What is Defect Management in Software Testing
- Learning Hub
- What is Defect Management in Software Testing
CHAPTERS
- Overview
- What is the Defect in Software testing
- What is Defect management
- Why should you consider Defect management
- Benefits of Defect management
- Limitations of Defect management
- Defect management life cycle
- Phases of Defect management
- Role of Defect Report in managing defects
- How to manage your defects effectively
- Important Defect metrics
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
OVERVIEW
Defect management is the process of identifying, documenting, and tracking defects (bugs or issues) in a software product. It is an important part of the software development process that ensures defects are identified and addressed in a timely manner.
Analyzing bugs that need identification, documentation, monitoring, and addressing large codebases of complex software applications can be a daunting task. In addition, satisfying the expectations of end-users is also crucial. This is where Defect management comes to the rescue.
Since making a software application 100% defect-free is impossible, Defect management helps minimize defects, identify defects in the earlier stages of the software development lifecycle, and mitigate the impact.
What is the Defect in Software testing?
Defects in software testing are variations between the end’s requirements or business requirements. A defect in a software application is an error in the application’s code that provides the expected output.
Testers who validate a code snippet see deviations or differences between the expected and existing outcomes. These variations are known as defects. They typically identify defects during test execution.
The defect is also known as bugs, issues, or incidents.
What is Defect management?
Defect prevention is far more successful and efficient in lowering the number of flaws when managing defects. It also makes it very affordable to repair any shortcomings discovered early in the software development process. Simply put, finding and addressing issues constitutes the Defect management process.
Less buggy software will be readily available in the market if Defect management is conducted more effectively and with full attention. Most businesses use a Defect management process that includes defect discovery, removal, and improvement.
The primary objectives of adopting Defect management for various projects or organizations are:
- It offers operational help for fixing and retesting discovered flaws.
- It provides information for a defect status and progress report.
- It gives suggestions for guidance on defect release.
- It determines the primary cause of the condition and suggests fixes.
Why should you consider Defect management?
A reductive process, defect data management requires as much input as feasible. Customers, product managers, quality test engineers, software engineers, and tech support staff have important fault input that needs documentation. It functions best when everyone notifies the system of any uncovered flaws.
You must consider Defect management because it helps in several ways, such as -
- Removing false positives brought on by test environment anomalies, test code or data problems, or test process flaws.
- Deleting duplicate entries when a bug produces results that appear to testers to be a collection of unrelated issues.
- Removing items from the list won't deter people from reporting defects on a timely basis.
Benefits of Defect management
Before proceeding further in this Defect management tutorial, let us look at the benefits of the Defect management process, which optimizes the organization's workflows. Software tools involve the detection or tracking of non-technical issues.
- Existence of defect tracking tools: Defect tracking is one of the critical steps in the Defect management process. Many defect tracking tools are available to track flaws like Jira, Trello, Asana, Hive, etc.
- Verify resolution: Defect management process also aids in determining whether or not all issues that are discovered or tracked have been addressed. Simply say, it enables us to ensure the rectification of tracked issues.
- Provide useful metrics: The Defect management process offers defect metrics and automation tools. These defect metrics are helpful for reporting and ongoing development.
Limitations of Defect management
Having looked at the benefits, you must also consider the limitations for adequately implementing the process in the correctly designated areas.
- If you do not handle the Defect management process correctly, there will be a significant cost increase over time, and consequently, it would escalate the product price.
- If faults or defects are not handled correctly at an early stage, they may later cause more harm and increase the cost of repair.
- If the Defect management process does not execute correctly, further drawbacks such as loss of revenue, customers, and tarnished brand reputations can occur.
Defect management life cycle
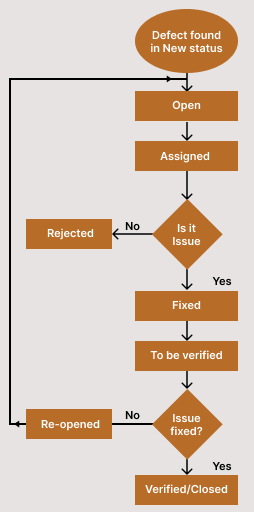
The below defect life cycle describes the workflow of the Defect management process -
- Whenever the testing team discovers a bug in the software, they mark it as "New."
- An “Open” status indicates that the issue is ready to be assigned to the development team once a QA lead assesses it and determines it to be valid.
- The status of the defect changes to "Assigned" when a QA lead assigns it to the appropriate developer. At this point, a developer needs to start identifying and fixing the flaw.
- The developer rejects the flaw when they believe it to be untrue or invalid. The testing team receives a new assignment, and the defect has the status of "Rejected."
- An “Open” status indicates that the issue is ready to be assigned to the development team once a QA lead assesses it and determines it to be validThe defect status is changed to "Duplicate" if the problem is reported twice or if both defects have the same symptoms and procedures for reproduction.
- If difficulties or hurdles in the current release prevent a specific flaw from being fixed, that defect receives the status of "Deferred" or "Postponed."
- Developers can identify a flaw as "Not Reproducible" if they cannot reproduce it using the "Steps to Reproduce" provided by the testing team. The testing team should now give developer-specific reproduction instructions
- Developers can flag bugs as "Need additional information" if they are unclear about the procedures provided by QA to reproduce the fault. The testing team must give the development team the necessary information in this situation.
- A flaw is marked as a "Known defect" if it is already known and present in the production environment.
- The error is "Fixed" when a developer makes the required adjustments
- The developer now changes the status to "Ready for Retest" and sends the bug to the testing team for verification.
- The tester marks the defect as "Closed" if it correctly validates and there are no new issues.
- The remark of the problem is "Reopened" if the tester discovered during retesting that it was still reproducible or only partially fixed. The developer must now investigate this flaw once further
Phases of Defect management
We are often involved in designing, testing, deploying, and shipping products that we cannot get ahead to put proactive Defect management processes and tools to reduce the risks upfront
So, let us look at the Defect management phases in detail to manage our defects effectively
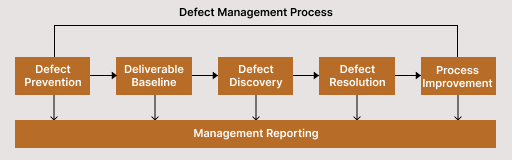
- Defect prevention: Defect prevention is the first step in the Defect management process. The optimal approach is to correct any flaws discovered early in the testing process rather than waiting until they are found and fixed.
Because it is less expensive, you can lessen the impact in the initial stages of addressing or resolving faults. But for later stages, finding flaws and then fixing them can be expensive, along with exacerbating the impacts of a problem.
The following are the main steps in defect prevention:
This approach saves money because addressing flaws discovered during early testing doesn't need much. The best method for minimizing the impact of a defect is to remove it within the initial development stage.
- Determine critical risks: By identifying the risk, we can analyze the projected financial impact of each crucial situation. Determine the system's critical risks, which will have a more significant impact if they arise during testing or later. The risk of defects is reduced in this stage by following procedures, methodology, and best practices.
- Estimate expected impact: Once we identify every considerable risk, we may focus on the higher risks to the system and attempt to reduce or eliminate them. You can't eliminate options that will lessen their likelihood of happening and their economic implications. For each critical incident, determine the financial impact of the risk.
- Reduce predicted impact: After identifying all significant defects, focus on the top defects that, if present, could affect the system and attempt to reduce or remove the risk. Because when it comes to defect prevention, we can immediately pinpoint the system's key risks that will have a more significant impact if they materialize during testing or at a later stage.
- Deliverable baseline: The Deliverable baseline is the second step in the Defect management process. Here, the delivery defines the design, documentation, or development.
When a deliverable (or product) hits its predetermined milestone during development, we can state that it is a baseline. As the product is transferred from one milestone to the next, the defect in the deliverable has a more significant impact on the existing system. In other words, we may claim that you can control the further changes once a deliverable is baselined.
- Defect discovery: It is the next step in the Defect management process. It is impossible to make a system defect-free by eliminating all of its flaws. Additionally, it could result in longer-term harm. However, you can spot the flaws early on before they increase the project's cost.
The following steps in the defect discovery process:
Only a flaw is detected if developers have acknowledged or recorded it as a valid one. When a fault is officially reported to the development team and recognized as a defect, we can claim the defect's detection.
- Find a defect in the system before it becomes a significant issue. It is the first step in the defect discovery process.
- As soon as the testing team discovers a defect, they have to inform the development team that there is a problem that needs to be looked into and fixed.
- If a genuine issue is assigned to the development team by the testing team, it is the development team's job to acknowledge the defect and go forward with fixing it.
- Defect resolution: It involves fixing the flaws step-by-step. The method of fixing a defect starts with assigning it to a developer, who then schedules it for correction according to priority, sets it, and sends a resolution report to the test manager. To fix the issue, you can take the actions below.
To fix the issue, you can take the actions below.
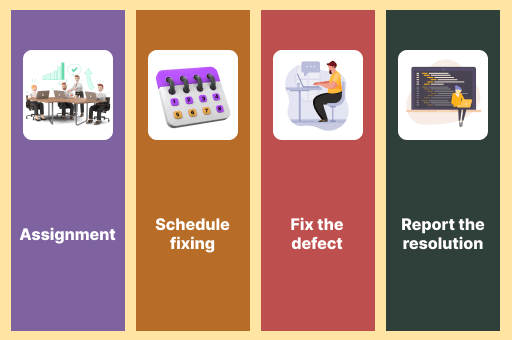
- Assignment: It involves assigning a task to a developer (or other technicians) and changing the status to ‘Responding.’
- Fixing the schedule: Fixing the schedule: The developer side is in command in this phase. Depending on the priority of the issues, they will develop a plan for improving them.
- Fix the flaw: The test manager keeps track of the defect-fixing process compared to the above timeline while the development team is working to address the shortcomings.
- Report the resolution:When you fix the bugs, ask for a report from the developers detailing the resolution.
- Process improvement: All the stages mentioned above involve organizing and fixing the defects. We will now examine the lower priority issues because they are still crucial and impact the system during the process improvement phase. From the standpoint of the process improvement phase, all acknowledged issues are equivalent to significant defects and must be fixed.
Everyone involved in the project must look back and determine the source of the issue to improve the process. Though you need to prioritize faults and address them during the defect resolution process, this does not imply that lower priority issues are unimportant or do not significantly influence the system from a process standpoint.
All flaws found are considered critical problems from the process improvement perspective. Based on that, you can adjust the base-lining document, review process, and validation process to catch defects earlier in the Defect management process when they are less expensive.
Role of Defect Report in managing defects
A defect report is a detailed document that contains defect information like its description, stack traces, expected and actual outcomes, and other vital information. It ensures the defect is identified and fixed before it affects our users. A defect report can be 2 to 20 pages or more.
You should include the following information in your Defect report.
- Defect ID: Maintain a unique defect ID. You can also generate it via bug tracking tools.
- Heading: Give a short and crisp heading that defines the problem statement.
- Description: A summary of the defect describes how and when the defect was found.
- Screenshots and video recordings:Attaching a screenshot of the defect and its video recording can help you locate the issue quickly.
- Expected vs. actual results:Convey what should be the expected results and what is the actual result to help the developer get a clear picture of what’s expected and what’s not.
- Environment: Include the necessary information about the test environment like browser, version, operating system, resolution, etc.
- Source URL: It helps developers know the defect's exact location.
- Priority and severity: Specify the severity of the defect and prioritize it accordingly.
- Additional information:Provide extra chunks of information like your name, due date, developer to whom the task has been assigned, etc.
Intrigued to know how to write a good bug report? Check our advanced guide on how to write a bug report.
How to manage your defects effectively?
Defect management is the key aspect of the software development process. Irrespective of whether the bug is minor or major, it’s vital to log, manage and fix each defect to build effective and scalable applications. Hence, choosing a defect management platform is critical. Several solutions like LambdaTest available in the market come with defect tracking features.
LambdaTest is a cloud-based cross browser testing platform that enables developers and testers to perform live-interactive and automated testing of their websites and applications across 3000+ real browsers, devices, and operating system combinations.
It also offers testing on a real device cloud that helps you identify all the bugs while testing your web and mobile apps in real-world scenarios. LambdaTest supports different developer tools for app and web testing that make it easier to identify and fix defects instantly.
While testing applications, if you come across any defects, you can directly mark and report them using LambdaTest’s one-click bug logging feature to your favorite bug tracking tools like Jira, Asana, Trello, Bugasura, etc.
You can subscribe to the LambdaTest YouTube Channel and get the latest tutorials around Automation testing, Playwright, Responsive testing, and more.
LambdaTest has an in-built Issue Tracker that allows you to track and manage defects in one place. You can share your logged defects across various platforms to your team members via e-mails and shared links, export them in PDF and XLSX formats, and do much more. Issue Tracker also has the Reproduce at LambdaTest feature to retest your defects on the same test environment.
LambdaTest also has a Test Logs library that contains all the logs of your browser and app testing.
Important Defect metrics
Let’s consider that you reported 52 bugs, and out of them, only 34 are identified as actual defects. It implies that 18 reported defects were incorrect and involved some error while performing software testing. So, how can you estimate the quality of test execution?
A few metrics are helpful when it comes to measuring the quality of test case execution
- Defect rejection ratio: Number of defects rejected/Total number of defects identified)*100
- Defect leakage ratio: Number of defects missed/Total number of defects identified)*100.
If the value of DRR and DLR is low (5~10%), the better the quality of the test execution
For the above scenario, the defect rejection ratio is 34.61%, and the defect leakage ratio is 52.94%
Conclusion
Defect management is the core of software testing. The entire software development process should adhere to the Defect management approach, not just specific testing or development activities.
You can find and fix software issues as a part of the Defect management process. The entire Defect management procedure will assist in identifying the issue as early as possible and ensuring that the end-users get a high-quality product.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the purpose of Defect management?
The primary purpose of Defect management is to minimize the issues or bugs in the software development process. It helps continuously monitor application quality throughout the entire software lifecycle.
What is Defect management cycle?
It is the cycle of a defect, right from identifying defects to its closure. The defect cycle ensures the software is of optimum quality. Preventing, identifying, and rectifying defects is essential to improve software quality.
What is the difference between Bug and Defect?
The terms 'bug' and 'defect' are often used interchangeably in software testing, but they have distinct meanings. A bug refers to a specific error or flaw in the software code that causes it to malfunction or produce unexpected results. On the other hand, a defect is a more general term used to describe any flaw or imperfection in a product that hinders its value or usability. While both represent issues in the software, bugs are more specific to coding errors, while defects encompass a broader range of imperfections.
Author's Profile

Swapnil Biswas
Swapnil Biswas is a Marketing Specialist at LambdaTest, a tech enthusiast, and a passionate writer with deep expertise in Search Engine Optimization. Known for his innovative marketing strategies, Swapnil's prowess has earned him a place on the Wall of Fame for marketing. His unwavering dedication to professional growth and his enthusiasm for technology mark him as a standout professional in the marketing industry.
Reviewer's Profile

Shahzeb Hoda
Shahzeb currently holds the position of Senior Product Marketing Manager at LambdaTest and brings a wealth of experience spanning over a decade in Quality Engineering, Security, and E-Learning domains. Over the course of his 3-year tenure at LambdaTest, he actively contributes to the review process of blogs, learning hubs, and product updates. With a Master's degree (M.Tech) in Computer Science and a seasoned expert in the technology domain, he possesses extensive knowledge spanning diverse areas of web development and software testing, including automation testing, DevOps, continuous testing, and beyond.
Try LambdaTest Now !!
Get 100 minutes of automation test minutes FREE!!
 Christmas Deal is on: Save 25% off on select annual plans for 1st year.
Christmas Deal is on: Save 25% off on select annual plans for 1st year.