What is Ad Hoc Testing: A Complete Guide
- Learning Hub
- What is Ad Hoc Testing: A Complete Guide
OVERVIEW
Ad hoc testing is the process of creating tests based on a need to test. These tests are not created as part of a set plan or to test specific features but rather to ensure that specific areas of the product work correctly. It is also performed as part of regression testing to ensure that new patches and fixes do not cause any issues with the current version of the product.
A tester must be willing to challenge any idea, no matter how good or absurd. One of the best ways to test your ideas is through Adhoc testing which is a great way to discover new issues and risks with minimal effort. It allows you to take a more creative approach and try new things to find a problem by not formalizing the process.
In this testing tutorial, let’s deep dive into what Adhoc testing is, its advantages, disadvantages, best practices, characteristics, etc.
What is Adhoc testing?
Ad-hoc testing is a style of informal, unstructured software testing that seeks to break the testing process to discover potential flaws or faults at the earliest. It is performed randomly and is typically an unplanned activity that does not adhere to test design principles or documentation when writing test cases.
Here, the software test is carried out without adequate planning and documentation. If we don't find any flaws, such tests are merely run once.
Ad-hoc tests are conducted after the application has undergone formal testing. As there are no test cases aligned for certain scenarios, problems discovered using this method are challenging to recreate.
Testing is done with the tester's knowledge of the application, and the tester tests randomly without adhering to the requirements or specifications. Therefore, the ability of the tester who does the test determines the success of the Ad-hoc test. Without adequate planning or documentation, the tester must rely exclusively on intuition to uncover flaws.
Importance of Adhoc testing
The primary goal of a Ad hoc test is to identify any flaws through random testing. The tester improvises the steps by randomly executing them. This can reveal highly specific and relevant defects that are often ignored when using other approaches.
Running Adhoc tests help you,
- Identify loopholes in your test strategy.
- Avoid costly setbacks.
- Streamline testing workflows and scripted methods.
- It quickly detects flaws using out-of-the-box testing.
Characteristics of Adhoc testing
To maximize the benefits of testing efforts, Adhoc testing possesses some of the following characteristics:
- This testing takes place after the program has undergone formal testing procedures. They are used to identify application irregularities that cannot be predicted before testing.
- Testers and developers employ exploratory testing, generating random testing processes and running tests based on error guessing instead of creating test designs.
- Only testers who are extremely familiar with the application's inner workings are capable of performing this testing. This is true because effective "error guessing" can only be performed when the tester is aware of the functions and workings of the software.
- They always align with the test's goal.
- This approach is best suited for identifying errors and inconsistencies that lead to serious application flaws. These mistakes are frequently quite challenging to find.
Advantages of Adhoc testing
Ad-hoc tests can be completed in a short time. It helps to develop unique test cases. This test aids in creating a robust product that is less vulnerable to issues in the future. Let's look into some of its additional advantages.
- Adhoc test can be carried out at any point in the Software development Life Cycle (SDLC) as it need not adhere to any process.
- It is not only the domain of the testing team; the developer can also participate.
- Because of the many cutting-edge techniques that may be used to test the software, the major advantage is that a tester can identify more flaws than traditional testing.
- A quality product can be delivered on deadline even when in-depth testing is needed in a short amount of time.
- Because there is no requirement for documentation, the tester is not subjected to an additional load. The focus of a tester can be on comprehending the underlying architecture.
- It aids in identifying unknown areas in test scenarios, enhancing the product's immunity.
- The testers can freely explore the program according to their intuition and comprehension. They can then run the tests as they go, assisting them in identifying mistakes as they go.
Limitations of Adhoc testing
The main problem with Ad-hoc tests is that it's hard to track what has been tested, what hasn't been tested yet, and what the test results mean. Since there are no plans for the tests ahead of time, there's no way to know what edge cases and error conditions have been tested or haven't been tested yet. In fact, there are a few more limitations that we will discuss here.
- Ad hoc test depends on the test engineer's product knowledge because they are familiar with the application's flow and are aware of potential points of failure, whereas a new test engineer may not be.
- It is exceedingly challenging for the tester to recreate an issue because the testing method is not defined, and no specific test case is used. This is because the tester must recall his precise steps to obtain that error, which is not always achievable.
- Invalid errors are occasionally reported due to the tester's random selection of invalid test cases, which causes a problem for the subsequent error-fixing procedures.
- To accurately identify the problems in any model, one needs to have a solid understanding of both the product and testing concepts.
- The lack of planning throughout this testing makes it sometimes difficult to reproduce the error.
- There is no assurance that a mistake will be discovered.
- There is no way to account for the time and effort put into this form of testing because it is not planned or scheduled.
When to conduct Adhoc testing and when not to?
Most of the time, test teams are constantly weighed down by having too many things to test within constrained timeframes. Numerous testing tasks developed from the formal process must also be completed in that short time. Ad hoc testing has a small chance of making it into the testing in these circumstances.
It is typically performed when there isn't enough time to finish extensive testing, which entails creating test requirements documents, test cases, and test case designs. The best time to conduct this type of testing is after formal testing techniques are finished.
On the other hand, Ad-hoc testing can be done as the software is being developed. It can be done after just a few modules have been produced or even after the entire program has been developed. Additionally, it could be done as a part of the formal testing process. There are a few situations, though, where this testing is unnecessary. Every tester must therefore be aware of when to refrain from conducting this form of testing.
When not to conduct Adhoc testing?
Ad-hoc tests can be efficient and productive, but as skilled and experienced testers, we also need to determine when to forego this kind of testing. Here are some suggestions when it is not essential, though it is up to the tester's choice in each case.
- When Beta testing is being done, Ad-hoc testing is not allowed. Because clients evaluate the software that has been produced to suggest new features that should be added or to alter the requirements for it as beta testing involves clients.
- Additionally, it is suggested against performing this testing on test cases that already contain mistakes. Before the errors are eliminated from the system, they must first be accurately documented. The test cases must be retested to confirm proper operation after being fixed.
- Another instance is the addition of a very basic UI interface. Here, conventional positive and negative testing should be sufficient to identify most flaws.
Types of Adhoc testing?
Adhoc testing is categorized into three types as listed below:
- Buddy Testing
- Pair testing
- Monkey Testing
A test member and a development member will work on the same module during this testing. The tester and developer get down and work on the module together right after the developer finishes the unit testing. The two ‘buddies’ team works together on that module to create valid test cases. This testing type helps the tester and developer examine the feature from a broader perspective.
Also, both the tester and the developer will better understand the several tests the other performs, which will assist the tester in avoiding creating invalid situations and hence avoid invalid faults. It will enable one to think similarly to another.
In this testing, two testers collaborate on a module using the same test environment. This type of testing is designed to find a variety of flaws by having the two testers brainstorm ideas and approaches. Both buddies can collaborate on the testing process and create the necessary documentation for any findings.
Together, they use the same machine to share knowledge, opinions, and ideas to find flaws and errors. Testers are partnered according to their levels of competence and knowledge to gain a diverse perspective on any issue.
During the development process, the software is tested using arbitrary inputs, or "monkey testing," to uncover obscure or unusual problems. Any number of developers and testers can perform monkey testing. It doesn't follow set rules, such as the number of developers or testers using it, is generally referred to as "monkey testing" in general. This testing is mainly performed at the unit testing level.
Skills required to perform Adhoc testing
There are numerous skills that need to be acquainted with while performing Ad-hoc tests. Some of them are:
- The product should be thoroughly understood by the testers.
- The application should be tested with real-world expertise.
- The group should concentrate on giving priority to crucial aspects.
- Rough planning to give the testing process a direction.
- The ability to record observations and recording errors.
- Testers should think out-of-the-box scenarios.
Adhoc testing vs Exploratory testing
Exploratory testing can identify bugs more quickly and earlier in the development cycle. Ad-hoc testing has many of the same advantages as exploratory testing. However, by definition, there is little distinction amongst the two. And being aware of the difference would prevent any potential misunderstandings. Let’s know the comparison.
| Adhoc Testing | Exploratory Testing |
|---|---|
| Learning the application is the initial step, followed by performing the actual testing procedure. | The process starts with testing the application, followed by an investigation to understand it. |
| There is no need for any kind of documentation. | Documentation on the details of the testing is required. |
| Adhoc test requires knowledgeable testers who are aware about the program. | An expert is not required to explore the application. |
| After all the necessary data has been gathered, testing can begin. | Data gathering and testing occur simultaneously during exploration testing. |
| It works for negative testing scenarios. | It mainly goes with positive scenarios. |
| It concentrates on improving the testing procedure. | It emphasizes learning the application. |
| The tester's creativity and intuition will determine this. | The tester's perception and curiosity will determine this. |
| There is no time restriction. | It is a time-boxed method. |
Adhoc testing tools
Ad-hoc testing tools allow you to create a test case without having to go through the process of creating a formal test plan. These tools are often used in agile testing environments where rapid, iterative testing is necessary to keep pace with development cycles.
Here is a list of tools. Let’s have a read.
- Selenium
- QTP
- Cucumber
When it comes to automated browser testing, Selenium is undoubtedly the most well-known tool. The open-source framework Selenium is a wonderful choice for a team that wants to adopt Ad-hoc testing. Selenium is the tool of choice for Quality Assurance (QA) engineers with a high level of programming proficiency. Setting up and integrating a framework into your current development cycle demands a thorough understanding of how it functions.
For cross browser testing, Selenium supports many well-liked OSs (Windows, macOS, Linux) and browsers (Chrome, Firefox, Safari).
QTP, aids testers in running automated tests to find any flaws, faults, or gaps that deviate from the application's intended results. It allows testers to refer to the screen object properties while recording scripts on an active screen. It has a great system or procedure for identifying objects. Micro Focus’s UFT uses VBScript to automate applications.
Cucumber is another testing tool that enables Behavior Driven Development. It provides a means to write tests everyone can comprehend regardless of technical ability. Before developers create their code in BDD, users (business analysts, product owners) first write scenarios or acceptance tests that describe the behavior of the system from the perspective of the customer. These scenarios and acceptance tests are then reviewed and approved by the product owners. The Cucumber framework uses Ruby programming.
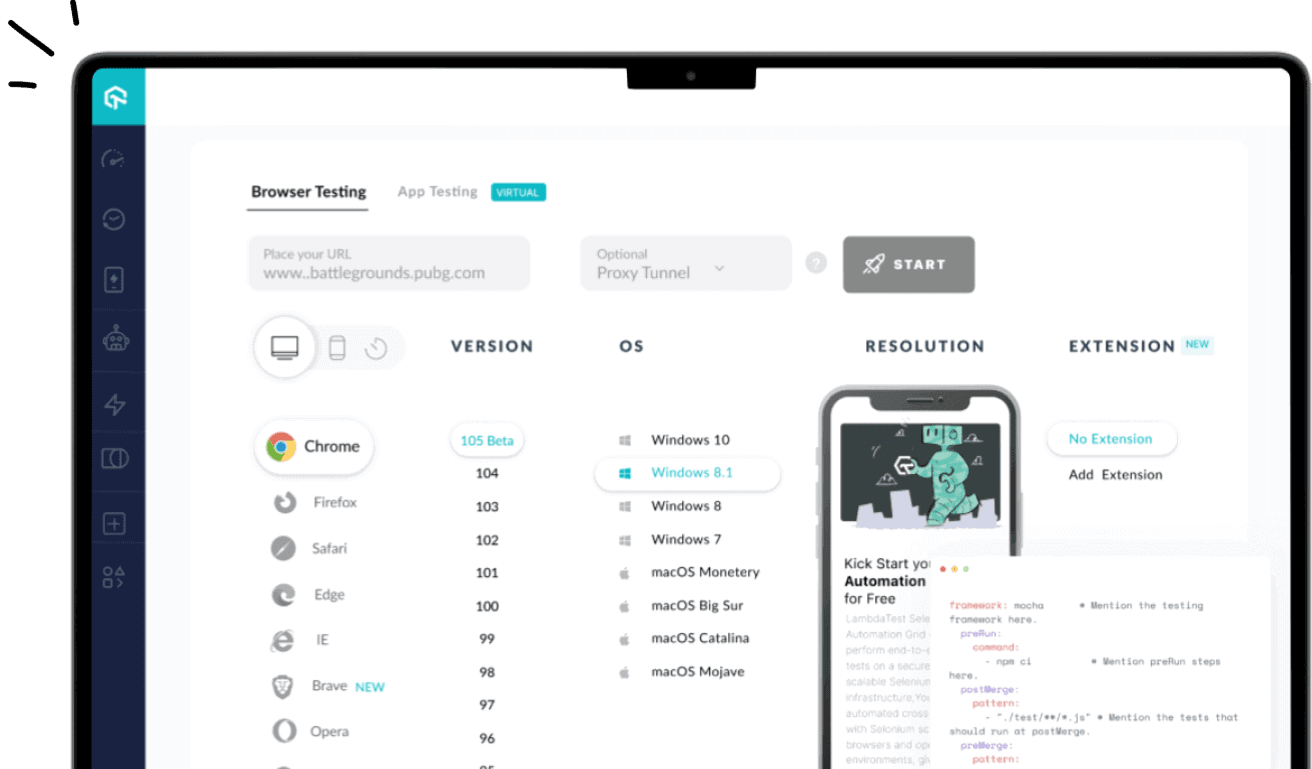
How to perform Adhoc testing on LambdaTest?
Every organization cannot and need not set aside budget or data center capacity to support such a massive testing environment for their testers. Instead, businesses might investigate cloud-based platforms like LambdaTest, a platform for cross browser testing that enables access to an online browser farm of 3000+ browsers and OS for web testing and mobile app testing.
Businesses can produce perfect outcomes in real-time situations with the help of LambdaTest's cloud infrastructure.
Customers can use LambdaTest Infrastructure with other testing tools like Selenium, Cypress, Appium,and HyperExecute. Organizations can integrate with best CI/CD tools (Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment) like Travis, Circle CI, Jenkins, Bamboo, AWS CodePipeline, and others with the LambdaTest platform to increase the productivity of the entire team working on the Ad-hoc testing process.
Performing manual Adhoc testing
In the case of manual testing, one might use browsers to examine the visual and behavioral characteristics of the components by invoking any relevant events. We could use LambdaTest's online testing cloud platform to quickly set up the necessary infrastructure and run our test cases with numerous browsers, operating systems, and devices needed to conduct these tests is immense.
For manual live testing of your web pages, LambdaTest's Real Time Testing is a fantastic option. If you haven't already, just register for an account on the LambdaTest Registration Page to play around with the features.
You could notice plenty of options from which to select to carry out Ad-hoc testing.
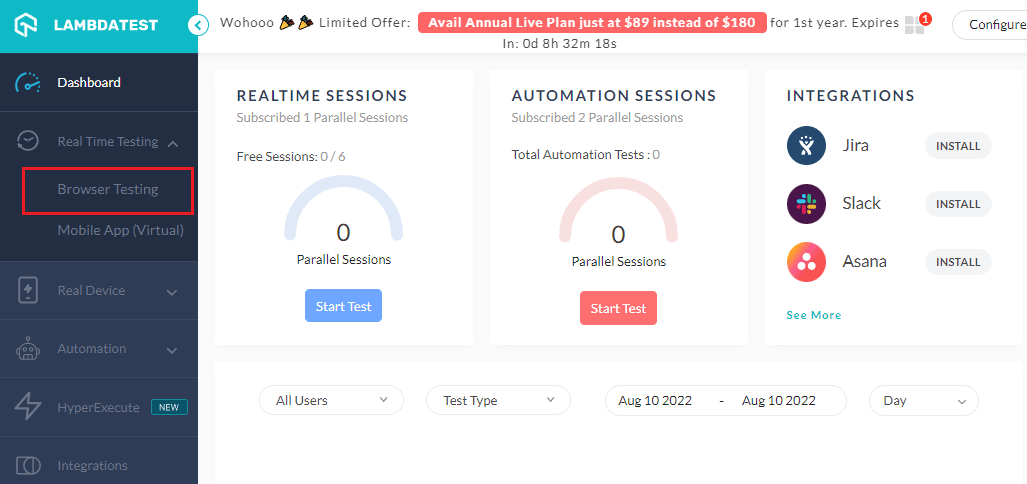
- Log in to your LambdaTest account. Don’t have an account yet? sign up for free.
- Go to Real Time Testing → Browser Testing.
- Enter the website URL and choose whether to test on a desktop or mobile device. Let’s say you want to test on Desktop, then select browser VERSION, OS, and RESOLUTION. After that, click START.
- It will take you to the cloud-based virtual machine where you can run manual Ad-hoc tests of your websites and web applications.
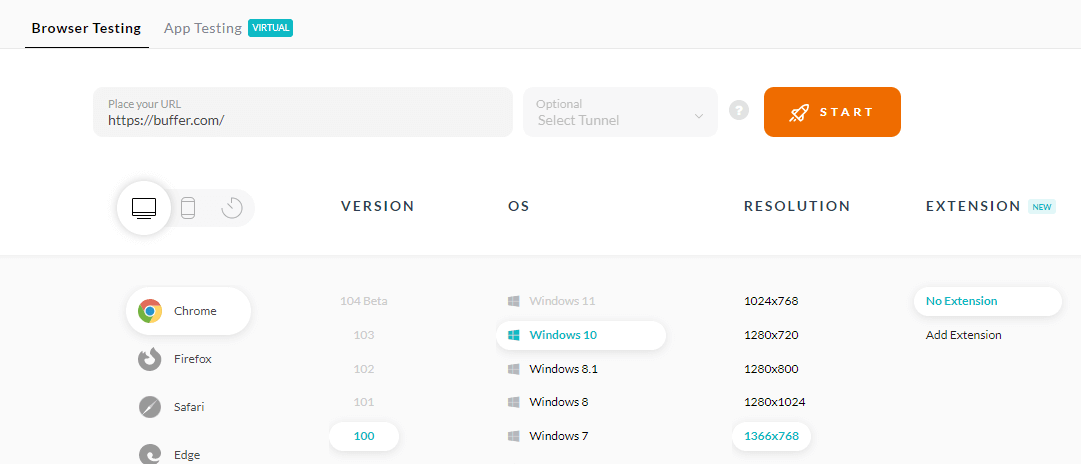
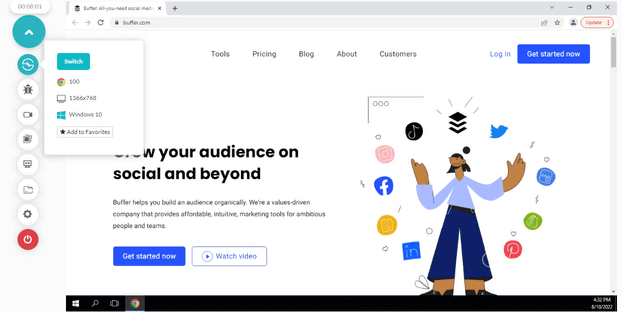
You, as a tester, have the freedom to alter the resolution, the browser versions, or the OS version at any time throughout the given duration. Your environment session will be automatically changed based on your selection.
Subscribe to the LambdaTest YouTube channel and stay updated with the latest tutorials around Selenium testing, Cypress testing, CI/CD, and more.
Performing automated Adhoc testing
The manual testing of your websites is a wonderful idea. However, it is time-consuming and exhausting to test the same scenarios whenever an application change is made. Therefore, performing automation testing is crucial to increasing the speed and effectiveness of test suite execution.
Testers could run end-to-end automation tests on a safe, effective, highly available, and scalable Selenium-based infrastructure with LambdaTest's online Selenium Grid.
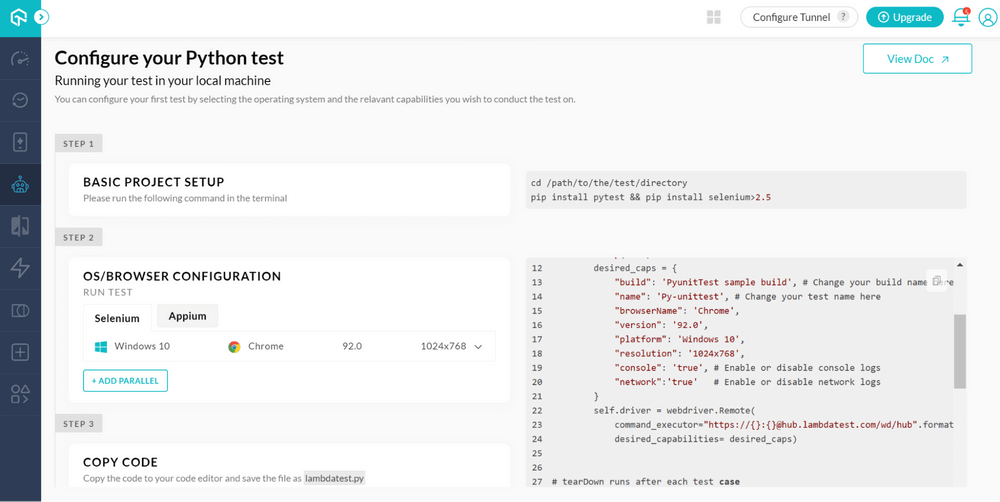
- To perform automation testing, click on the Automation → Build option from the LambdaTest Dashboard.
- If Python is chosen as the language, the following screen must be used to set up the project and the OS and browser. By setting up the necessary information, you may run your test case.

Best practices of Adhoc testing
Ad hoc testing is a great way to help ensure quality and detect defects in a product. Here are a few best practices that you should know:
- Business expertise:The knowledge base and comprehension of the business requirements of the testers should be solid. A thorough understanding of the procedure will make it simple to find errors. Because they are more skilled at predicting errors, experienced testers identify more flaws.
- Preparation:Finding flaws in the application at hand is more likely if there has been a defect analysis of a comparable program. Instead of wasting time testing randomly, such preparation can assist testers in concentrating on the weak regions.
- Testing key modules: It's crucial to choose essential business modules for Ad-hoc test. Additionally, business-critical modules must be evaluated first to boost confidence in the system's quality.
- Developing a rough concept: The tester will approach the testing with attention if they have a rough idea in place. Documenting a thorough plan for what to test and how to test is NOT needed.
- Record defects: All flaws must be noted or written down in a notepad. Developers must be tasked with fixing defects. Corresponding test cases must be written and included in the planned test cases for each legitimate defect. While we are arranging for test cases, these defect findings should be made into a lesson learned and used in the next system.
- Identify defect-prone areas: You will acknowledge that some software features are more prone to faults than others after you have a firm grasp on testing that particular piece of software. Check the features v/s defects opened against them if you're unfamiliar with the system. A feature's defect rate will indicate how sensitive it is, and you should specifically pick that area to conduct Adhoc test. This is an effective approach to finding some severe flaws in a short amount of time.
- Create test categories: As soon as you know the characteristics that need to be evaluated, set aside some time to consider how you would classify those features and put them to the test. Before everything else, you should choose to test the features that the user sees and uses the most, as these would seem to be crucial to the software's success.
- Divide and rule: By testing the application by parts, we will be able to concentrate more clearly and identify any issues.
- Using tools: Testing the feature frequently goes smoothly with no observed differences in how it behaves. Although they don't in any way interfere with the test aim, the logs kept in the background might be reporting certain exceptions that the testers might have missed. These might potentially be of extreme severity. Therefore, we must acquire tools that will enable us to identify this right away.
Wrap Up!
Ad-hoc testing methodologies have been thoroughly covered, including their advantages, disadvantages, best practices, when and when not to perform testing, types, etc.
It has always given the most delight because there is no end to how creative and knowledgeable you can be.
Having said that, the most important thing to take away from all of the information above is to figure out how to take advantage of Ad hoc test's benefits and make it contribute to improving the overall test process and the quality of the final product.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
When ad hoc testing is done?
Ad hoc testing is done when a software test is carried out without adequate planning and documentation. If we don't find any flaws, such tests are merely run once. Ad hoc tests are conducted after the application has undergone formal testing
Why do we need Ad hoc testing?
This is true because effective error guessing can only be performed when the tester is aware of the functions and workings of the software. The Ad hoc testing method works well for identifying flaws and contradictions in an application that cause significant gaps.
What are the types of Adhoc testing?
There are three types of Ad hoc testing: Buddy Testing, Pair Testing, Monkey Testing
What is Ad hoc testing?
Ad hoc testing is when testers explore a software application without following any specific test plan or predefined steps. They randomly test the software to find defects and assess its usability in an unplanned and informal manner.
What is a simple example of Ad hoc testing?
Ad hoc testing is like randomly exploring an application to find unexpected errors or issues. For example, testing how an application behaves when certain browser settings are changed or when it is used on different devices or platforms. It helps uncover potential problems that may not be covered by regular, planned tests.
What is Ad hoc testing in QA?
Ad hoc testing in QA refers to testing software without following a predefined plan or documentation. It is performed spontaneously to uncover defects and is typically done after formal testing. Ad hoc tests are executed once and help identify additional issues that may have been missed during planned testing.
Who performs Ad hoc testing?
Ad hoc testing can be performed by both test engineers and developers. Test engineers can explore the application in new ways to uncover bugs that may have been missed during formal testing. Developers can also conduct Ad hoc testing while coding to ensure better code quality.
Is Ad hoc testing negative testing?
No, Ad hoc testing is not exclusively negative testing. Ad hoc testing refers to testing performed without proper planning or documentation, while negative testing specifically focuses on testing for unexpected or invalid inputs to assess how the system handles them
Can Ad hoc testing be automated?
While ad hoc testing is usually spontaneous and unplanned, some aspects of it can be automated to make the process more efficient and consistent. Automating tasks like managing test data and repetitive actions can help save time and effort while improving the quality of the software.
Reviewer's Profile

Shahzeb Hoda
Shahzeb currently holds the position of Senior Product Marketing Manager at LambdaTest and brings a wealth of experience spanning over a decade in Quality Engineering, Security, and E-Learning domains. Over the course of his 3-year tenure at LambdaTest, he actively contributes to the review process of blogs, learning hubs, and product updates. With a Master's degree (M.Tech) in Computer Science and a seasoned expert in the technology domain, he possesses extensive knowledge spanning diverse areas of web development and software testing, including automation testing, DevOps, continuous testing, and beyond.
Try LambdaTest Now !!
Get 100 minutes of automation test minutes FREE!!
 Christmas Deal is on: Save 25% off on select annual plans for 1st year.
Christmas Deal is on: Save 25% off on select annual plans for 1st year.