Functional Testing Tutorial: Comprehensive Guide With Best Practices
- Learning Hub
- Functional Testing Tutorial: Comprehensive Guide With Best Practices
CHAPTERS
- Overview
- What is Functional testing
- Why run a Functional test
- Features of Functional testing
- What aspects are analyzed in a Functional test
- Functional vs. Non-Functional Testing
- Unit test vs Functional Test
- Benefits of Functional testing
- Types of Functional testing
- Example of a Functional test
- Functional Testing Techniques
- Steps to perform Functional testing
- Why automate your Functional tests
- How to select the right automation testing tool
- Functional testing tools
- How to perform Functional testing using LambdaTest
- Best practices of Functional testing
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
OVERVIEW
Functional testing is a type of testing that validates the functionality of a given application feature in accordance with software requirements. The output of each function is compared with the corresponding requirement to determine whether it meets the end user's expectations.
As technology evolves and rapidly transforms, the only constant remains the need for speed. Thus, businesses are accelerating that momentum and offering brand-new & unique features daily or, at most, every week to their customers.
However, failures are still risky unless you test each application properly. For example, a flaw in the website's function, a security issue, etc., can significantly impact your website or app's overall user experience and also break or make your customer. The development and QA teams are under constant pressure to ensure smooth operation, which is why functional testing is so critical.
What is Functional testing?
Functional testing validates if application features adhere to software requirements, ensuring consistent outputs aligned with end user expectations for optimal performance and user experience. Functional testing involves providing samples of inputs and capturing the outputs, and verifying that the actual outputs match the expected ones.
Unlike non-functional tests, it is not concerned with identifying the application's underlying code's quality, security, or performance. Instead, it focuses on the processing results, excluding its intricacies, and determines whether the application meets the basic end-user requirements.
Functional test involves evaluating various functionalities like user interface, database, APIs, client/server communication, security, and other components. The software testers are not required to know the internal code structure or the application's source code. The tests are solely based on requirements and functionality, and the internal system design is not taken into account.
Why run a Functional test?
Did you know your website growth depends on the user experience? For enterprises, small or big, working on agile development principles wants to give the best user experience to customers, but that can be challenging for the testing team. Running multiple tests at the last minute can lead to human errors; thus, functional test is executed to inspect software bugs and improve customer experience.
The tests are run with a combination of manual and automation testing. Manual tests rectify bug bugs caused by user interaction, while automation testing thoroughly checks repetitive tasks.
For a business to keep a competitive edge, it is essential to create cost-effective & highly scalable strategies that will help the company increase business efficiency. So, whether you are designing an API, website or web app, run it through functional test to check if it displays the expected outcomes. So, to ease the process, you can add tools to your strategies to keep up with the momentum across developer & testing teams.
Features of Functional testing
A functional test is usually conducted on a specific feature or functionality within a software application or system. The tester may have access to these features in the form of specifications, or they may be fully implemented to try them before designing and performing a test.
The complexity of functional test increases when you test multiple related functions at once. However, this is also when it penetrates deeper into the code, exposing more profound defects.
Let's look at its features.
- In conjunction with other functions, functional test can become more complex.
- It can be done in-depth using boundary value analysis and state transition testing techniques.
- In many cases, you can automate it.
- It can be informal (like exploratory testing) and formal, using formal test design techniques and comprehensive test cases and procedures.
What aspects are analyzed in a Functional test?
In functional test, the main objective is to verify the software's functionality. The following aspects are analyzed during functionality testing.
- Usability: A functional test involves testing the user's ability to navigate freely through screens without difficulty.
- Accessibility: It tests the accessibility of the specific features to ensure it is usable by people with impairments.
- Mainline functions: It tests the primary function or feature.
- Error conditions: It checks for the error condition if an error message appears.
Functional vs. Non-Functional Testing
In a functional test, you can test mobile and web applications against different specifications and requirements. Non-functional testing concerns testing the readiness of a system per other non-functional parameters.
Let's look at the difference between them.
| Functional Testing | Non-functional Testing |
|---|---|
| Verifies the actions and operations of the software application. | Verifies how the application behaves. |
| This type of testing relies heavily on customer requirements. | In this type of testing, customer expectations play an important role. |
| It is easy to enhance the behavior of an application. | It is easy to enhance the application performance. |
| It is performed before non-functional testing. | It is performed after functional testing. |
Unit test vs Functional test
In the context of software testing, unit tests and functional tests play distinct yet complementary roles. Unit testing involves scrutinizing individual components of an application, confirming their precise functionality. On the other hand, functional testing takes a broader stance, verifying whether the application as a whole aligns seamlessly with business requirements. While unit tests focus on the nitty-gritty of elements, functional tests provide a comprehensive evaluation of overall application performance.
Benefits of Functional testing
In this section, let's discuss some of the benefits of running a functional test.
- It focuses on the requirements of the guidelines for end-users to test the various models of the applications.
- It helps to reduce the gap between the defects and ensures that the results are accurate as desired.
- Testing security evaluates software vulnerability to various attacks. There can be illegal break-ins; thus, good security testing is executed to ensure protection.
- It indicates the flaws essential for decision-making; it prioritizes the demands of features upon the risk and allows focusing on creating functions that work efficiently.
- Once the software's functionality is tested, all the minute bugs and errors will be detected and eradicated. You'll get an application that's free from all types of glitches.
Subscribe to the LambdaTest YouTube channel to learn more about Selenium automation, Cypress testing, and much more.
Types of Functional testing
There are numerous types of functional tests. Here is a quick breakdown.
- Unit testing: From the initial stage of the development process, unit testing involves testing individual units of the web app to ensure that each block of code/unit performs as intended. Also, developers (the one who has written the unit code) usually execute the test.
- Integration testing: Functional Integration Testing ensures the different components are combined and tested to check if they work effectively. This testing connects modules as expected and enables operational commands and data to act as a whole system rather than individual components. In addition, it aims to expose the faults in the interaction between the integrated units.
- Smoke testing: It is also known as build verification testing. Smoke testing is a subset of test cases performed on any new release to test the basic functionalities of the web app and ensure that it works well enough to move on to additional tests.
- User acceptance testing: Often referred to as the final phase of testing, user acceptance testing verifies if the software can run smoothly & manage required tasks in real-world scenarios, according to specifications.
- Sanity testing: Encountering bugs post-deployment? Sanity testing assures that the modification in the new build has resolved the bug without additional bugs. It is to verify that all the functions are running combined and individually.
- Regression testing: Releasing a new feature to your web app? It is of utmost importance that the new code, enhancement, or feature doesn't affect the existing code. Therefore, regression testing focuses on ensuring that the code changes should not disrupt the system's existing functionality.
Unit tests also provide additional assurance to functional tests by identifying the components that can cause an app outage. As software development progresses, it becomes harder to identify failed tests. Thus, developers often write unit tests to ensure individual units function correctly before integrating them with other parts of the code.
By testing early in the software development cycle, you can deliver your product faster with better quality.
Both developers and testers can execute integration testing.
For example, smoke testing verifies that the application launches successfully and will check that GUI is responsive. However, if the test fails, it signifies the current release is not stable and needs to be fixed.
It is often confused with smoke testing; however, smoke testing is executed to verify the end-to-end functionalities of a web app, whereas sanity testing is performed to verify new functionalities of a web app.
Regression testing is often time-consuming and exhausting, as testers need to perform it every time a new feature is added to the application. However, you can easily overcome this issue by switching to test automation. This process helps you automate repetitive tests and scale them to increase your test coverage with the help of the Selenium grid.
Run your Selenium tests across 3000+ desktop and mobile browsers. Try LambdaTest Now!
Example of a Functional test
Let's consider the following scenario where a user tries logging into an HRMS portal. The HRMS portal's login page contains two text fields—one for users to enter their username and the other for their password—and two buttons - Cancel and Login.
The user enters their login details into the input field, clicks the Login button, and is routed to the HRMS home screen. When the user clicks the Cancel button, the login gets canceled.
Specifications:
- The username field must contain a minimum of six characters and a maximum of ten, numbers (0-9), letters (A-Z, a-z), special characters (period, hyphen, and an underscore), and cannot be left blank. The user ID must begin with a number or letter.
- The password field must contain a minimum of six characters and a maximum of eight, numbers (0-9), letters (A-Z, a-z), and special characters, and cannot be left blank.
Functional Testing Techniques
Here are some techniques you might consider using to create a functional test suite.
- Boundary value tests: It checks to see if the input is valid by evaluating what happens if a user enters a number that is too large or attempts to enter non-numeric input.
- Decision-based tests: It verifies the results after a user takes action.
- User-based tests: It verifies how components of an application interact with each other.
- Ad hoc tests: At the end of the development phase, you can run ad hoc tests to see if there are any bugs that other methods did not uncover.
Steps to perform Functional testing
Now that we've learned what functional test is and its different types, it's time to discuss how to perform it. Here are the steps to help you with that.
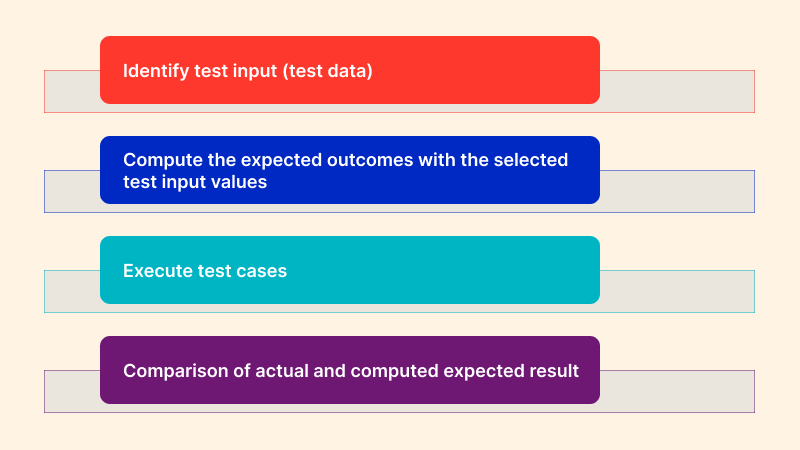
- Identify and define: Before starting, you need to know why you are building it. Initiate with the broader purpose, strategically define your goals, and narrow your focus on what you expect from the application. Testing goals should be intended for successful test executions and efficiently handling errors and unexpected scenarios.
- Create: Create the input data (all-important) scenarios based on a predefined functional specification you need to test in the main component of the testing. Ensure that the data simulates normal use conditions based on your identified test scenarios.
- Determine: Based on the functional parameter, determine the expected outcome (both negative and positive you want from the test.
- Execute: Write the test cases and run them to gather the test data.
- Compare: Once the test results are generated, compare the actual and expected results.
Why automate your Functional tests?
Test automation is a practical approach to doing things in a streamlined manner. With so much agile development, it is essential to automate functional tests where internal regulating processes rigidly lead to more accurate test results.
Automated functional tests can run 24/7 without human intervention. As a result, it is much faster than the manual and thus takes a much shorter time, and the chances of errors are lowered as human errors, such as skipping tests & inaccurate data. Further, one can tweak tests simply by changing the test data, enabling you to efficiently run sequential tests with slightly different data to compare the results.
How to select the right automation testing tool?
Before starting with functional test automation, you need to decide which kind of tests to automate. Once the test definition is ready, select the right set of tools to help you perform the tests.
Selenium is the most popular web automation framework for automation testing, allowing you to test web applications across different browsers (Chrome, Firefox, Internet Explorer, etc.). However, choosing the right tool is crucial in an automation process.
When choosing an automation tool, keep the following in mind:
- How simple is creating and maintaining scripts with the test tool?
- How many platforms is the tool compatible with? Web, mobile, desktops, etc.
- How many different languages does the test execution tool support?
- Is there a reporting mechanism built into the tool?
Functional testing tools
There are numerous tools available to perform automated functional test, but choosing one can be confusing. In this section, we list down some of the best tools for you.
- Selenium: Selenium is an open-source tool covering a variety of tools and libraries for browser automation. It offers a playback tool for building functional tests in modern web browsers, eliminating the need to learn a test scripting language.
- JUnit: JUnit is the default choice of developers to automate unit testing. Developed by Erich Gamma and Kent Beck, it is primarily used for scripting and automating repetitive test scenarios. It can also be used to automate web application testing with WebDriver.
- Avo Assure: Avo Assure is a solution that provides complete test automation with no code. Its heterogeneous capability lets you test apps on the web, mobile, desktop, ERP applications, and more.
To run a functional test of the software application, you need to test it in multiple environments like different browsers, browser versions, and operating systems. You need access to real devices, browsers, and operating systems when running the tests to check the app's behavior in different environments.
Continuous quality cloud platform like LambdaTest enables you to perform manual and automated testing of your software applications (websites and mobile apps) across 3000+ real browsers, devices, and operating systems. With its real device cloud, you can test applications in real-world environments and get instant, accurate results.

How to perform Functional testing using LambdaTest?
With LambdaTest, you can run manual and automated functional tests of websites and mobile apps on an online browser farm. You can leverage other features that the LambdaTest platform offers, like visual regression testing, responsive testing, HyperExecute, and more.
In this section, we will discuss how to get started with your first manual (or real-time) and automated functional test.
Real Time Testing
LambdaTest offers live-interactive testing, which will help you deliver error-free software applications as you perform tests to check the intended functionality of features on your website.
Here are the steps to run a manual functional test on the LambdaTest platform.
- Sign up for free and login to your LambdaTest account.
- From the left sidebar menu, visit Real Time Testing > Browser Testing
- Enter your test URL, and select a desktop or mobile. If you want to test on a desktop, choose the RESOLUTION, OS, and VERSION of the browser. Then, click START.
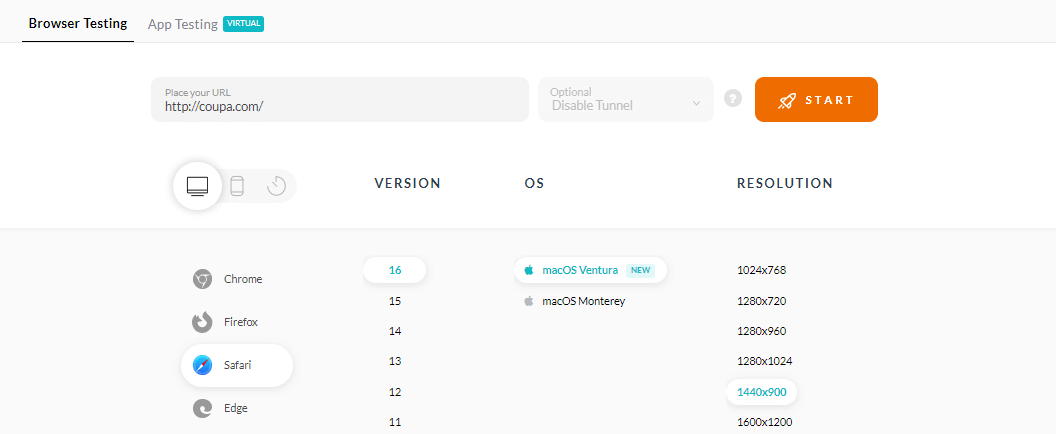
It will launch a cloud-based real operating system running the real browser. You can now start your manual functional test.
Automation Testing
LambdaTest supports automation testing frameworks like Selenium, Cypress, Playwright, Puppeteer, Appium, and more. Furthermore, you can leverage the parallel testing feature to expedite your software release cycles.
Check out the steps to get started with your first automated functional test.
- Login to your LambdaTest account.
- From the left sidebar menu, navigate to Automation > Builds.
- Select your preferred programming language and testing framework, then begin automating your functional tests.

Best practices of Functional testing
Running a functional test is an eminent way to ensure the great quality of your application. Here are some tips and tricks that will help you do it efficiently.
- Shift left and test early: Want to ship faster without any hurdles? It is time to adopt the shift-left approach. Detect issues with functions on your app or website early in the software development lifecycle (SDLC) and prevent them from having a real impact. By testing functionality early, you can save money by identifying design issues with specific functions before they become too costly and delay the launch process.
- Understand the end user's perspective: Whenever executing functional test, ensure to include the end user's thought process. Defining the scenarios per your target audience can enable you to precisely define the cases, thus saving time. Furthermore, each type of user has a different utilization; plan the navigation of the application post considering the audience.
- Prioritize: Remember, testers have limited time and resources; thus, proceeding vaguely can skip some of the features. Mark the application features on high priority and take their testing precedence over lower priority features.
- Reduce and reuse: Developing new & unique test cases is time-consuming; instead, adopt the approach of reducing and reuse. Reuse the prepared test cases by writing them in simple languages and further modify them according to the need. This way, instead of creating new test cases every time, you will reduce your time & focus on other tasks than this.
Conclusion
Your goal as a developer, tester, or product manager is to prevent failures and setbacks entirely. The key is to frame strategies that test every function or requirement. However, remember to focus on the "big-picture" and resolve the higher priority task, preferably by automation testing before release. The aim is to build a product that embraces your user with a great experience. The rest of the bugs can be fixed with the importance of the functionality you are testing.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is functional testing in QA?
Functional testing in QA involves verifying the quality, stability, and functionality of your website or web app. It executes tests on each function & validates output as per the requirement. The aim is to create an error-free web app by testing the usability, specific error conditions, accessibility features, and other important aspects of the software.
What are the different types of functional tests?
The different types of functional tests include unit testing, regression testing, user acceptance testing, integration testing, etc.
What is the difference between unit test vs functional test?
Unit testing focuses on testing individual components or units of code to ensure they function correctly in isolation, while functional testing verifies the overall functionality of the application and checks if it meets the intended business requirements.
What is functional and non functional testing?
Functional testing focuses on verifying the functional requirements of a software system by testing its individual features or components. Non-functional testing, on the other hand, assesses the system's performance, usability, security, reliability, and other quality aspects
How to perform functional testing?
To perform functional testing, identify the functional requirements, design test cases that cover various scenarios, execute the tests by providing inputs and evaluating outputs, and compare the actual results with expected results. Use testing techniques like black-box testing or white-box testing as appropriate.
Who performs functional testing?
Functional testing is typically performed by dedicated testers or quality assurance professionals who have expertise in understanding the functional requirements, designing test cases, executing tests, and reporting defects. In some cases, developers may also perform functional testing to ensure their code meets the specified functionality.
Did you find this page helpful?
Reviewer's Profile

Salman Khan
Salman works as a Digital Marketing Manager at LambdaTest. With over four years in the software testing domain, he brings a wealth of experience to his role of reviewing blogs, learning hubs, product updates, and documentation write-ups. Holding a Master's degree (M.Tech) in Computer Science, Salman's expertise extends to various areas including web development, software testing (including automation testing and mobile app testing), CSS, and more.
 Christmas Deal is on: Save 25% off on select annual plans for 1st year.
Christmas Deal is on: Save 25% off on select annual plans for 1st year.