing), CSS, and more.
Reviewer's Profile

Shahzeb Hoda
Shahzeb currently holds the position of Senior Product Marketing Manager at LambdaTest and brings a wealth of experience spanning over a decade in Quality Engineering, Security, and E-Learning domains. Over the course of his 3-year tenure at LambdaTest, he actively contributes to the review process of blogs, learning hubs, and product updates. With a Master's degree (M.Tech) in Computer Science and a seasoned expert in the technology domain, he possesses extensive knowledge spanning diverse areas of web development and software testing, including automation testing, DevOps, continuous testing, and beyond.
Did you find this page helpful?
More Hubs
Try LambdaTest Now !!
Get 100 minutes of automation test minutes FREE!!
 Christmas Deal is on: Save 25% off on select annual plans for 1st year.
Christmas Deal is on: Save 25% off on select annual plans for 1st year.