Integration Testing Tutorial: A Comprehensive Guide With Examples And Best Practices
- Learning Hub
- Integration Testing Tutorial: A Comprehensive Guide With Examples And Best Practices
CHAPTERS
- Overview
- What is Integration testing
- What is the purpose of Integration testing
- Difference between Unit testing and Integration testing
- Difference between Integration testing and System testing
- Benefits of Integration testing
- Types of Integration testing
- How is Integration testing done
- Entry and Exit Criteria for Integration testing
- Example: Integration Test Cases
- Manual and Automated Integration testing
- Integration testing tools
- Challenges of Integration testing
- Best Practices for Integration testing
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
OVERVIEW
Integration testing is an approach where different components or modules of a software application are tested as a combined entity. You can run integration tests seamlessly regardless of whether one programmer or other programmers code these modules.
Before a release, a software application undergoes various operations like extensive testing, iteration, and exception handling to identify bugs and make the software business ready. Integration testing is a primary phase of the software testing process when testing is done at the development stage.
What is Integration testing?
Integration testing is the crucial second stage of software testing, assessing how individual components collaborate to ensure proper functioning and identify defects within a software project. As the second level of software testing, integration testing ensures components harmonize flawlessly.
When separate modules are combined and tested as a whole, this software testing phase is referred to as integration testing. It takes place before the verification and validation process and after the unit testing.
What makes integration testing essential is its ability to check the behavior of different units of a system altogether. When these units are taken individually, they function correctly with almost no errors, but when they are brought together, they uncover incorrect behavior if that exists.
Integration testing is crucial because it's done at an early stage of development and helps prevent serious issues that may arise later by costing high fixing measures. You should run integration tests every time you change the existing code.
What is the purpose of Integration testing?
Initially, software testing was not dependent on integration testing, and nobody had ever thought about building an advanced testing phase with the capability of finding issues during the development process. But with the growing digital sphere, the demand for integration testing has increased.
Here are some major reasons why integration testing is crucial:
- To analyze integrated software modules: Analyzing the working of integrated software modules is the primary objective of integration testing. As per the test plan requirements, integration testing ensures connectivity between individual modules by examining the rendering values and logically implementing them.
- To ensure seamless integration between third-party tools and different modules: It's crucial to ensure the data accepted by the API is correct so that the response generated is as per the requirement. Integration testing for the interaction between modules and third-party tools helps to ensure that the data is correct.
- To fix exception handling: Before releasing the final build, it is crucial to pinpoint the weak spots and red flag them to minimize exception handling defects as much as possible. Missing these defects in the initial or developing stage will be expensive to fix after the release.
Difference between Unit testing and Integration testing
| Unit testing | Integration testing |
|---|---|
| It is a white box testing process. | It is a black box testing process. |
| It is performed by developers. | It is performed by testers. |
| Finding defects is easy as each unit is tested individually. | Finding defects is hard as all modules are tested together. |
| It is always performed first before going through any other testing process. | It is performed after unit testing and before system testing. |
| Developers are aware of the internal design of the software while testing. | Testers are not aware of the internal test design of the software. |
Difference between Integration testing and System testing
| Integration testing | System testing |
|---|---|
| It ensures all combined units can work together without errors. | To ensure that the total build fills the business requirements and specifications. |
| It is black box testing. | It is a white box and black box testing or grey box testing. |
| It doesn’t fall in the acceptance testing class and performs functional types of tests. | It falls in the acceptance testing class and performs functional and non-functional tests. |
| It is level two testing. | It is level three testing. |
| It identifies majorly interface errors. | It helps to identify system errors. |
Benefits of Integration testing
Integration testing helps expose any defects that can arise when these components are integrated and need to interact with each other through integration tests.
- It makes sure that integrated modules work correctly as expected.
- It is a quick testing approach, so once the modules are available, the tester can start testing them.
- It detects all errors that are related to the interface between modules.
- Helps modules interact with third-party tools and, most importantly, different APIs.
- It is more efficient because it typically covers a large system volume.
- Increases the test coverage and also improves the reliability of tests.
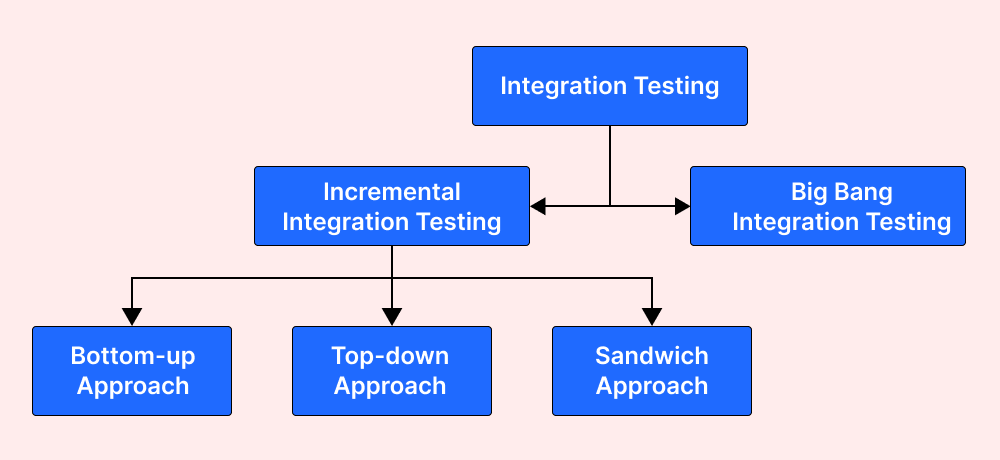
Types of Integration testing
Integration testing is performed by combining different functional units and testing them to examine the results. There are four types of integration testing, each of which focuses on testing the software differently. Integration testing consists of the following types:
- Incremental integration testing
- Non-incremental/Big bang integration testing
Incremental integration testing
In the incremental testing approach, all logically related modules are integrated, and then testing is done to check the proper functionality of the application as per the requirement. After this, the other related modules are then integrated incrementally, and the process continues until all the integrated, logically related modules are tested successfully.
The incremental approach is carried out by two different methods:
- Top Down Approach
- Bottom Up Approach
- Sandwich Approach
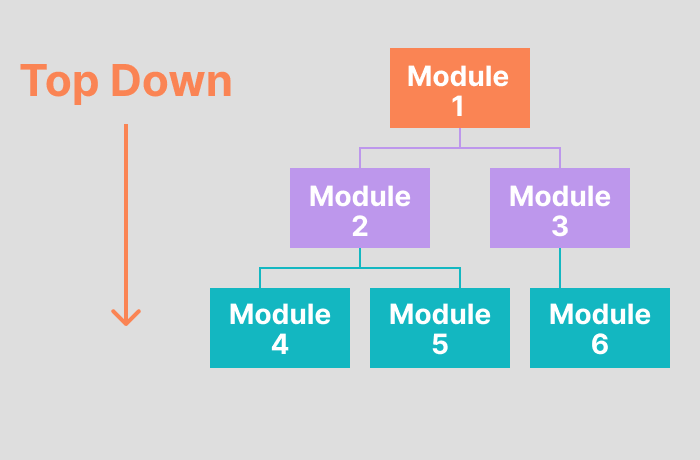
Top Down Approach
The top-down integration testing approach involves testing top-level units first, and lower-level units will be tested step-by-step. Test Stubs are needed to simulate lower-level units, which can’t be available during the initial phases.
Advantages
- It requires little planning.
- Convenient for small systems.
- It covers all the modules.
Disdvantages
- The top-down testing approach is not recommended for large-scale systems as fault localization is complicated.
- As the prerequisite of this approach is completing all modules, the testing team remains extremely time-bound when executing the test.
- Since all the modules are tested simultaneously, you can't test modules based on priority or critical functionality.
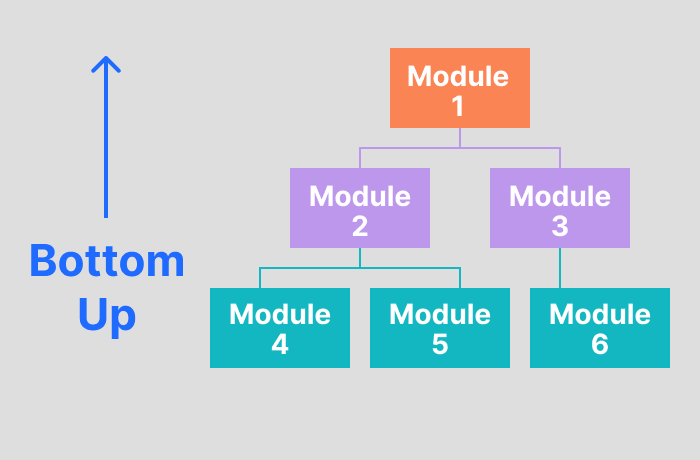
Bottom Up Approach
Bottom-up approach involves testing bottom-level units first, followed by the upper-level units testing. In the bottom-up testing approach, test drivers are needed to simulate higher-level units, which may not be available during the initial phases.
Advantages
- Fault localization is much easier based on the application's control flow.
- This approach allows you to develop and test simultaneously to meet customer specifications efficiently.
- By the end of the testing cycle, you can quickly identify defects between interfaces.
Disadvantages
- All modules except the top control need to have test drivers.
- Modules that control the application flow are tested last and may contain defects.
Difference Between Stubs and Driver
| Stubs | Driver |
|---|---|
| They are mainly used in top-down integration testing. | They are mainly used in bottom-up integration testing. |
| Stubs can be understood as modules of software during the development process. | Drivers are used to invoke the component individually that requires testing. |
| They are crucial to test different features and functionalities of modules. | They are used when the main module of the software is not ready or developed for testing. |
| Stubs play a crucial role when low-level modules are not available. | Drivers get crucial when high-level modules are unavailable or sometimes in the absence of low-level modules. |
| In the case of a partially developed low-level module, you can use Stubs to test the main module. | In the case of a partially developed high-level module, you can use Stubs to test the main module. |
| Stubs are only considered when the upper levels of modules are done. | Drivers can be considered in both cases- When upper-level or lower modules are done. |
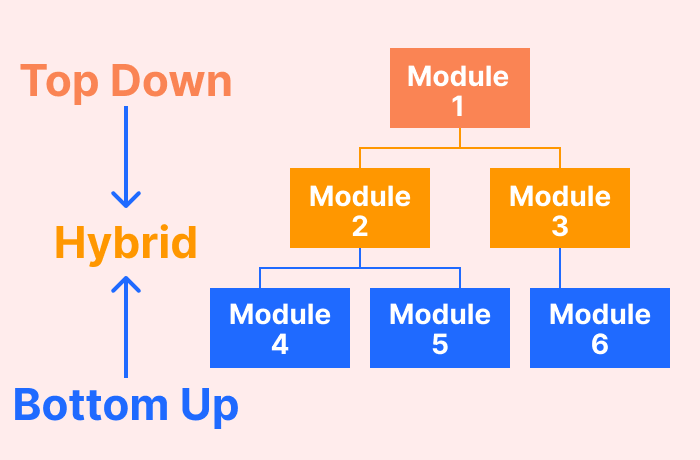
Sandwich Approach
The Sandwich testing approach is known as "hybrid testing" because it combines top-down and bottom-up testing approaches. In this strategy, the low modules are tested in conjunction with the higher-level modules and vice versa. This strategy uses both stubs and drivers.
Advantages
- Sandwich testing approach allows parallel performing both top-down and bottom-up approaches.
- It is suitable for large-scale applications.
Disadvantages
- It is an expensive approach.
- Not suitable for small-sized applications.
Non-Incremental/Big bang testing
In this non-incremental testing approach, all the developed modules are tested individually and then integrated and tested once again. This is also known as big bang integration testing.
Big Bang integration testing:
This type of integration testing involves coupling most of the developed modules into a larger system, which is then tested as a whole. This method is very effective for saving time. Test cases and their results must be recorded correctly to streamline the integration process and allow the testing team to achieve its goals.
Advantages
- Good for testing small systems.
- Allows finding errors very quickly and thus saves a lot of time.
Disadvantages
- Fault localization is tough.
- Finding the root cause of the problem is quite difficult.
Functional Integration Testing: Functional integration testing, or FIT, is a crucial part of software testing that ensures different system modules or components integrate seamlessly. It involves testing how interactions occur between various software application components to ensure correct system functionality and expected output.
How is Integration testing done?
When the system is ready and the units are successfully tested individually, they can be integrated and tested. The complete process of integration testing includes several steps and has a range of frameworks and continuous integration.
Here's how you can perform integration testing-
- Firstly, prepare a test integration plan and the required frameworks.
- Decide the type of integration testing approach: Bottom-Up, Top-Down, Sandwich testing, or Big Bang.
- Design test cases, scripts, and scenarios.
- Deploy the chosen components to run the integration testing.
- You must track and record the testing results if there are any errors or bugs or if the test goes bug-free.
- Finally, you must repeat the same process until the entire system is tested.
Entry and Exit Criteria for Integration testing
Integration testing has both entry and exit criteria that one should know before starting.
Entry Criteria
- Approval: The integration test plan document has been signed off and approved.
- Preparation: Integration test cases have been prepared.
- Data creation: Test data is created.
- Unit testing: Unit testing of each developed module/component is complete.
- Dealing with defects: All the high-priority and critical defects are closed.
- Test environment: The test environment is set up for integration testing.
Exit Criteria
- All the integration test cases on different parameters have been successfully executed.
- All critical and priority P1 & P2 defects are closed.
- The test report has been prepared.
Example: Integration Test Cases
Integration test cases mainly focus on the data transfer between the modules as modules/components that are already unit tested, interface between the modules and integrated links.
For example, let's take integration test cases for Linkedin applications:
- Verifying the interface link between the login and home pages. That means when a user enters the correct login credentials, it should get directed to the homepage.
- Verifying the interface link between the home page and the profile page. When the user selects the profile option, the profile page should open up.
- Verify the interface link between the network page and your connection pages. On clicking the accept button for received Invitations on the network page, it should show the accepted invitation on your connection page once clicked.
- Verify the interface link between the Notification pages, and say congrats button. On clicking the say congrats button, the user should get directed toward the new message window.
These are the steps of how LinkedIn works and how Integration test cases are included in testing.
Manual and Automated Integration testing
Integration testing usually doesn't require specific tools. These tests are often run manually by QA teams. In most cases, it happens in parallel with the development process, which is the most efficient approach.
First, individual software units are created, and then these units are checked by a development team. After successful checks, QA engineers start combining different units and inspecting them, focusing first on the interfaces and then on the connections between these units.
QA engineers don't require specific tools to inspect these features, even if they are separate.
Regarding automated testing, Selenium is the most widely-used framework for integration testing. If you start with integration testing, don't waste time setting up expensive in-house test infrastructure. Opt for cloud-based testing platforms like LambdaTest. Using LambdaTest's online browser farm, you can run integration tests on 3000+ multiple browsers, devices, and OS combinations.
Its simple onboarding process makes it easy to perform mobile app and web testing. LambdaTest supports automated testing tools like Selenium, Cypress, Playwright, Puppeteer, Appium, Espresso, and XCUITest, among others.
Devs and testers can also leverage LambdaTest’s HyperExecute - an end-to-end test orchestration cloud to run automated tests at a blazing speed of up to 70% more than any other traditional cloud grids.
Also, subscribe to LambdaTest YouTube Channel and get detailed tutorials around Selenium, Cypress automation, Appium and more.
Integration testing tools
With the help of automated tools available, integration testing can greatly impact the various modules of the software applications. These simplify the process and make it more agile. Here are some of the best integration testing tools:
Selenium: Selenium is the leading large-scale open-source test automation framework to automate integration test suites for your web applications. Here are some primary features and highlights that make Selenium a top-popular tool:
- It supports multiple languages – C#, Ruby, Java, JavaScript, PHP, Java, Python, Ruby, and Perl.
- Run in different system environments – Mac, Windows, Linux.
- Works with all popular browsers, including Firefox, Safari, Chrome, and Headless.
- W3C standardization makes testing and scripting seamless.
- It allows running parallel tests with different hybrid test data.
Pytest: Pytest is widely used for writing and running test code for Python automation testing. It can also scale up and works perfectly while testing complex libraries and applications. Here are some amazing features that make pytest an excellent choice for automated integration testing:
- Pytest can significantly reduce the overall testing time by running tests parallely.
- If test files and features are not directly indicated, pytest will automatically define them.
- Pytest has built-in command-line support and test discovery support.
RFT: RFT stands for IBM Rational Functional Tester. It is a popular tool that makes creating scripts that mimic the behavior of human testers easy. To enhance your testing experience, IBM offers different other software solutions that you can integrate with RFT.
Not just maintaining test scripts, RFT provides a couple of different features as well; these are:
- Storyboard mode simplifies editing and test visualization, in particular, through screenshots.
- Applying recording tools to make test scripting easy.
- Data driven testing for the same series of actions using varying data sets.
- For collaborative SDLC management, it allows integration with other software.
VectorCAST: The VectorCAST software testing platform is one of the best in the market to automate testing activities across the software development lifecycle. Advantages of using VectorCAST are-
- Focus on embedded systems.
- Enable continuous and collaborative testing.
- Works with your existing software development tools.
Embedded developers can use this highly automated unit and integration test tool to validate business-critical embedded systems and safety.
LDRA: LDRA drives the market for software tools that can effortlessly automate code analysis and testing for safety, mission, and business-critical needs. With LDRA, you get-
- Customer-focused certification services.
- Consultancy offerings.
- LDRA tools to achieve early error identification and elimination.
- Tracing requirements through static and dynamic analysis to unit testing.
- Verification for various hardware and software platforms.
Challenges of Integration testing
Like any other testing technique, integration testing also has some challenges that testers and developers encounter. These challenges include-
- Integration testing management is complex sometimes because of various factors like databases, platforms, environment, etc.
- Integrating a new system into one or two legacy systems requires a lot of change and testing efforts.
- Compatibility between systems developed by different companies is quite challenging for programmers.
- There are many different paths and permutations to apply for testing integrated systems.
Best Practices for Integration testing
Before starting your integration testing, you should follow or implement a few best practices.
- Run integration tests before unit testing: It’s crucial to discover bugs early in the development cycle because the later you discover the bug, the more expensive it is to fix. For a smooth development cycle, making things perfect on initial development is mandatory before stepping to "big things," like Integration testing.
- Avoid business logic tests: Unit tests are typically high-speed, so they are run for every build triggered in the CI environment. Since they target the fundamental correctness of code, running them frequently is critical to detect bugs early on in business logic so that the developer who introduced the bug can fix it immediately.
- Keep your testing suites separate: Integration tests should not be run together with unit tests. Developers working on the specific business logic in the code must be able to run unit tests and get near-immediate feedback to ensure that they haven't broken anything before committing code.
- Log extensively: A unit test has a specific scope and tests a tiny piece of your application, so when it fails, it's usually relatively easy to understand why and fix the problem.
All in All
The main objective of integration testing is to ensure that the entire software system works flawlessly when it is put together. During the unit testing phase, if any critical aspects are overlooked, they are highlighted and, in turn, can be corrected before the final launch.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the main purpose of integration testing?
Integration testing exposes faults in the interaction between integrated units or modules/components. It begins after unit testing has been completed for all modules.
Is API testing integration testing?
API testing takes place at the message layer without a GUI. As part of integration testing, it determines whether APIs are reliable, fast, and secure and meet the testers' expectations.
What is integration testing?
Integration testing is a software testing technique where multiple components or modules are combined and tested as a group to ensure they work together seamlessly. It focuses on detecting interface or integration issues between different parts of the system.
What is system integration testing
System integration testing is a level of integration testing that verifies the interaction and communication between different subsystems or components of a complete system. It tests the system as a whole to ensure its components integrate correctly.
What is the key objective of integration testing?
The key objective of integration testing is to uncover defects arising from the interaction between integrated components. It aims to validate the correctness of interfaces, data flow, communication, and behavior of the integrated system.
What is continuous integration testing?
Continuous integration testing is the practice of frequently integrating code changes into a shared repository and running automated tests to detect integration issues early in the development process. It ensures that new code integrates smoothly with the existing codebase.
What are the types of integration testing?
The types of integration testing include top-down testing, bottom-up testing, sandwich testing, and bi-directional testing. Each type focuses on a specific approach to integrating and testing components.
How to do integration testing?
To perform integration testing, identify the components or modules that need to be integrated. Define test cases that cover various integration scenarios and execute them to verify the behavior and functionality of the integrated system.
Who is responsible for integration testing?
Integration testing is typically the responsibility of both developers and testers. Developers ensure that their components integrate correctly, while testers design and execute integration test cases to verify the system's integration.
Reviewer's Profile

Salman Khan
Salman works as a Digital Marketing Manager at LambdaTest. With over four years in the software testing domain, he brings a wealth of experience to his role of reviewing blogs, learning hubs, product updates, and documentation write-ups. Holding a Master's degree (M.Tech) in Computer Science, Salman's expertise extends to various areas including web development, software testing (including automation testing and mobile app testing), CSS, and more.
Try LambdaTest Now !!
Get 100 minutes of automation test minutes FREE!!
 Christmas Deal is on: Save 25% off on select annual plans for 1st year.
Christmas Deal is on: Save 25% off on select annual plans for 1st year.