- Automation
- Home
- /
- Learning Hub
- /
- Mobile App Testing Tutorial
- -
- April 17 2023
Mobile App Testing Tutorial: A Comprehensive Guide With Examples And Best Practices
Learn how to unearth hidden bugs and optimize your mobile apps with this comprehensive mobile app testing tutorial
Total Chapters (14)
Chapter 1 : Mobile App Testing Tutorial
OVERVIEW
Mobile app testing is the process that involves checking and verifying the functionality and quality of the mobile app. In other words, with mobile app testing, you can ensure that the mobile app meets all the end-users and technical requirements before its release in the market (App Store for iOS devices and Play Store for all Google or Android-based handheld devices). Every developed mobile app for handheld devices undergoes tests to check them for functionality, usability, and stability.
For a long time, mobile device uses are not just limited to communication but have also expanded to perform our daily life activities. Such dependency on mobile devices has increased rapidly due to the development of various mobile apps. These apps can perform multiple activities in our everyday life and help achieve business requirements.
Organizations are now turning to mobile apps as a significant means of expanding their business and reaching out to their audiences. The rapid development of mobile web, hybrid, and native apps has made mobile app testing a vital part of the app development process.
According to Statista - the number of mobile devices is expected to reach 18.22 billion by 2025.
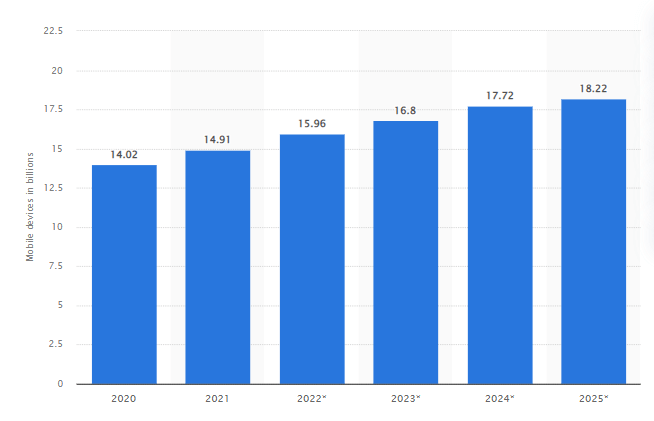
Due to the surge in mobile devices, the demand for mobile apps has grown substantially worldwide. Another survey shows that the global mobile app market is booming, with revenue expected to reach $613 billion by 2025.
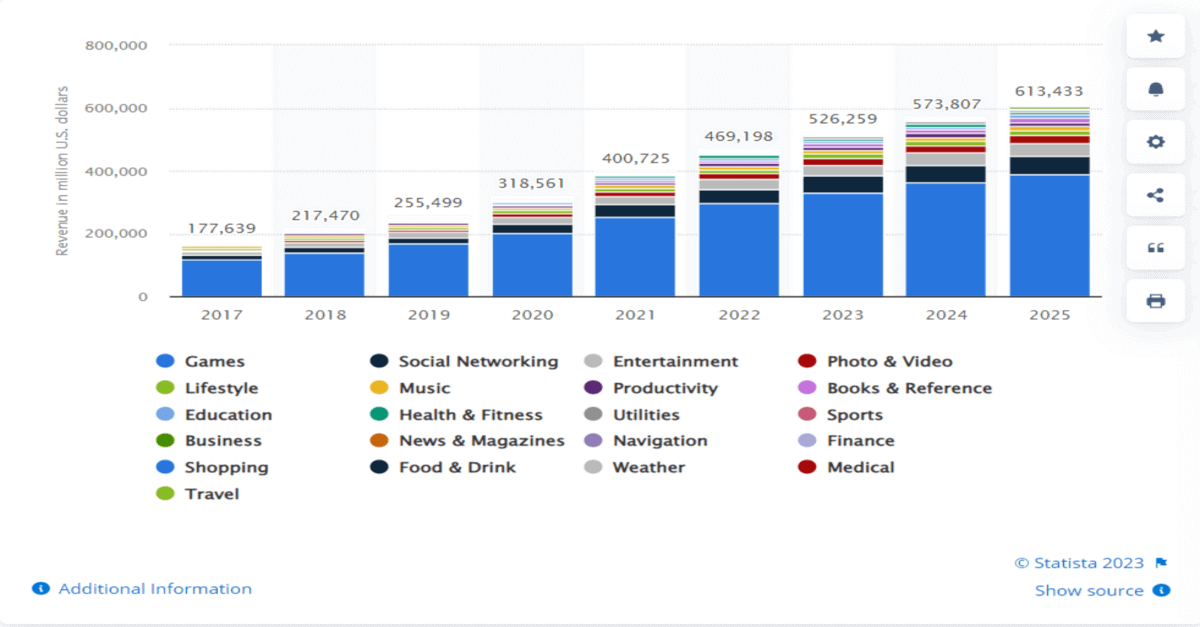
Hence, ensuring that an app delivers a consistent experience across all devices and OS versions is important. This is where mobile app testing helps teams to test apps on multiple devices and operating systems for functionality, usability, and consistency
What is Mobile App Testing?
Mobile application or app testing is the process by which developed mobile apps are tested for their usability, performance, security, and functionality. Performing mobile app testing helps ensure that it aligns with technical and business requirements.
Testing a mobile app often involves looking through its functional and non-functional components. Additionally, it is put to the test by highly qualified professionals for consistency, usability, performance, and compatibility with different platforms and devices. The number of mobile app downloads in 2022 was 255 billion, emphasizing the need to deploy carefully thought-out apps to grab users' attention.
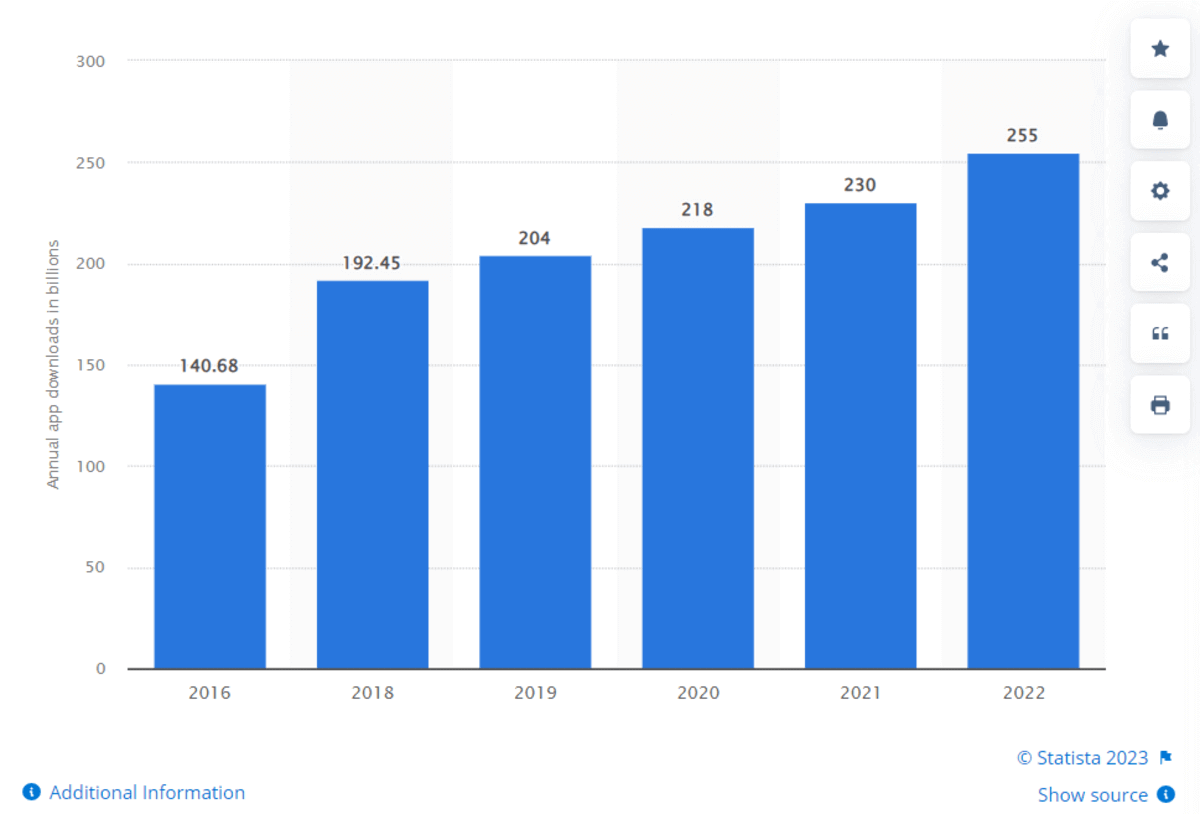
Considering the high demand for mobile apps, it is crucial to ensure their correct functioning before they are released in the market. This is achieved by performing mobile app testing involving functional, security, and performance testing activities.
Through the implementation of various testing approaches, mobile apps are tested across numerous screen resolutions, devices, OS versions, and network bandwidths. Not only this, the compatibility of mobile apps, their security, user experience, and performance are also tested in mobile app testing.
In the development of mobile apps, mobile app testing is a crucial part that identifies the issues and ensures their early fixes. This gives a better user experience, increases user satisfaction, and lowers the risk of negative reviews, loss of revenues, and app abandonment. Hence, businesses and developers need to prioritize mobile app testing to ensure that mobile apps are of high quality and meet user expectations.
In the next section of the mobile app testing tutorial, let’s look at the importance of testing mobile apps.
Why Mobile App Testing?
The primary goal of developing mobile apps is to expand the business and reach the maximum number of users worldwide. However, what if developed mobile apps are faulty and difficult to use by the user? There is a high chance that the users will uninstall the mobile apps. This is something any business would not want their end user to uninstall the mobile apps and switch to their competitors. Here, mobile app testing is highly significant as it gives information on the app's functionality.
To ensure that mobile apps meet end-user requirements and goals, adequate and robust mobile app testing is important. However, if the mobile apps are not tested, there is a high probability of a prevalence of bugs or errors that may disrupt the functionality of the apps. This gives a bad user experience; they may delete or uninstall an app. Therefore, mobile app testing is an important process that should not be missed.
When you perform mobile app testing, you can find potential bugs and errors that can impact the functionality and performance of the mobile apps. Those errors and bugs could be fixed at the earliest, giving end-user satisfaction with the mobile apps. Therefore, it is essential that mobile apps are tested entirely before they are released to the end users to ensure that they are reliable, secure, and user-friendly.
Types of Mobile Apps
In this section of the mobile app testing tutorial, we will discuss different types of mobile applications.
To perform mobile application testing, you first need to understand what mobile apps are and how they differ from websites or web pages.
A mobile app is a software designed to run on mobile devices such as smartphones, tablets, and wearable devices. App shops or mobile marketplaces run by the device's operating system provider, such as Apple's App Store or Google Play Store, are where most mobile apps are downloaded. There are three main types of mobile apps:
- Web apps: A web app is a website that one can visit via a desktop or mobile browser. Online web apps are less expensive than mobile apps. They are also less challenging to build and maintain.
- Native apps: Native applications are made specifically to run on a single operating system. As a result, native apps are available for Android, iOS, and Windows. This prevents native Android apps from being used on iOS, Windows, or vice versa.
- Hybrid apps: Hybrid apps integrate elements of native and web apps. These apps provide developers the freedom to reuse code across a range of platforms and operating systems with minimal to no script modifications
You can refer to our earlier mobile app testing tutorial on web vs hybrid vs native apps to learn more about it.
Mobile App Testing vs. Web App Testing
In this mobile app testing tutorial, as we explain mobile app testing, you might think about its similar terms, web app testing. You should know about interrelated terms in software testing, including mobile app testing and web app testing. The difference between the two is based on their purpose, intended users, and complexity. Let us see this in detail in the below-given table.
| Mobile App Testing | Web App Testing |
|---|---|
| Test the mobile apps mainly for devices with smaller resolutions like tablets. | Test the web apps for larger screen resolution. |
| Performing mobile app testing is challenging because of the huge complexity of mobile apps. | Web app testing is comparatively easier. |
| The test is performed on different combinations of device configurations like OS, hardware configurations and resolutions, and others. | Web apps are tested across various browser versions and OS combinations. |
| One of the major dependencies of mobile devices is that it requires power, and drainage of the battery is a major concern. Therefore, a test of mobile apps should be done on fully charged and drained mobile devices. | There is no such dependency on web app testing as it mainly relies on browsers. |
| Testing is done based on the device's interaction with user actions like noise and gestures. This is needed in mobile app testing because different mobiles allow users to interact with diverse applications. | Web browsers have limited options to interact with user actions. Therefore, the scope of testing is less. |
| Currently, mobile apps are accessible to other peripheral devices associated with mobile like pacemakers. Therefore, mobile app testing also needs to be performed on these devices. | Web apps are mainly accessed on browsers. However, other peripheral devices like a webcam and controller are used. But, they are not used on a large scale. |
| Some commonly used tools for mobile apps are Appium, Espresso, XCUITest, etc. | Some widely used tools for web apps are LambdaTest, Selenium, Cypress, and others. |
Test your web and native apps on real devices. Try LambdaTest Now!
Benefits of Mobile App Testing
Mobile app testing is a crucial part of the development process that the testers perform with utmost adequacy. If you want to get started with mobile app testing, you should know its benefits so you don’t miss this crucial process. Some of the benefits of mobile app testing are mentioned below:
Ensure User Interface (UI)/ User Experience (UX) Usability
App testing allows the testers to test applications according to the end-user perspective. They check the mobile app's usability and user-friendliness by simulating typical users' behavior and testing their look and feel. Testers identify any navigation issues and logical flow and test mobile apps on different devices and screen sizes by performing mobile app testing. This helps to evaluate the UI/UX usability of the mobile app.
Ensure proper functioning
Mobile app testing allows checking mobile app performance and functions without any errors, issues, or glitches. For example, testers can find out whether users can successfully download the app to multiple devices. Or whether the mobile app interacts with supported infrastructure. Hence, you can verify the seamless functioning of the mobile app with mobile app testing.
High end-user loyalty
When you get assured of mobile apps' usability, functioning, and performance, it tends to provide a positive end-user experience. End-users are more likely to use the app and recommend it to their friend leading to a good reputation and high revenues in the software industry.
Identify security vulnerabilities
Mobile app testing is also performed to verify and check any security vulnerabilities in the mobile apps, like data leaks or unauthorized access. Thus, one of the major benefits of app testing is to prevent any potential data breaches and security-related issues.
Lower mobile app development cost
You can easily and early identify errors or bugs in the mobile app during its development process. This further ensures that they are fixed at an early stage and prevents the high cost of fixing bugs later.
In the next section of the mobile app testing tutorial, we will discuss different mobile app testing types.
Types of Mobile App Testing
In mobile app testing, applications must be tested for usability and functionality to give a seamless experience. Testing of mobile apps is not just limited to single-type testing; rather, various types of tests are performed to ensure the complete quality of the mobile app. This ensures that each mobile app aspect, feature, and component are tested.
In this section of the mobile app testing tutorial, we discuss some different types of mobile app tests:
Functional Testing
Functional Testing in mobile app testing determines whether an app functions properly. This type of test verifies that the components are functioning properly, are responsive, faithful to their intended use, adhere to the requirements, and preserve the app's flow.
Some of the different types of functional testing are
- Unit testing: In this method, individual components or modules of mobile apps are tested to ensure they meet expected behavior and functionality.
- Smoke testing: It is the testing method where a set of critical functionalities of mobile apps are tested to ensure that the application is stable and ready for further testing. You can perform smoke testing after the release of the build and find issues that may prevent further testing or deployment.
- Regression testing: It is the testing method that helps to ensure that the existing function of the mobile app is not affected by any changes made to the codebase. It detects new code issues and ensures that previously fixed issues have not been reintroduced.
- Sanity testing: It allows verification of critical functions of the mobile apps rather than testing the entire application.
- Integration testing: The integration testing method checks the performance of the mobile app's different integrated modules and components. For example, you test the user interface, database, network communication, and third-party libraries and their seamless integration
Non-Functional Testing
Non-functional testing involves validating the non-functional aspects of mobile applications like performance, reliability, and utility. It also evaluates the system readiness for non-functional parameters that aren't addressed in functional testing.
- Compatibility testing: It is a non-functional technique to determine whether an application is prepared to perform flawlessly on various hardware configurations, operating systems, and devices.
- Forward compatibility testing: In this testing type, you can ensure the working of mobile apps is according to the newer version of the OS or different components on which they are intended to run. For example, suppose any mobile app is developed to run on Android 10; with a forward compatibility test, you will test the working when the device is updated to Android 11.
- Backward compatibility testing: In this testing type, you can ensure the working of the mobile app is correct with the old version of the OS or different components on which they are intended to run. Suppose a mobile app is developed to run on Android 10; here, you will test its working on Android 9.
- Usability Testing: The user's experience is prioritized through usability testing. It determines whether a mobile app needs issues patches, how user-friendly it is, and how simple it is to navigate around its UI. Usability testing offers a comprehensive report on a user's experiences with the application.
- Response speed
- Work in multitasking mode
- Logic of navigation
- Layout
- Resume and termination in the same state
- Look and size of buttons and icons
- Text clarity
- Performance and Load Testing: Performance testing and load testing ensure that an app functions properly when subjected to specified workloads. Furthermore, these tests show that device resources like power, time, and memory are not being used to their full potential.
- Stress testing: It involves testing mobile apps and verifying their function under the huge workload stress to define their breaking points. Stress testing is done to check how mobile apps can handle expected traffic and data processing load without being crashed.
- Spike testing: This involves testing mobile apps to check how they handle sudden and unexpected spikes in user traffic. It is done by simulating sudden increases in user traffic to evaluate their behavior and performance under such situations.
- Scalability testing: It involves testing mobile apps for their ability to handle increases in user load over time. In other words, you can test how the app handles additional users and data processing without affecting its performance.
- Endurance testing: It tests the mobile app to check its ability to handle the sustained workload over an extended period. The main goal of endurance testing is to find any performance issue which occurs when they run for a long time, like memory leaks or slow response times.
- Volume testing: It tests mobile apps to check their ability to manage large volumes of data. For example, you can identify performance issues in mobile apps due to a large amount of data like database performance, server capacity, etc.
- Load testing: It tests the mobile apps' performance by giving the expected user load. For example, you can easily find performance issues that arise when the mobile app is under normal operating conditions, like slow response time.
- Security Testing: Security testing in mobile app testing plays a major role in application usage and download. If users do not feel secure while using applications, there is a 100% chance they will remove applications from their devices.
- Risk assessment: You can identify potential risks associated with security and further classify them as per their severity level.
- Ethical hacking: In this type of testing, you make authorized attempts to penetrate mobile apps to find any security vulnerabilities.
- Penetration testing: In this test, you simulate attempting to attack mobile apps and check for underlying vulnerabilities by gaining access to data and others. In simple terms, it is similar to ethical hacking, but it is done to see how far an attacker could get into the app and what damage they could do.
- Security scanning: Here, you scan the mobile app to find any potential vulnerabilities and give recommendations to solve the identified error.
- Vulnerability scanning: You use automated tools to scan mobile apps to check for any issues known to be exploited by attackers.
- Security auditing: You systematically review the mobile app and its code to find any flaws.
- Posture assessment: It includes different types of security testing like ethical hacking, security scanning, and risk assessment to comprehensively assess the mobile app's security posture. It ensures how the mobile app works against security threats and attacks.
- Installation Testing: As users need to install an app to use it, installation testing comes into the picture. Installation testing determines whether an app's installation and uninstalling methods are simple.
- Localization Testing: Localization testing guarantees an app is ready for use in various local markets. An app should ideally be able to manage everything from currency changes to cultural changes, especially if it targets a diverse demographic of people worldwide.
- Exploratory Testing: It checks and verifies various functionality and usability of the mobile app. It is done to find errors and ensure the expected working of the mobile app.
- Storage Testing: It is the testing type that verifies and checks the mobile app’s performance related to its storage-related function. Some examples of storage-related functionalities include the app can store data on the device's storage system, retrieve data from the storage system quickly and accurately, delete data from the device's storage system correctly, and the app behaves when there is low or no storage available on the device.
- Interrupt Testing: A mobile app user gets many interruptions each day from push notifications which can be annoying, like low/full battery, alarm, push notifications, incoming call/SMS, etc. To this, an interrupted test is performed to analyze the disturbance due to interruption and resolve it optimizes the user experience. For this, QA analysts consider user Interface issues and related performance issues while executing interrupt testing.
- Input Testing: It is the type of test performed by executing various input actions on devices to check the functionality of mobile apps. It is done to find how effectively mobile apps handle such actions and user interaction. Some examples of input testing that a tester performs to test mobile apps:
- Multi-finger inputs: It involves testing finger gestures supported by the apps, such as pinch, zoom, swipe, tap, double-tap, and long press.
- Voice inputs: Mobile apps are tested to check whether the app can process voice inputs correctly, even in the presence of external noise.
- Sensor inputs: It involves testing several sensors on the mobile device, such as the ambient light sensor, acceleration sensor, proximity sensor, gyroscope, pressure sensor, magnetic sensor, temperature sensor, and humidity sensor.
- Device Testing: Many apps' functions rely heavily on a mobile device's internal hardware specs and operating system. Device testing ensures an app is ready to run on various devices with varying specifications.
- Battery Usage Testing: Here, you check the mobile app without excessively draining the device’s battery. You perform tests for mobile apps’ power consumption under different conditions, like while the app is in use or standby mode.
- Installations & Update Testing: You check whether the mobile app can be installed or updated smoothly on the device.
- Hardware Specific Testing: It checks the mobile app compatibility with diverse hardware configurations like screen size.
- Standby Testing: You test mobile app behavior when the device is in standby mode. It is crucial to be executed to check how quickly and smoothly mobile apps resume normal function when the device is awakened from standby mode.
- Beta Testing: You test the mobile app in a real-world environment and gain feedback from the performance, functionality, and user experience of the mobile app. Such feedback is addressed to improve the mobile app before its release
There are two types of compatibility testing:
It helps verification of following elements of mobile apps:
There are different types of performance testing:
In security testing, you can verify the cookies, protect against attacks, file caching, logins and passwords, and an encryption system.
Different types of security tests can be performed to verify above mentioned aspects in mobile apps. Some of those are as follows:
Apart from the above testing approach, some of the other testing types which should be performed to check the functionality of the mobile app include:
In the next section of the mobile app testing tutorial, we will learn about creating a mobile app testing strategy.
Creating Mobile App Testing Strategy
Every app success story has a key ingredient: a pleasant user experience. As a result, most successful apps have a thorough testing process and plan to ensure that the app is delivered with the greatest possible quality. And this quality should be uniform for all users, regardless of device. As a result, you must test your app on all popular devices that your users can use. That is why you will need to create a top-notch strategy for mobile application testing.
In this section of the mobile app testing tutorial, let’s look at some factors you should keep in mind while building an app testing strategy:
Decide your device before you start testing
Achieving comprehensive device compatibility in mobile software testing is an impractical task because it is infeasible to test your app on all existing devices. Therefore it is crucial to review documentation and identify the specific Android versions required for your features to function correctly. This allows you to create a reliable matrix of devices compatible with your application. You can decide on the device with the following steps:
- Market share
Market share will assist you in determining which devices must be included in the matrix. The same is true for operating systems. Many customers are stuck on outdated versions since mobile devices are expensive and manufacturers rarely deliver more than three major updates. As a result, assuming that most individuals are using the most recent Android versions can be inaccurate.
This is also obvious in the graph below:
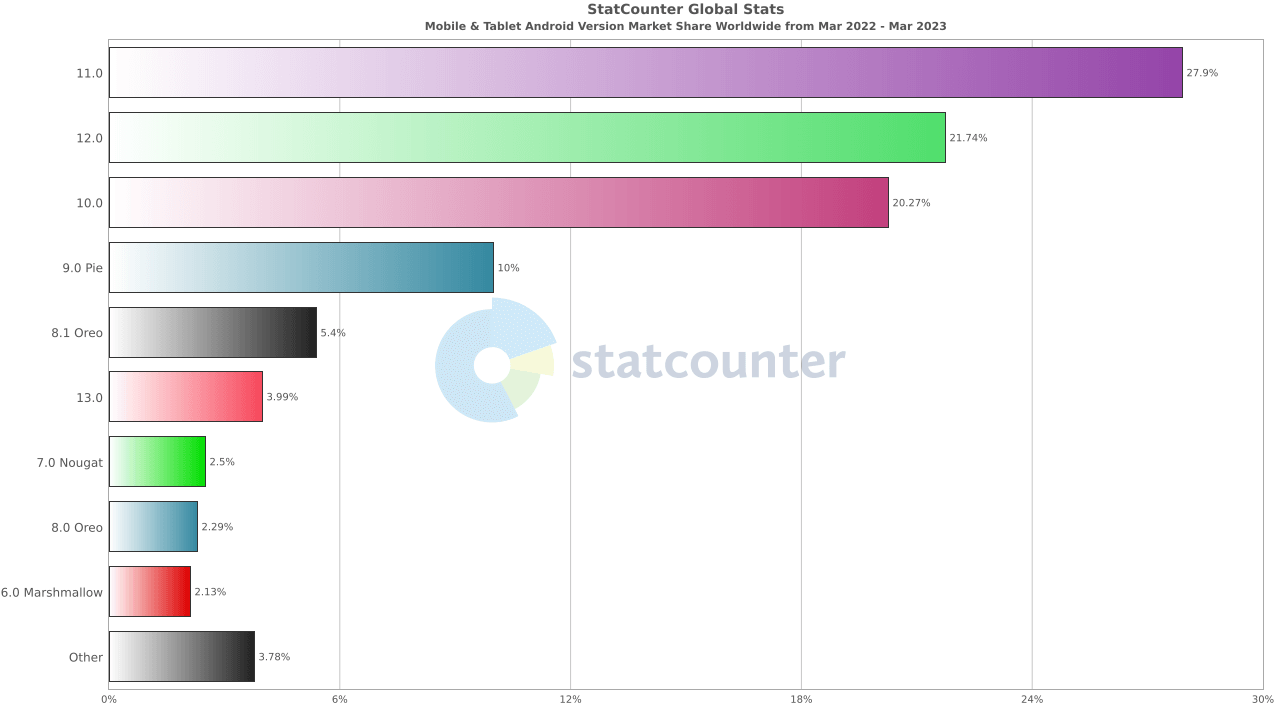
Google Analytics
Google Analytics statistics help you to determine which devices are most likely to access your app. This option is helpful if you already have a website and are transitioning to a mobile app. If available, you can also look at your competitors' analytics.
Having a good grasp of the tools
Tool is the mediator of your test script and mobile apps, so having a thorough understanding of tools will give certainty to the test quality. To understand which tools will be suitable for your project, you can follow the below strategy:
- Manage your requirements: Even though there are various tools with many similar functions, it is mandatory to accept that all tools are different. The best strategy to eliminate many tools from the pool is to organize the project's required criteria. This can differ depending on the project you're working on (the mobile app).
- Evaluate your team skills: Once the criteria have been defined and categorized, the following stage is to analyze your team and their talents. The ideal approach is always to use the tools that your team is most comfortable with.
- Take a look at current tools and frameworks: Current tools and frameworks provide a few options for optimizing your mobile app strategy. If your software project has already been tested, your team is already familiar with the tool's issues. You can either brainstorm this with your teammates or decide whether continuing to use the same tool is the best option for you
Prioritize Documentation
Documentation is an essential step in enhancing your testing strategy and other areas of software development. The same is true for testing mobile apps. While documentation is not a key component of "testing" or "coding," it is as vital as developing a mobile app testing plan.
Here are some relevant important document projects for mobile application testing:
- Document containing the software requirement specifications
- Documentation for test design
- Specification of test cases
- Specification of the testing technique
- Test strategy reports on test results
- Documentation for the test log
- Documentation for the test plan
- Documentation of bug reporting
- Documentation of test data
- Report on a test incident or an issue
- Analyses of tests
Cross-platform testing
The same tests may be performed on Android and iOS applications using cross-platform mobile app testing tools and frameworks. It is an excellent strategy because of the time it saves.
With single test scripts in place, you can edit the tests in a single location and concentrate on developing new test scripts rather than writing duplicates. Using such frameworks will also assist you in decreasing future work.
Define the scope of automation testing
To reduce time and minimize repetitive work, automated testing is implemented into the Software Development Life Cycle. But, to achieve these objectives, we must first decide what we will leave to the system and what we will manage ourselves. To put it another way, how should we separate our automation tests to maximize productivity while testing a mobile app?
Deciding how to separate automation testing is usually dependent on the project. Each project has its uniqueness and demands. Hence, before you begin, carefully divide your tests into different portions, as these may continue as your mobile app goes through consecutive updates.
That was a brief summary of the strategy. However, you can learn in detail each step in our dedicated mobile app testing tutorial on strategizing mobile app testing.
Difference between Emulator, Simulator, and Real Device
The method used to execute the tests is an integral part of developing a solid testing regime. As a result, when performed on different devices, the demanding testing procedures can produce varied findings.
In this section of the mobile app testing tutorial, let's take a closer look at the difference between emulator, simulator, and real device for mobile app testing to gain a better understanding.
Emulator-based app testing
A mobile app emulator is a virtual platform that duplicates an Android handset on your computer, making mobile software testing easier. As a result, you can test Android apk files without a physical device by using an online APK emulator.
Simulator-based app testing
A simulator is a virtual platform that emulates the iOS operating system and executes the program on the specified Apple device (e.g., iPhone app emulator) by taking over the computer's operating system without the requirement for a physical device. Utilizing a simulator helps you to execute iOS app testing quickly.
Real device-based app testing
It is critical to test a website on various devices to ensure that it is compatible with multiple screen sizes, resolutions, operating systems, and browsers. Testing on real devices allows testers to find issues that may otherwise go undetected when testing on emulators or virtual computers
| Feature | Real Device | Emulator/Simulator |
|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | As it tests on real hardware and software, it produces the most accurate results. | Mimics the behavior of the gadget, it may not deliver accurate results. |
| Performance | It correctly tests performance since it uses actual hardware and software. | Performance is relatively low compared to real devices. |
| Cost | It is usually the most expensive option because it necessitates the purchase of physical devices. | Because they use programs that emulate or simulate devices, it is free or low-cost. |
| Set up | Setup of the real device is required, and manual testing may be required. | Easy to set up |
| Availability | It has limited availability | Emulators and Simulators for the majority of popular devices that are widely available. |
In the next section of the mobile app testing tutorial, we will discuss different approaches to mobile app testing.
Approaches to Mobile App Testing
Knowing the correct strategy to perform mobile app testing, you may think about the different techniques that can be leveraged to execute tests. Mobile app testing can be achieved by two different approaches: manual testing and automation testing.
However, both approaches exist with advantages and disadvantages. Hence, a combination of both approaches is used to perform mobile application testing.
In this section of the mobile app testing tutorial, let us learn about these approaches specifically.
Manual Testing
As the name suggests, manual testing is a test approach executed manually without any automated procedure. It is dependent on human input in testing the features and functionality for quality assurance. Here, the manual testers manually execute the test case, record the result, and identify any potential bugs.
In manual app testing, testers test the application from the user’s perception and check its usability and performance. Even though manual testing is an error-prone approach, it should be ignored because it simulates real-world scenarios that automated testing cannot replicate.
When should you prefer manual testing?
- When you perform exploratory testing, usability testing, and ad hoc testing
- When you execute device compatibility and UI interaction
Automation Testing
In automation testing, test tools are used to execute the test cases with little human intervention. You can run as many test plans for a mobile app, which increases the test coverage. However, you should consider only automating test cases that are easily executable, have expected results, and are impossible to do manually.
When should you prefer automation testing?
- It is best for regression testing, repetitive tasks, and performance testing.
- Complex mobile app
Mobile App Testing Frameworks
This section of the mobile app testing tutorial discusses frameworks used for mobile application testing.
Various mobile app testing frameworks have different functionality, making it difficult for the app tester to choose the right one for the situation. In this mobile app testing tutorial, we have three main divisions of mobile testing frameworks, as mentioned below:
Android Testing Frameworks
Here is a list of some best Android testing frameworks for mobile testing, such as
- Espresso: It is an open-source UI testing framework for Android applications. It allows fast and easy writing of the test through its easy-to-read syntax. It integrates seamlessly with Android Studio and supports different testing scenarios like testing UI elements, verifying user flows, and handling asynchronous operations.
- Selendroid: It is an open-source mobile testing framework supporting Android and iOS applications. One of the advanced features of Selendroid is that it tests mobile apps across multiple devices and interacts with native apps. You can write tests in different programming languages like C#, Python, and Java.
- Robotium: It is an open-source mobile testing framework supporting Android applications. You can write tests in Java through concise and easy-to-read syntax. Also, it is highly configurable and provides an easy-to-use API for writing tests.
- MonkeyRunner: It is an open-source mobile testing framework that automates UI testing for Android applications. It integrates with a range of testing tools such as Eclipse, Android Studio, and Maven, making it easy to incorporate into existing testing frameworks
iOS Testing Frameworks
Below are the app testing frameworks for iOS mobile applications.
- XCUITest: It is Apple’s native UI testing framework for iOS applications which allows fast and reliable testing with supporting different testing scenarios like performance testing and functional testing. You can write tests in Swift and Objective-C, and it offers an easy-to-use API that integrates seamlessly with Xcode.
- XCTest: It is a test framework that allows writing unit and integration tests in macOS and iOS applications. Its most amazing features are test discovery, test parallelization, and test reporting.
- EarlGrey: It is an open-source UI testing framework for iOS apps, allowing easy and fast testing similar to XCUITest.
- OCMock: It is an open-source mocking framework for iOS and macOS applications written in Objective-C. It provides a simple, easy-to-use API for creating mocks and stubs and supports class and instance methods.
- KIF: KIF stands for Keep It Functional. It is an open-source UI testing framework for iOS applications written in Objective-C. You can write tests in plain English, which simplifies writing UI tests.
- Detox: It is an open-source end-to-end testing framework for iOS and Android applications. It seamlessly integrates with testing frameworks like Jest and Mocha.
Cross-Platform Testing Frameworks
Cross-platform testing frameworks mean you can test Android and iOS on these platforms.
- Appium: It is an open-source test automation tool for automating native, mobile web, and hybrid applications on iOS and Android platforms.
- Calabash: It is a test automation tool for testing native and hybrid mobile apps on iOS and Android platforms.
Feel free to look at our mobile app testing tutorial, where we have discussed all ins and outs of some best mobile app testing frameworks.
How to Choose the Right Mobile App Testing Tool?
The first step for mobile automated testing is to find a suitable app testing tool for developing test scripts. After you've decided on a tool, you may begin configuring the test environments.
Here is the checklist you can refer to while choosing the right tool for mobile software testing:
- It is usually preferable to use an app testing tool that allows the tester to write test cases in various programming languages.
- Tools that offer code-free solutions for creating and running test scenarios. You can reduce the execution time for repeating test cases by using a codeless mobile app testing solution.
- Ensure that the mobile apps testing tool you select is compatible with numerous operating systems, such as Android and iOS.
- Tools should be able to detect, record, play, and automate every activity in the test scenarios.
- Any mobile QA tool ought to be able to log test reports with a thorough plan description, screenshots, defect points, and so on.
In this section of the mobile app testing tutorial, we have covered some of the best app testing tools.
- LambdaTest: It is a cloud-based digital experience testing platform that supports mobile app testing and provides both real device cloud and virtual device cloud for real-time browser and app testing. You can run tests on an online device farm and OS. Some of its exciting features for mobile app testing include visual regression testing, debugging, and real-time testing.
- Apptim: It is a mobile testing platform where you can perform both manual and automation testing. It has features like performance testing, usability testing, and crash reporting. It also integrates with development tools like Slack, Jira, and Jenkins.
- TestComplete: It offers automation testing for the mobile app supporting iOS and Android platforms. It has unique features like object recognition, visual testing, and test script creation. It also integrates with some development tools like Jira, Git, and Jenkins.
- Kobiton: It is a cloud-based mobile testing platform. You can perform real device testing for both iOS and Android platforms. It also supports various development tools like Jira and programming languages.
In the next section of the mobile app testing tutorial, we will learn more about different parameters for mobile app testing.
Parameters for Mobile App Testing
It’s important to keep the parameters in mind while choosing between the virtual device or real device cloud.
User interface
The user interface does not require any hardware to be evaluated. If you have an application that can run on low-level specifications and the only thing it cares about is how well it looks, a virtual testing platform is an ideal option for you, and you should utilize it.
Network condition
Virtual testing platforms have begun to provide network throttle settings to help you lose or tighten the bandwidth quantity for testing. Nevertheless, none of these alternatives are sufficient for testing your application's performance in real-world scenarios.
When we talk about bandwidth, we don't only mean reception but also hardware difficulties and latency in network reception caused by other factors. Real device testing with network options is the best option for this.
Sensors
The sensor problem is too delicate to be left to the emulators. They certainly support these sensors and should be utilized in the early phases of testing. However, once development and early testing are complete, it is critical to test on a real device to ensure that the application reacts precisely to each sensor data. This is not something that should be left to chance or emulators.
Performance
Aside from network circumstances, load time and threshold can be adjusted in virtual testing. In general, virtual and real device testing load time should not exceed one second. But, you may need network conditions data and offline application operating data to compile a complete performance report. Both of these may eventually necessitate real-world device testing.
Cost
Even if you wish to use real devices, you may have to refrain because they are far more expensive than emulators. Many virtual testing platforms, such as Android Studio and other open-source ones, are even free to use. Nevertheless, they lack the functionality required of a tester and instead focus on simple app rendering.
Maintenance
Virtual testing platforms are rather simple to keep up with. You only need to access the platform from the cloud or download it to your system. On the other hand, if you want to test on a genuine device, you must first purchase that new device. Furthermore, the real device has considerable operational and maintenance costs.
CPU usage and battery
The two categories, battery and CPU utilization, are even related, as more CPU usage generates more heat and consumes more power. Because there are hundreds of processes running in a real device, this is the only method to get a realistic picture of CPU usage. Don't forget to look at the RAM and GPU use numbers as well.
View App Profiling for your Appium tests. Try LambdaTest Now!
What is Mobile App Beta Testing?
Beta testing is a technique of application testing in which people from outside the organization test the product and provide feedback. Beta testers install an application, use it as if they were a regular user, and provide their comments. Furthermore, enterprises benefit from the real-time performance data obtained throughout the mobile app beta testing period.
Beta testing is frequently performed after alpha testing. The developers and testers participating in the application development perform alpha testing, often known as the first step of user acceptability testing. The procedure is similar to that of beta testing a mobile app. Once the developers and testers are satisfied, the product is released for real-world testing, also known as mobile app beta testing.
In this section of the mobile app testing tutorial, we have covered some of the benefits of mobile app beta testing:
- Beta app testing can assist you in identifying corner instances that would have been more difficult to locate manually.
- It is economical, and the procedure assures that the software satisfies the product design and development specifications.
- The number of criteria included in the testing domain grows due to beta app testing. Once we have completed the mobile app beta testing and addressed all of the testers' feedback, we will have a high-quality application at our disposal.
There are two types of mobile beta app testing:
- Open beta testing: In open beta testing, any number of interested testers can participate, and they provide feedback for improvements. Hence, if anyone wishes to test the application as a beta user, they can either download it directly or submit a request to the organization for the executable file.
- Closed beta testing: The organization restricts closed beta testing. Only those invited by the organization can download and use the software as beta testers. Such restrictions are imposed for various reasons, which we will address throughout this piece.
In the next section of the mobile app testing tutorial, we will see the steps to follow while performing mobile beta app testing.
Steps to follow in Mobile Beta App Testing
Mobile app beta testing is a relatively straightforward procedure. There are just two groups of individuals involved: developers and testers. Here are the steps to follow beta testing:
- Design: The design of the mobile app is the first step in beta app testing. Designing is the first process completed before we begin development on our application or have any application renders.
- Planning: The planning phase establishes a step-by-step strategy for moving forward with beta app testing. Given the application and its business aims, we must separate different areas before proceeding with a detailed study.
- Put together a list of beta testers: The following step is to select beta testers for your application. Because you've already decided what kind of beta testers you want, you just need to find or create a platform to connect them with you.
- Create a tester pool: After you've contacted all possible testers, wait for them to respond and accept your proposal. Give them your mobile app beta link from the Play Store/Apple Store or a downloading link, and inform them of what you're looking for.
- Feedback from testers: The next step is to take constant feedback from beta testers and work on it on a regular basis.
- Implement the feedback: Once you get the feedback, you have to evaluate them. This input might be positive or destructive, but it will undoubtedly assist in building your application to meet the needs of the intended audience. Also, remember that you do not have to work on every input. You only need to evaluate the feedback that is relevant to your design and fits the business objectives.
Mobile App Testing Checklist
Every mobile app you've downloaded on your phone, regardless of genre, is designed to provide seamless and quick navigation. Having a limited attention span, app users are constantly on the lookout for something new that can provide them with value. At the same time, they always want a great app experience. As a result, quality is the foundation of any high-quality mobile app.
As a developer, you should ensure that your software fits the most important criteria before releasing it. Refer to the below given mobile app testing checklist to ensure that you have considered all crucial aspects of the mobile app.
- Test the mobile apps for different functionalities like handling calls, exchanging messages, reacting to notifications, handling interruptions, and others.
- Checking mobile apps for cross-platform compatibility across all applicable OS, devices, screen resolutions, and others.
- Checks if the mobile app can perform correctly by considering different traffic levels, stress/load levels, end-user conditions, CPU and GPU frequencies, install time, app launch and unload time, power modes supported by devices, and network conditions.
- Ensure mobile app accessibility by addressing color ratio and contrast, zoom in/out, font size, speech recognition, and VoiceOver and TalkBack features.
- Ensure the mobile app works in different locations and languages.
Please check our mobile app testing tutorial on the mobile apps testing checklist that will assist you and your team in identifying and resolving issues before the final product's release.
How to perform Mobile App Testing?
To perform accurate and robust testing of mobile applications, it is important to perform end-to-end testing. It ensures the seamless functioning of mobile apps.
This section of the mobile app testing tutorial discusses the steps to perform mobile application testing:
Step 1: Create test plan
Firstly, you should prepare a clear outline of the test to be executed for mobile apps. Try to include all the test plans and utilize cases in the list. Following this, decide on the test briefly that you want to perform with the expected outcome for the sprint.
Step 2: Choosing test type
Now you have a test plan, and you have to choose the type of mobile testing approach you intend to perform. For example, whether you want to test the mobile app manually or automate it. However, choosing the testing type, you have to focus on certain factors. For example, in this section of the mobile app testing tutorial, we have covered a few cases where you should perform automation testing:
- If the test process has the expected outcome: For any type of conditional testing where you are already aware of the outcome, you should choose to perform test automation.
- If the use case is required to be run often: If there is any routine test that has to be run regularly for testing basic mobile app functions, it is better to automate it.
- The mobile devices vary with different screen dimensions and resolutions. To ensure the compatibility of mobile apps, performing manual testing across various devices will be too time-consuming. Hence, automation is suggested.
You should remember that testing small components of mobile apps is more efficient and manageable when automated. However, always prefer performing manual testing when you have to test the system repeatedly.
Step 3: Preparing test cases
When you have decided on the type of mobile testing, you now have to create test cases to execute the test. In this step of the mobile app testing tutorial, you must select the appropriate approach, like requirement-based testing and business scenario-based testing.
The type of test cases you define depends on the test you will perform. To this, there are two broad categories of testing that mobile apps undergo, which include:
- Functional testing: It includes unit testing, system testing, acceptance testing, regression testing, etc.
- Non-functional testing: It includes security testing, volume testing, performance testing, load testing, compliance testing, etc.
Step 4: Manual testing
When you choose an Agile testing framework, it is always advised to use both manual and automation testing approaches to perform effective testing. However, when you start to test mobile apps, the testing sprint should always begin with exploratory testing.
Since it does not require any initial investment, it is always preferred at the first stage. To maintain a record of the test, you should keep logs of the entire testing session in an Excel or Word document.
Manual testing can be done in two different ways:
- Testing on emulators or simulators: They are the tools to mimic real mobile devices and run them on your computer system to perform the test.
- Testing on real devices: Real devices are physical hardware components used for testing software applications or systems. A real device is anything physical, such as a smartphone, tablet, laptop, desktop computer, server, or anything else wired into the Internet.
Step 5: Automated testing
Testing is an exhaustive process and requires verifying each functionality of the mobile app, depending just on manual testing can be time-consuming. Therefore, for the regular and expected tests, it is recommended to automate the test.
Automation testing saves time and human effort. Further, testers mainly perform automation testing for load testing, performance testing, spike testing, and stress testing. You should be particular in choosing the right automation tools as per your test requirement (discussed in the above section of the mobile app testing tutorial).
Step 6: Usability & Beta testing
Usability and beta testing are crucial parts of mobile app tests in unmasking hidden and critical errors before their release in the market. You can initiate usability testing during the design phase to get feedback from real users. It allows developers to exhibit potential features and reduce the list of those users have received perfectly.
Beta testing is conducted when the mobile app is ready, and developers are all set to welcome feedback before releasing it.
Step 7: Performance testing
Performance testing helps determine the mobile app's complete function. Now that you have tested specific features of your application, you are required to test the whole application’s performance. You can quickly identify the scalability, speed, and stability of the mobile app in case there is high traffic from end users. It also checks the mobile app for any system error.
Step 8: Security testing
Before releasing the mobile app in the market, you need to test the security of the mobile app. You must perform security testing and ensure it follows various data security guidelines, such as HIPAA, PCI DSS, and FFIEC. You will be able to analyze the risk associated with viruses, application hackers, and unauthorized access to sensitive data.
Step 9: End-to-End testing
On completion of all intended tests of the mobile apps, developers should finally execute an end-to-end test sprint. It is done to ensure the working of the mobile app as per expectation on the server level and back end. This will give assurance that the mobile app is ready to be uploaded.
In case any issues are found in the mobile app, you can quickly fix them by repeating end-to-end testing. However, if no major bug is found, the mobile app is released to the App stores.
In the next section of this mobile app testing tutorial, we will analyze two different methods to perform mobile app testing - on real and virtual devices.
Mobile App Testing on Real or Virtual Devices?
To perform accurate and robust testing of mobile apps, it is important to perform end-to-end testing. It ensures the seamless functioning of mobile apps.
When it comes to testing mobile apps, you get two options: test on real devices or virtual devices (emulators and simulators). Most organizations prefer to test on real devices so that mobile apps have seamless functions. However, most QA analysts are often confused about whether to use real or virtual devices to test a mobile app. Let us clarify this in this section of the mobile app testing tutorial.
Testing on real devices
When you intend to test the mobile app's performance, you should choose to test it on a real device. They give accurate results on the working of the mobile app as testing is done on the same conditions as the end users. In this section of the mobile app testing tutorial, we have mentioned a few benefits of testing on real devices, which include:
- Testing is done in real conditions where you can find any error related to the user interface.
- You will efficiently perform payment gateway testing on real devices.
- You can perform high-level testing of AI games on real devices.
Thus, testing on physical devices is essential for ensuring the app performs well in real-world scenarios.
Testing on virtual devices
Use of virtual devices to test mobile apps is also preferred as it mitigates the situation of having multiple physical devices. You get most of the features of real devices on virtual devices, which allows mobile app testing.
You can choose to test on an emulator when you test the mobile’s external behavior. On the other hand, simulators are less effective than emulators and are unable to debug the issue found in mobile apps.
However, it is essential to note that simulators do not provide an accurate representation of a real device's performance and behavior, so it is recommended to use them in conjunction with real devices. It’s preferred to select a cloud-based platform that offers real device cloud to test mobile apps. It provides a range of Android and iOS devices that simulate app behavior in real-user scenarios, eliminating the need for an in-house library.
In the next section of the mobile app testing tutorial, we will learn about performing mobile app testing on the cloud.
Mobile App Testing on the Cloud
Mobile app testing on the cloud has been the most preferred approach for a long time by the QA analyst. You can leverage the true capability of mobile app testing on cloud-based platforms as it provides testers and developers with access to multiple OS, devices, and tools. You can quickly test mobile apps across multiple environments.
Real device testing in the cloud allows end-users to access real devices (Android and iOS devices) directly from the desktop browser. You don’t have to get multiple physical devices to test the functionality and compatibility of mobile apps. This will save you cost and time in testing mobile apps and ensure wide device coverage.
In the cloud, the most significant advantage it offers is the ability to test across multiple devices and OS simultaneously. This ensures the seamless working of mobile apps across all platforms. You can leverage mobile app testing by performing testing in cloud-based digital experience testing platforms like LambdaTest.
Let us learn this in more detail in the below section of the mobile app testing tutorial.
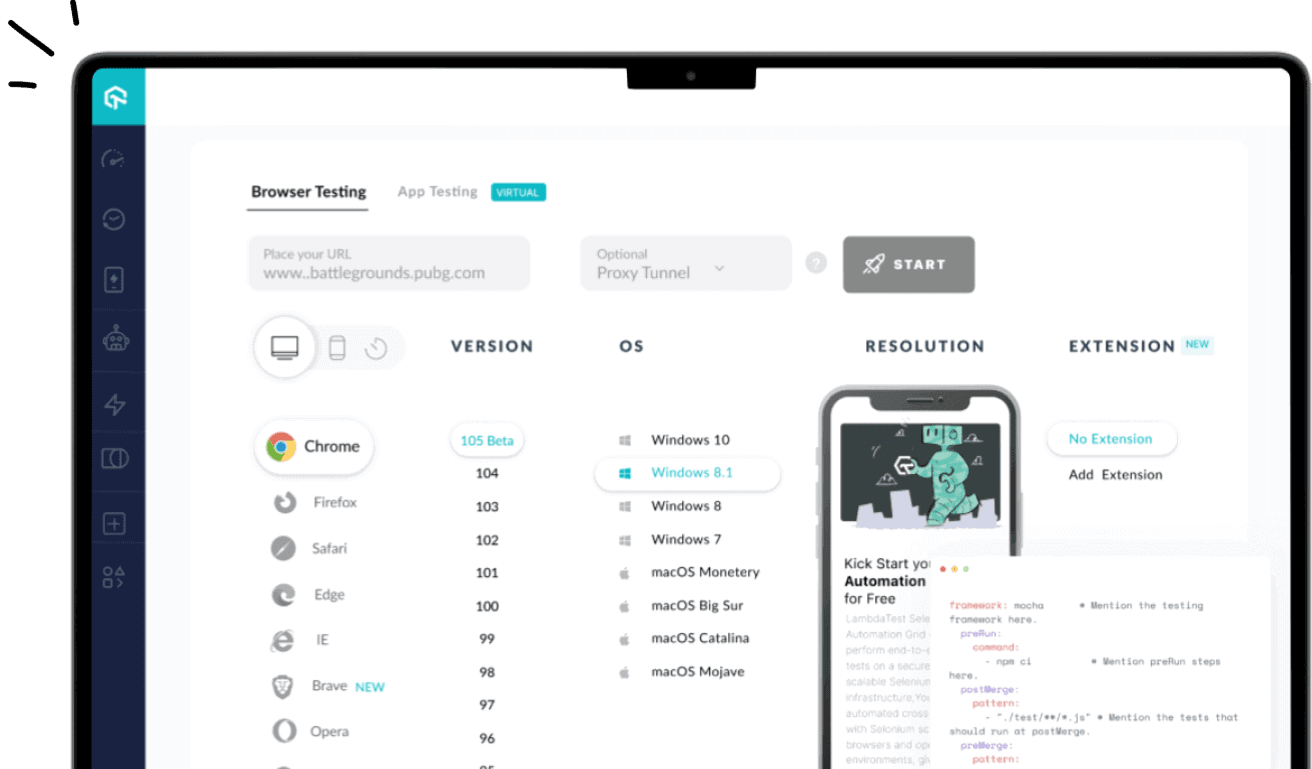
How to perform Mobile App Testing with LambdaTest?
We have already discussed different methods, frameworks, and strategies for mobile app testing in the earlier section of the mobile app testing tutorial. However, if you want 100% hassle-free mobile app testing, you must consider LambdaTest.
LambdaTest is a digital experience testing that lets you test on both real and virtual devices. This gives access to a diverse collection of iOS and Android devices with different OS, screen sizes, etc. This allows a more efficient real-device testing process in cloud infrastructure and delivers high-quality mobile apps.
Features:
- With LambdaTest's one-click upload feature, you can upload .apk, .ipa, .app, and .zip files in a single click for hassle-free and instant app testing.
- You can test your apps locally before you push them into a live environment.
- LambdaTest detailed test logs and insights will help to deploy quality builds faster.
- Mark bugs directly on the LambdaTest platform or integrate with CI/CD tools as required.
You can perform both manual and automated mobile app testing on LambdaTest.
In the next section of the mobile app testing tutorial, we will learn how to perform mobile app testing on the LambdaTest platform
Manual App Testing using LambdaTest
LambdaTest offers manual testing (real-time testing) of mobile apps on real devices and virtual devices (emulators and simulators). Below are the given steps to perform mobile app testing.
Real Time App Testing on Emulators and Simulators
- Register free on LambdaTest and login to your account
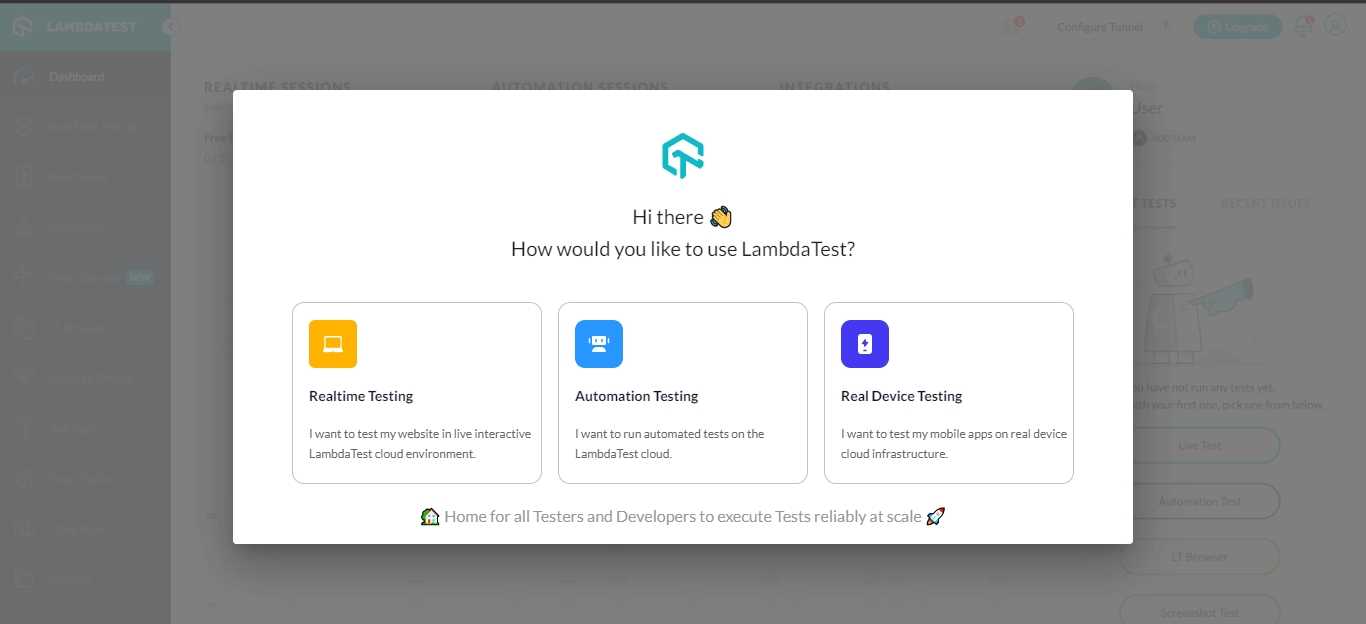
- You will get a Modal Box showing a Realtime Testing card.
- Click on Realtime Testing and then navigate to the App Testing tab.
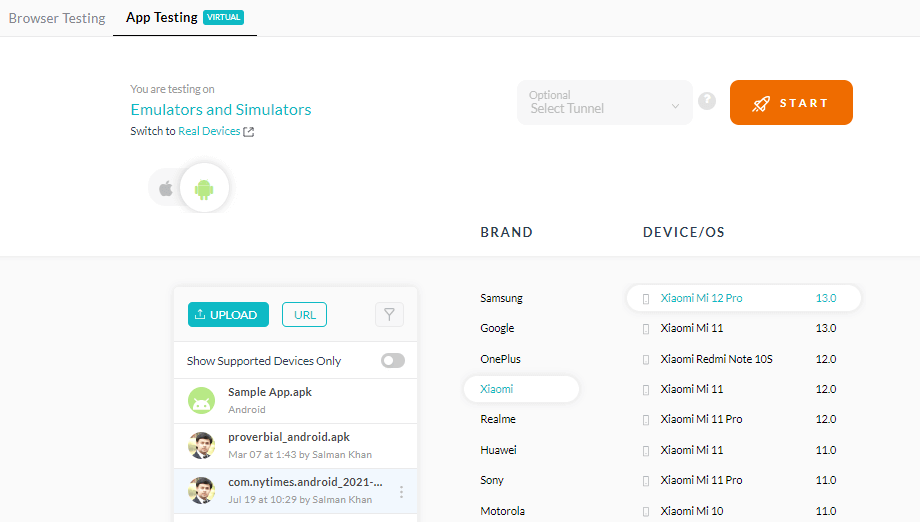
- Select Android or iOS. Upload your mobile app (.apk or public URL), and select device BRAND and DEVICE/OS. Then click START.
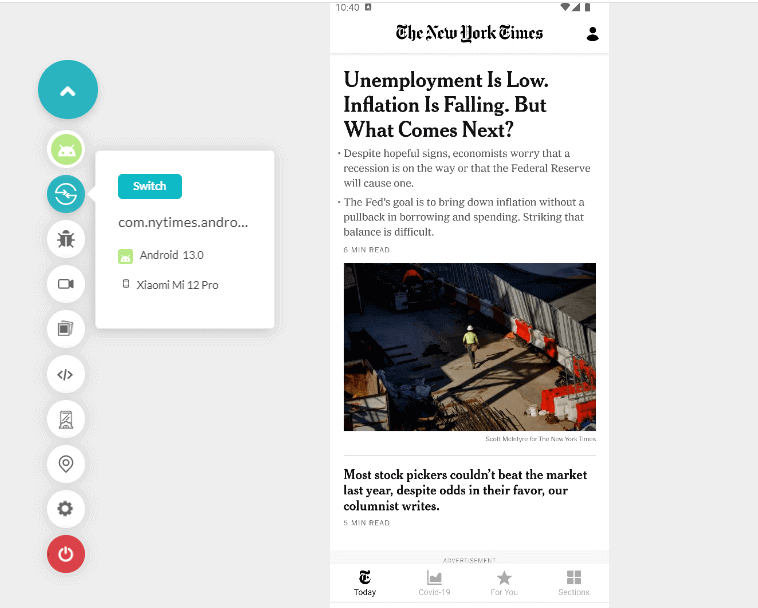
- It will launch an emulator or simulator where you can execute the test.
Real Time App Testing on Real Devices
Similarly, you can also test a mobile app on real devices as LambdaTest offers a real device cloud, which allows Real-Time App Testing on various real device environments. You can follow below mentioned steps to execute it.
- Login in the same manner as mentioned above.
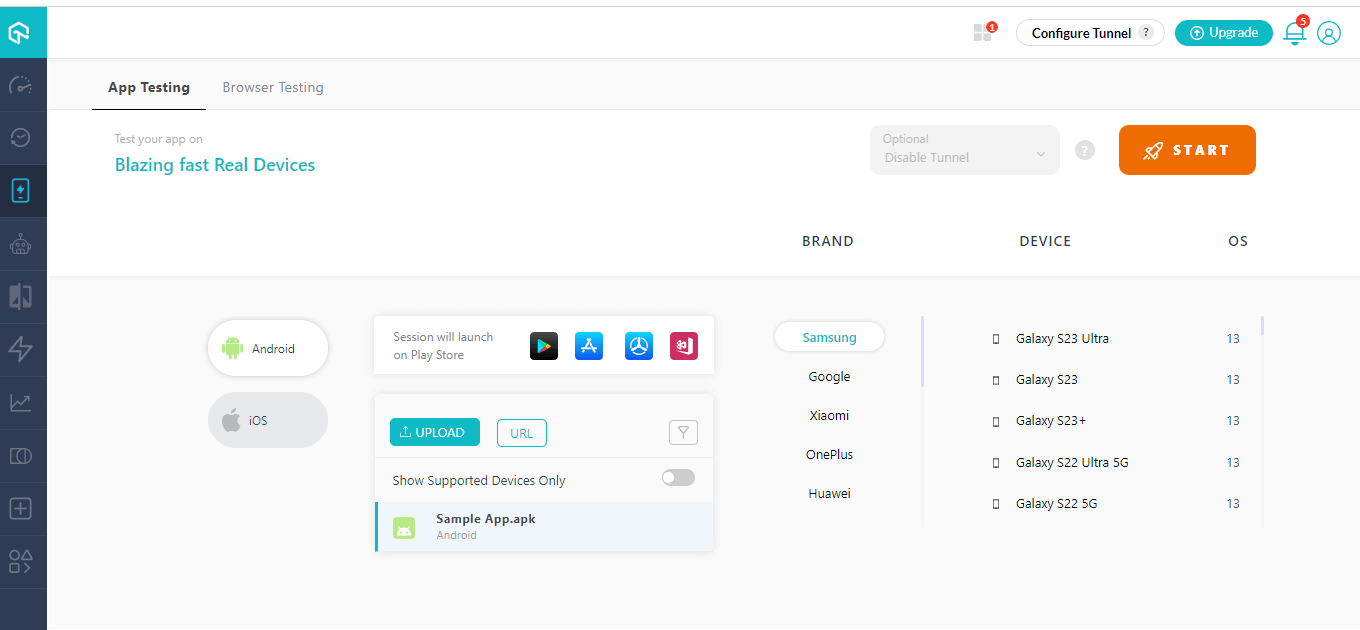
- In the Modal Box, select Real Device Testing, and you will get the Real Device App test console.
- Select Android or iOS, upload your mobile app (.apk or public URL), and select your device BRAND, DEVICE, and OS. Click on START.
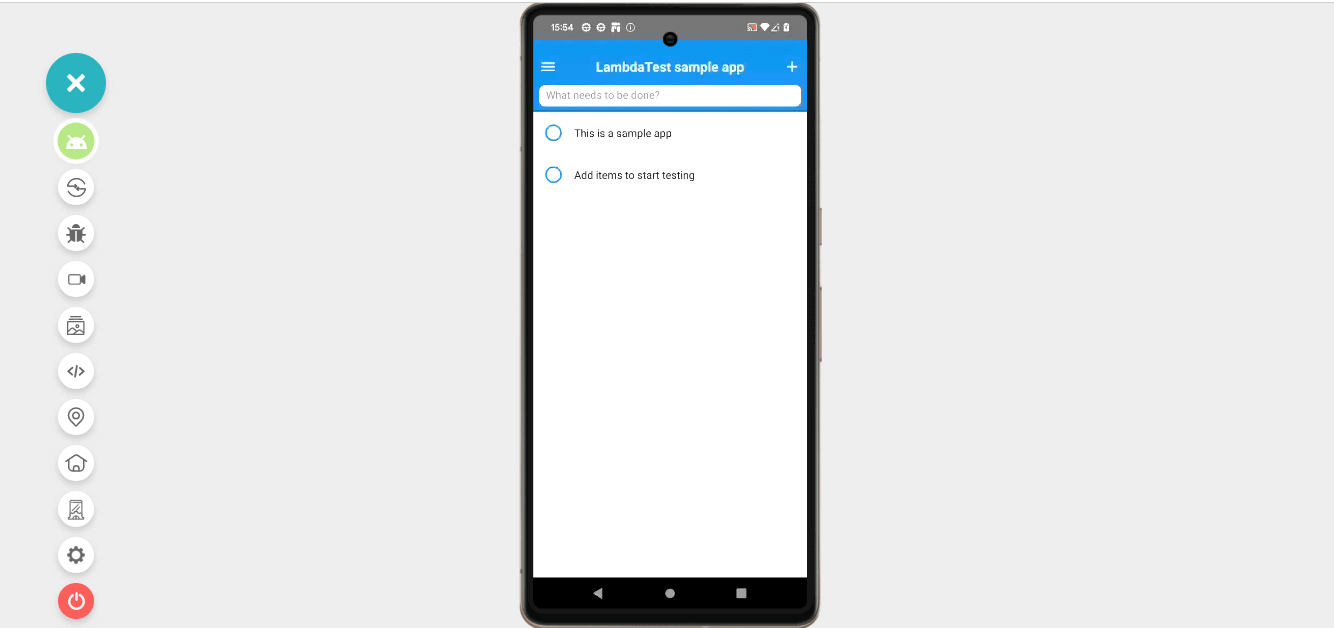
- It will launch a cloud-based real device, and you can start testing your mobile app in real-world conditions.
App Automation Testing on Real Devices
LambdaTest lets you perform app test automation on a real device cloud using Appium, Espresso, and XCUITest. You can also perform automation testing on mobile browsers using the Appium framework.
Here are the simple steps to follow to automate mobile app testing.
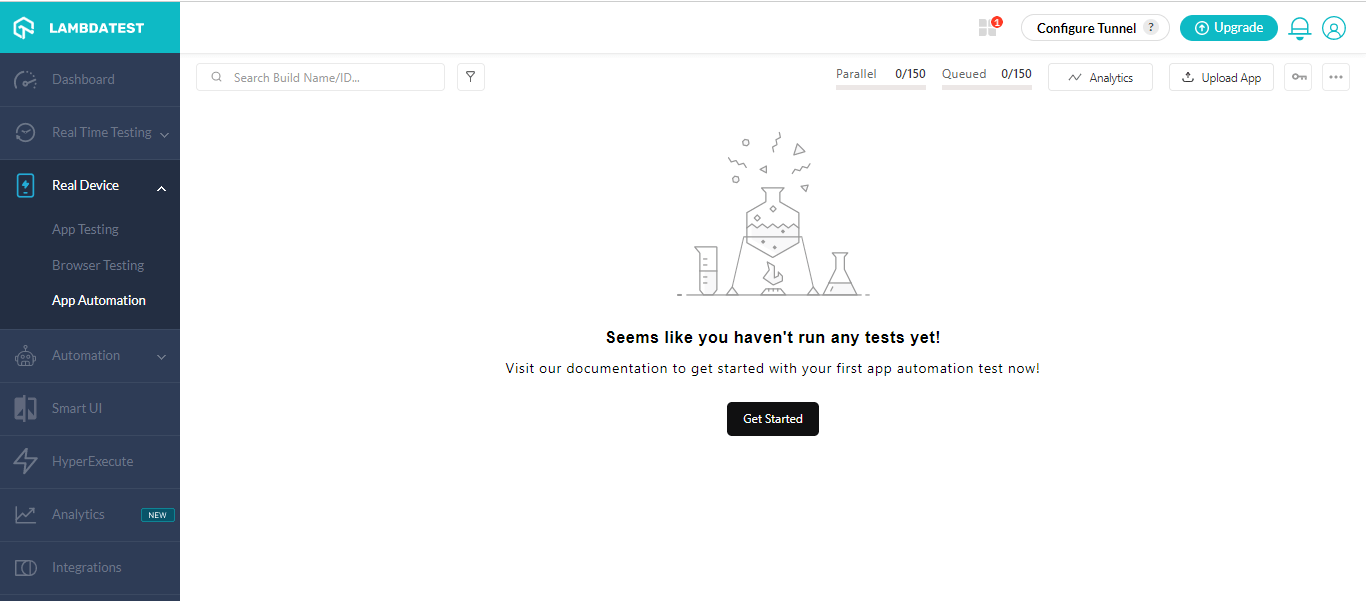
- Follow the same login process as explained.
- Select App Automation on the left panel under Real Device
Refer to our documentation to get started with app automation with Appium, Espresso, and XCUITest:
In case you wish to perform mobile browser automation on the real device, check out the documentation - mobile web automation on real devices.
Subscribe to our LambdaTest YouTube Channel to get the latest updates on tutorials around Selenium testing, Cypress testing, Appium, and more.
In the next section of the mobile app testing tutorial, we will discuss some of the challenges of mobile app testing
Challenges of Mobile App Testing
Mobile app testing is not an easy task. Testing apps on all platforms takes a significant amount of time and work.
This section of the mobile app testing tutorial focuses on the challenges that testers might face during mobile app testing.
- Device fragmentation is one of the most significant app testing challenges since the number of active devices running an app at any given time grows yearly.
- Businesses all across the world create smartphones with varied screen sizes. To appeal to a wider spectrum of customers, multiple variants of the same model have varied resolutions and screen sizes. As a result, apps must be built in tandem with each new screen specification given to the market.
- Testing mobile network bandwidth is an important component of mobile app testing. End users expect fast mobile apps, which the backend team must deliver. But there's more. An app that struggles to provide faster results also struggles with data transfer.
If you are looking for a list of all possible challenges and solutions for those, you can go through our earlier mobile app testing tutorial on mobile app testing challenges.
In the next section of the mobile app testing tutorial, we will learn some of the best practices for mobile app testing.
Best Practices for Mobile App Testing
Now, you have learned how to perform mobile app testing and its underlying challenges in the mobile app testing tutorial. It is important to optimize your mobile app testing process and address any challenges to avoid missing the testing of important components of the mobile app.
In this section of the mobile app testing tutorial, we look at some best practices you should incorporate while performing mobile app testing.
- Before you dig into testing mobile apps, you should completely understand the working aspects of your app. It will help you develop correct test cases and ensure test coverage metrics.
- You should have a clear testing strategy with defined objectives, scope, and approaches before initiating the test. It will help to execute the test with every test procedure in the pipeline.
- You should test your mobile app on real devices as it ensures easy identification of issues that might not be visible on emulators and simulators.
- Testing for user experience is paramount in mobile app testing. You should be mindful in testing the usability, accessibility, and performance of the app to ensure that it gives a seamless experience.
- You should also test the mobile app under real-time conditions, which include different time zones, GPS locations, varying network conditions, and low battery warnings.
- The working of mobile apps should be appropriate when the OS gets updated. So testers need to keep an eye out for upgrades and update the app to keep it working properly.
- The testing of mobile apps should be done early and often using a test-driven approach. It ensures tests are executed at the early stages of development and at different phases of the project to develop a stable mobile app.
- Automation can significantly reduce the time and effort required for testing. You should use automated testing tools to test your app's functionality, performance, and compatibility across different devices.
Conclusion
Mobile has become an essential component of everyone’s day-to-day life. The more it grows, the more its different usages come to the surface. People use it for entertainment or to purchase all different kinds of purposes. As per the source, a user spends more than 200 minutes each day on their mobile device; what is the greatest option for a business to expand and be visible at all times? But, because everyone is aware of it, everyone develops it.
This situation makes it a highly competitive environment where you cannot have the tiniest error in your application. It makes mobile application testing crucial. We hope in this mobile app testing tutorial, you learned A to Z about mobile app testing, how to perform it, and how LambdaTest can be your best option for that purpose.
About the Author
Nazneen Ahmad is an experienced technical writer with over five years of experience in the software development and testing field. As a freelancer, she has worked on various projects to create technical documentation, user manuals, training materials, and other SEO-optimized content in various domains, including IT, healthcare, finance, and education. You can also follow her on Twitter.
On this page
- Overview
- What is Mobile App Testing?
- Why Mobile App Testing
- Types of Mobile Apps
- Mobile vs. Web App Testing
- Benefits
- Types
- Testing Strategy
- Emulator, Simulator, and Real Device
- Approaches
- Frameworks
- Choosing App Testing Tool
- Parameters for Testing
- Mobile App Beta Testing
- Mobile App Testing Checklist
- How to perform
- Testing on Real or Virtual Devices
- Mobile App Testing on the Cloud
- Mobile App Testing with LambdaTest
- Challenges
- Best Practices
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Frequently asked questions
- General
Author's Profile

Nazneen Ahmad
Nazneen Ahmad is an experienced technical writer with over five years of experience in the software development and testing field. As a freelancer, she has worked on various projects to create technical documentation, user manuals, training materials, and other SEO-optimized content in various domains, including IT, healthcare, finance, and education. You can also follow her on Twitter.
Reviewer's Profile

Salman Khan
Salman works as a Digital Marketing Manager at LambdaTest. With over four years in the software testing domain, he brings a wealth of experience to his role of reviewing blogs, learning hubs, product updates, and documentation write-ups. Holding a Master's degree (M.Tech) in Computer Science, Salman's expertise extends to various areas including web development, software testing (including automation testing and mobile app testing), CSS, and more.
Did you find this page helpful?
More Hubs
Try LambdaTest Now !!
Get 100 minutes of automation test minutes FREE!!
 Christmas Deal is on: Save 25% off on select annual plans for 1st year.
Christmas Deal is on: Save 25% off on select annual plans for 1st year.